![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
184 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Psychotherapy
|
Resolving personal, emotional, behavioural, and social problems to improve well-being
|
|
|
Barriers to treatment
|
- Money and time
- People MINIMALIZE condition (think their symptoms are less severe than they really are) - May not be aware they can be treat - Stigma |
|
|
Stigma
|
Collection of negative stereotypes
|
|
|
Why are males less likely to get help with mental health?
|
They are taught to be less emotionally in touch/attached and "be stronger"
|
|
|
Court-ordered treatments
|
Court orders those who are mentally unstable, driving while intoxicated, and lower classes
|
|
|
Minimalizing
|
When people believe their condition is not important enough or they underestimate condition
|
|
|
Clinical psychologists
|
- Has doctorate degree
- Purpose: Diagnose and treat mental health problems |
|
|
Counselling psychologists
|
- Helps people with COMMON problems like stress, coping, anxiety
- Does not do severe cases |
|
|
Psychiatrists
|
- Physician
- Purpose: Diagnose and treat disorders thru medicine |
|
|
How were mentally ill people treated back then?
|
- Treated like aliens
- Separated from society - Alienated them using straightjackets.. |
|
|
Deinstitutionalization
|
Put people from mental institutions back in community and treat them on an outpatient basis
|
|
|
Inpatient treatment
|
- Stays at a facility
- Protect patient from harm and return them to society as quickly as possible |
|
|
Residential treatment centers
|
Provide psychotherapy, teaches life skills to go back into society
|
|
|
Community psychology
|
Focuses how person's mental health has been influenced by surrounding people/neighbors and other community factors
|
|
|
Outpatient treatment
|
- Does not stay in a facility
- Checks into clinic for therapy and such |
|
|
What are treatments that have been "tested and evaluated using sound research" called?
|
Empirically supported treatments
|
|
|
__ __ is the relationship that emerges from therapy.
|
Therapeutic alliance
|
|
|
The use of self help books for treatment is called __.
|
bibliotherapy
|
|
|
Insight therapies
|
Dialogue between client and therapist to gain awareness and understanding of psychological problems
|
|
|
Psychodynamic therapies
|
Type of insight therapy that uncovers and solves unconscious conflicts
|
|
|
Psychoanalysis
|
- Developed by Sigmund Freud
- Purpose: understand past experiences to have better well-being - Access unconscious mind |
|
|
Unconscious
|
Person is not aware
|
|
|
Free association
|
Reveal all thoughts no matter how weird/meaningless
|
|
|
Dream analysis
|
Interpret unconscious thought
|
|
|
Manifest content
|
What happens in the dream
|
|
|
Latent content
|
Unconscious elements that motivated dream
|
|
|
Resistance
|
Avoiding directly answering questions from therapist
|
|
|
Transference + example
|
Patients who transfer emotions toward therapist
Example: patient who is angry about conflict may direct it towards therapist |
|
|
Object relations therapy
|
Focuses on how childhood experiences and emotional attachments affect later functioning
|
|
|
Give an example of object relations therapy
|
Child who had an imaginary friend (object) may treat real people as they treated their imaginary friend
|
|
|
Humanistic therapy
|
- Focuses on person's potential and strengths
- Therapist listens and understands |
|
|
Person/client-centered therapy
|
Focuses on person's ability to solve their own problems with encouragement from therapist
|
|
|
Conditions of worth + example
|
Losing affection for a person who doesn't live up to expectations
Example: dad who is disappointed by son has IMPOSED conditions of worth because they give an impression of loving the son less |
|
|
Humanistic therapists must show ___ through genuine, empathetic and nonjudgmental attention.
|
Unconditional positive regard
|
|
|
When should therapies be used?
|
When there is empirical evidence of them working.
|
|
|
Interpersonal therapy
|
Belief that illness rooted in interpersonal relationships
|
|
|
Behavioral therapies
|
Addresses problem behaviours, thoughts and the environmental factors that trigger them
|
|
|
Behavioural therapy believes: behaviour is the result of __ and learning.
