![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define drug addiction |
A behavioural pattern of drug use, characterized by overwhelming involvement with the use of a drug, the securing of its supply, and a high tendency to relapse after withdrawal |
|
|
Define substance dependence |
Disorder involving excessive and harmful drug use by an individual |
|
|
Explain the gateway theory of drug use |
Proposes the existence of developmental stages of drug use in adolescence who progress from one substance to another over time |
|
|
Describe the physical dependence model of addiction |
Once physically dependent, attempts at abstinence lead to highly unpleasant withdrawal symptoms, thus motivating the user to take the drug again to alleviate the symptoms. (common with alcohol & opiates) |
|
|
Discuss the neural mechanism of reward |
The reward-circuit: involves the DA pathway from the VTA to the nucleus accumbens (mesolimbic DA pathway). Activation of the pathway (i.e. from drugs) causes DA levels in the Nuc. Acc. to rise. |
|
|
The VTA is home to what two pathways? (VTA= Ventral Tegmental Area) |
Mesolimbic Pathway (extending from the VTA to the nucleus accumbens Mesocortical Pathway (extending from the VTA to the cerebral cortex) VTA is home to a large amount of DA neurons |
|
|
The anti-reward system |
Activated during drug withdrawal. Negative reinforcement produced by alleviating aversive withdrawal symptoms with drug use |
|
|
Incentive-sensitization model |
In drug addiction, the user "wants" the drug more, even though he doesn't "like" the drug more. Thought to occur because repeated drug use causes sensitization to the "wanting" system, but not like "liking" system. |
|
|
Opponent-process model |
The initial positive response to a drug is followed by an opposing withdrawal response as the drug wears off |
|
|
Describe the disease model of addiction |
Most widely accepted model Based largely on the dysregulation of brain function in addiction Has helped society have more remorse+understanding rather than blame. a.k.a. The Medical Model |
|
|
Explain how comorbidity and self-medication are relevant to compulsive substance use |
The presence of some other diagnosis (i.e. mood, anxiety, or personality disorder) can cause a person to develop a substance abuse issue by attempting to self-medicate |
|
|
Describe the process of alcohol metabolism |
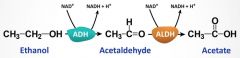
In the liver, alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) converts alcohol to acetaldehyde, which is then rapidly converted to acetic acid by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) |
|
|
What are DTs? |
Delirium Tremens Severe withdrawal effects. Irritability, headaches, confusion, agitation, convulsions, total disorientation, hallucinations, delirium. Small % of alcoholics withdrawing will experience DTs |
|
|
Discuss the neurotoxic effects of heavy alcohol consumption |
Produces a serious deficiency in Vitamin B1 (thiamine) causing cell death. Can lead to Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Enlarged ventricles due to shrinkage of brain tissue. Too much acetaldehyde can cause brain damage. |