|
conditioning
|
|
|
Exposure treatment
|
- Set of treatments
- Expose person to fear in gradual steps under controlled conditions |
|
|
Systematic desensitization
|
Gradual exposure to feared stimulus w/ relaxation training
|
|
|
Flooding
|
Directly exposed to fear in hopes that the patient will see there is actually nothing to fear
|
|
|
Modeling
|
Client observes another person interact with fear so they can do it themselves
|
|
|
Virtual reality exposure
|
Client is exposed to fear virtually through screens
|
|
|
Aversive conditioning + example
|
Replaces positive response with negative response; usually a punishment
Example: putting a drug into alcohol that induces vomiting to stop alcohol addiction |
|
|
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
|
Therapy that includes exposure, cognitive restructure and inoculation training.
|
|
|
Cognitive restructuring
|
Client changes perspective on negative events and views them less emotionally and rationally
|
|
|
Inoculation training
|
Relaxation techniques to regain emotional control; promotes well being
|
|
|
Pros of group therapy
|
- Less costly
- Groups organized to fit a particular purpose |
|
|
Family therapy
|
Deals with dynamics of family or with one particular person
|
|
|
Family therapy takes a s___ approach.
|
systems
|
|
|
Systems approach
|
Understanding that each family member contributes to the family dynamic
|
|
|
Behavioural therapies are most effective with what disorder(s)?
|
Anxiety disorders
|
|
|
Cognitive behavioural therapy is most effective with what disorder?
|
Depression
|
|
|
Psychopharmacotherapy
|
Treating psychological disorders with drugs
|
|
|
Medications that alter psychological functioning are called ___.
|
Psychotropic drugs
|
|
|
Antidepressant drugs
|
Elevated mood and reduces symptoms of depression
|
|
|
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOs)
|
Antidepressant that inhibits the MAO enzyme to reduce dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine (hormones that promote depression)
|
|
|
Earliest type of antidepressant that blocked reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine
|
Tricyclic antidepressant
|
|
|
Selective seretonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
|
Blocks reuptake of serotonin
|
|
|
Blocking neurotransmitters (as antidepressants do) is a __ and not a fact.
|
Hypothesis
|
|
|
Neurogenesis
|
Growth of new neuons
|
|
|
Mood stabilizers
|
Prevent + reduce manic side (extreme happiness) of bipolar disorder
|
|
|
Antidepressants do not make people ___ than they were before depression.
What do they do? |
happier
Antidepressants alleviate depression |
|
|
Antianxiety drugs
|
Alleviate nervousness, tension and reduces panic attacks
|
|
|
Antipsychotic drugs
|
- Treats schizophrenia and severe mood disorders
- Reduces not eliminate - However, effects weaken over time |
|
|
When are drugs useful?
|
When they are combined with therapy
|
|
|
True or False: Medication of depression alone is effective.
|
False - combination of antidepressants and therapy is more effective
|
|
|
Why is exercise beneficial to alleviating depression?
|
- Health benefits
- Requires change of lifestyle which prevents relapse - Increases energy levels |
|
|
A side effect of antipsychotics that involves motion control problems is called __.
|
Tardive dyskinesia
|
|
|
Removing regions of the cortex
|
Frontal lobotomy
|
|
|
Lesion
|
Damaged area of tissue like a cluster of nerve cells
|
|
|
Focal lesions
|
Purposely killing cells by making small lesions in brain
|
|
|
Electroconvulsive therapy
|
Electrical current is passed thru brain to induce temporary seizure
|
|
|
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
|
A very specific area of brain exposed to a powerful magnetic field which stimulates it; used for depression
|
|
|
Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
|
Electrically stimulating specific regions of the brain; used mostly for those with movement disorders like Parkinson's
|
|
|
When are technological and surgical treatments used?
|
When illness is a severe case
|
|
|
Neuron
|
A cell that sends and receives messages throughout body
|
|
|
The soma is also known as the __.
|
cell body
|
|
|
Cell body
|
- Part of the neuron
- Contains NUCLEUS that has genetic material |
|
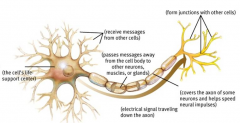
Label the diagram
|
CELL BODY - the cell's life support center
DENDRITE - receives msgs AXON - sends msgs NEURAL IMPULSE - electric signal traveling down axon MYELIN SHEATH - covers axon and speeds up signal TERMINAL - form junctions w/ others |
|
|
Dendrite
|
- Branches projecting from cell body
- Receives messages from other cells and sends them to the cell body |
|
|
Axon
|
Transports info from one neuron to another through ELECTROCHEMICAL reactions
|
|
|
What type of signals do neurons send?
a) Chemical b) Electrochemical c) Fluid d) Hormonal |
b) Electrochemical
|
|
|
Located within axon terminals are chemicals called __.
|
neurotransmitters
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters
|
Chemicals that function as messages that allow neurons to communicate
|
|
|
Synapses
|
Small spaces that separate nerve cells
|
|
|
What is the difference between SENSORY and MOTOR NEURONS?
|
Sensory neurons bring information from the senses INTO the brain.
Motor neurons bring messages AWAY from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles. |
|
|
Myelin
|
- Fatty sheath that insulates axons from each other
- Increases speed and efficiency in neural communication |
|
|
Glial cells
|
- Specialized cells of nervous system
- Synchronizes activity of nervous system, i.e. removes waste |
|
|
The __ and __ environments of a neuron differs in their ___ of charged atoms called ions.
|
inner, outer, concentration
|
|
|
What does the RESTING POTENTIAL of a neuron refer to?
|
Stable state where cell is not transmitting messages
|
|
|
At resting potential, the outside of the neuron has a relatively __ concentration of __ charged ions. The inside has a __ concentration of __ charged ions.
|
Outside neuron: high concentration of POSITIVELY charged ions
Inside neuron: high concentration of NEGATIVELY charged ions |
|
|
What causes a neuron to fire? Describe the steps.
|
1. Neuron is stimulated
2. Surface pores open up to let positively charged ions in 3. Threshold of neuron is reached (ex: -70 mV) 4. Action potential starts |
|
|
Action potential
|
- Wave of electrical activity
- Starts at base of axon - Travels down axon length |
|
|
During the action potential the net charge of the cell goes from __ to __.
|
negative --> positive
|
|
|
At each point of the axon, the sodium pores __ as soon as the action potential occurs.
|
shut
|
|
|
The minute space between the terminal and the dendrite is called the __.
|
synaptic cleft
|
|
|
What happens the action potential is at the end - the axon terminal?
|
1. Neurotransmitters released into synaptic cleft (space)
2. Binds to receptors on dendrites |
|
|
The action potential is followed by a ___.
|
refractory period
|
|
|
Refractory period
|
Brief period when a neuron cannot fire
|
|
|
A given neuron always fires at the same __ and __.
|
intensity and speed
|
|
|
All-or-none principle
|
Individual nerve cells fire at same strength and speed every time an action potential occurs
|
|
|
An action potential carries a __ electrical charge away from the cell body.
|
positive
|
|
|
What cells manufacture myelin?
|
Glial cells
|
|
|
A neuron will fire when the ions inside the cell are..
|
Shifted to a greater threshold than the resting potential.
|
|
|
What is the LOCK-AND-KEY analogy used to explain?
|
Neurotransmitters released at axon terminal bind to a specific receptor of dendrite like a key in a lock.
|
|
|
Name the 2 types of reactions when a neurotransmitter binds to a receptor
|
(1) Excitatory
(2) Inhibitory |
|
|
Excitatory reaction
|
Increases action potential
|
|
|
Inhibitory reaction
|
Decreases action potential
|
|
|
Reuptake
|
When neurotransmitters released are reabsorbed into presynaptic neuron
|
|
|
Monoamines are known to influence __.
|
mood
|
|
|
Dopamine
|
- Monoamine neurotransmitter
- Mood, control of voluntary movement, reward experiences |
|
|
Serotonin
|
- Monoamine
- Regulates mood, sleep, and appetite |
|
|
Norepinephrine
|
- Monoamine
- Regulates stress responses and increases arousal, attention, heart rate |
|
|
Acetylcholine is found between __ cells and __ muscles. They are very important for __.
|
- between nerve cells + skeletal muscles
- voluntary movement |
|
|
Glutamate
|
- Excitatory neurotransmitter
- Learning and memory |
|
|
GABA (gamma-amino butyric acid)
|
- Inhibitory neurotransmitter
- Prevents action potentials - Inhibits brain activity, facilitates sleep, reduces arousal |
|
|
Substance P
|
Neurotransmitter involved in pain
|
|
|
2 types of drugs that affect neurotransmission
|
(1) Agonists
(2) Antagonists |
|
|
Agonists
|
Enhances a neurotransmitter's action
|
|
|
Antagonists
|
Inhibits a neurotransmitter's action
|
|
|
Hormones are c__ secreted by the glands of the __ system.
|
chemicals, endocrine
|
|
|
Homeostasis
|
Balance of energy (metabolism, temp., etc.) for body to work properly
|
|
|
Hypothalamus
|
Brain structure that regulates biological needs and motivational needs
|
|
|
Pituitary gland
|
- Master gland
- Produces hormones and sends commands about hormone production to other glands of the endocrine system |
|
|
What part of the brain prepares your body for stress?
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
In time of stress, the hypothalamus sets __ events that signals the __ to release a hormone into the bloodstream and stimulates the __ glands.
|
chemical
pituitary gland adrenal glands |
|
|
Adrenal glands
|
Releases stress hormones like cortisol and epinephrine
|
|
|
Endorphin
|
- Produced by pituitary gland and hypothalamus
- Reduces pain + induces feelings of pleasure |
|
|
Testosterone
|
Drives physical and sexual development, surges during sexual activity
|
|
|
2 divisions of the nervous system
|
(1) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
(2) Central Nervous System |
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
Transmits information to and from CNS
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system is divided into:
|
(1) Autonomic nervous system
(2) Somatic nervous system |
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
Regulates activity of organs and glands
|
|
|
Somatic nervous system
|
Receive sensory input, controls skeletal muscles for voluntary + reflexive movement
|
|
|
The sympathetic + parasympathetic divisions come from the ___ nervous system.
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
|
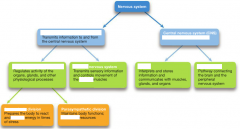
Fill in the blanks.
|
2nd row: Peripheral nervous system, the brain and the spinal cord
3rd: Autonomic nervous system, somatic nervous system, brain, spinal cord 4th row: Sympathetic division, expend, conserves |
|
|
Central nervous system
|
The brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
The spinal cord connects what 2 structures?
|
Connects the peripheral nervous system to the brain
|
|
|
The hindbrain controlls basic __sustaining processes.
|
life-sustaining
|
|
|
At the top of the spinal cord is called the __.
|
brain stem
|
|
|
Brain stem
|
Consists of the medulla and pons
|
|
|
Function of Medulla
|
Regulates heart rate, breathing, salivating, sneezing
|
|
|
Function of Pons
|
Wakefulness and dreaming
|
|
|
Cerebellum
|
- Lobe-like structure at the base of the brain
- Movement, balance, learning new motor skills |
|
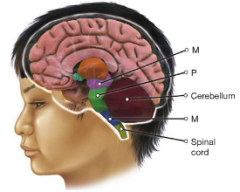
Label the hind/midbrain diagram
|
Top to bottom: Midbrain, pons, medulla
|
|
|
Midbrain
|
- Relay station between sensory and motor areas
- Voluntary movement |
|
|
Forebrain
|
- Obvious part of brain
- Consists of many structures |
|
|
Basal ganglia
|
- Forebrain
- Movement and reward processing |
|
|
Amygdala
|
- Forebrain
- Emotion, recognizing emotional stimuli - Facial expressions |
|
|
Hippocampus
|
- Forebrain
- Learning and memory - Forms new memories |
|
|
Hypothalamus
|
- Forebrain
- Temp. regulation, motivation (hunger, thirst, sex) |
|
|
The integrated network involved in emotion and memory is what system?
|
Limbic system
|
|
|
Thalamus
|
Relays sensory info to different regions of brain
|
|
|
Cerebral cortex
|
Wrinkled outer layer of brain involved in cognition like thought, language, and personality
|
|
|
Dark region of brain is called __.
|
gray matter
|
|
|
White region of brain is called __.
|
White matter
|
|
|
Gray matter
|
Composed of cell bodies and dendrites
|
|
|
White matter
|
Myelinated axons
|
|
|
Ventricles
|
- Fluid filled (cerebrospinal fluid) spaces
- Eliminates waste and provides nutrition |
|
|
What fluid are ventricles filled with?
|
Cerebrospinal fluid
|
|
|
The four major ares of the brain are called __.
|
lobes
|
|
|
Frontal lobe
|
- For cognition like planning, regulating impulses, language, voluntary movement
|
|
|
Corpus callosum
|
Thick band of axons that connect the left + right hemispheres of brain
|
|
|
Primary motor cortex
|
Control of voluntary movement
|
|
|
The frontal lobe is active when moving a body part as well as when..
|
Planning the movement
|
|
|
Parietal lobes
|
- Behind the frontal lobes
- Touch + bodily awareness |
|
|
Occiptal lobes
|
- At the rear of brain
- Visual information is processed here |
|
|
Temporal lobes
|
- At sides of brain near the ears
- Hearing, language, higher aspects of vision - Face recognition |
|
|
What is the right hemisphere involved in?
|
Visual and spatial skills
|
|
|
What is the left hemisphere involved in?
|
Language and math
|
|
|
What is the phenomenon of the 2 brain hemispheres performing different functions called?
|
Hemispheric specialization
|
|
|
What did Paul Broca do?
|
- Examined a dead person who was unable to speak for the last 30 years of his life
- Found his LEFT brain hemisphere (language and math) was damaged - Called the damaged area, "Broca's Area" for speech production |
|
|
Loss of speech function
|
Broca's aphasia
|
|
|
Aphasia is the impairment of __ functioning.
|
language
|
|
|
Wenicke's area
|
Area involved in comprehension of speech
|
|
|
Patients with Wernicke's aphasia have what problem?
|
Speech comprehension
|
|
|
How does one become a split-brain patient?
|
Corpus callosum is severed so the 2 brain hemispheres are not connected and are separated.
|
|
|
How does SPLIT-BRAIN work?
|
*Remember the brain hemispheres process opposite sides
(1) Objects presented on the right side are verbalized b/c the left hemisphere is in charge of language (2) Objects on the left are pointed out because the right hemisphere is in charge of spatial skills |
|
|
Measuring the pattern of brain activity with electrodes attached to the scalp is called __.
|
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
|
|
|
Brain imaging - PET Scan
|
- Radioactive glucose injected in blood and moves to brain
- Tasks are performed by patient and the glucose movement is measured |
|
|
MRI stands for
|
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
|
|
|
MRI
|
- Detailed images of brain
- Radio waves passes through brain to create a signal that can be translated into a 3D image |
|
|
Functional MRI (fMRI)
|
- Allows to see blood flow in brain
- Sees blood with oxygen and those without |

