![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hue; Saturation; Brightness
|
wavelength; purity; intensity
|
|
|
Three types of movements eye makes
|
VERGENCE (i.e. look at finger then move it closer to face), SACCADIC (abruptly shift gaze- reading), PURSUIT (when looking at moving objects, slow movement of eye)
|
|
|
Accommodation
|
ciliary muscles focus lens for near and far objects
|
|
|
Fovea
|
central retina, where cones are
|
|
|
Optic Disk
|
responsible for blind spot
|
|
|
Bipolar cells; Ganglion Cell
|
BIPOLAR CELLS (middle of retina) convey info to GANGLION CELL (its axons give rise to optic nerve)
|
|
|
Lamella
|
layer containing PHOTOPIGMENTS (RETINAL and OPSIN).
|
|
|
Two photopigment types
|
Retinal and Opsin. found in both cons and rods, 10,000!
|
|
|
Rhodopsin
|
photopigment- when exposed to light, breaks into rod opsin and retinal and changes colour from pink to pale yellow
|
|
|
Dorsal Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
|
in thalamus, receives inputs from retina and projects them to Primary Visual Cortex. It has 6 layers.
1,2 = MAGNOCELLULAR LAYER (transmits info for depth, movement, form), are large, quick, and rods. colourblind 3,4,5,6= PARVOCELLULAR LAYER( transmits info for perception of colour (green n red) and fine detail) have small receptive fields, are cones, and are slower. KONIOCELLULAR Cells = small, between m and p layers, for blue cones |
|
|
Location of Primary Visual Cortex
|
on the Calcarine Fisssure in occipital lobe inner surface of posterior cerebral cortex
|
|
|
PVS is also called
|
STRIATE cortex because it has a dark staining layer
|
|
|
Optic Chaism
|
where optic nerves join at base of brain shaped like a X
|
|
|
3 types of orientation-sensitive cells in the striate cortex
|
SIMPLE CELLS are orientation sensitive (based on position of object in visual field) COMPLEX CELLS respond to the presence of a line segment with particular orientation, and HYPERCOMPLEX CELLS respond to the presence of a line segment with particular orientation that end at a particular point
|
|
|
Square-wave Grating vs Sine-way Grating
|
(look up picture) eye responds more to sine-waves. - the sine wave is designated by its spacial frequency (relative width of stripes measured in cycles per degree of visual angle) the visual angle is smaller if sine waves are closer together
|
|
|
Cytochrome Oxidase Blob
|
parococellular region, contains wave-length sensitive neurons
|
|
|
Extrastriate Cortex
|
region that surrounds the striate cortex, part of visual ass cortex receives axons from PVC and superior colliculi and send to inferior temporal cortex
|
|
|
What is the highest level of the dorsal and ventral streams?
|
Dorsal: Posterior parietal cortex (involved in perception of movement and location)
Ventral: inferior temporal cortex (involved in perception of objects and faces) |
|
|
Ventral stream is for___ , dorsal is for ___
|
recognition of things; spatial location
|
|
|
Cerebral Achromatopsia
|
inability to distinguish colour- caused by damage to extrastrigiate cortex
|
|
|
Visual Agnosia
|
can see but can't identify objects, other defects in visual perception, due to damage to inferior temporal cortex
|
|
|
Occipital complex vs Extrastriate body area
|
area of extra striate cortex involved in perception of objects other than faces
vs involved in perception of body other than faces |
|
|
Parahippocampal place area
|
involved in perception of 'scenes'
|
|
|
Optic flow
|
provides info about relative distance of objects and movement direction. In MST (v5a)
|
|
|
Ankinetopsia
|
inability to perceive movement caused by damage to V5
|
|
|
What length of electromagnetic energy do our eyes respond to?
|
380-760 nm long
|
|
|
Sclera
|
tough outer white of eye, attached to extraocular muscles
|
|
|
vitreous humour
|
clear, gelatinous fluid that light passes through
|
|
|
periphery
|
where rods are
|
|
|
blind spot
|
no receptors
|
|
|
horizontal and amacrine cells
|
in retina, interneurons without axons which combine msgs from adjacent cells
- amacrine connect ajacent ganglion with bipolar - horizontal connect photo with bipolar cells |
|
|
each cone in fovea...
|
connects to a single bipolar cell which in turn connect to a single ganglion cell
|
|
|
describe eyes of birds
|
most brids have two foveae per eye - one for detail in the periphery and have more receptors on top half of retinal (for looking down)
to see up they have to turn their heads way far back |
|
|
rods, cones, mono vs trichromatic
|
rods are monochromatic, cones trichromatic
|
|
|
in the dark...
|
ion channels on photoreceptor membrane are open, channels admit cations and are held open by cGMP cyclic guanosine monophosphate. the entry of cations depolarizes the membrane resulting in a continuous release of glutamate
|
|
|
in the light...
|
rhodopsin molecules split. a chem reaction involving g protein and a phosphodiesterase enzyme will destroy the cGMP, closing the ion channel. membrane hyperpolarized cuz no cations enter and glutamate release decreases
|
|
|
ganglions increase rate of firing ...
|
hyerpolarising effect of light on the photo. membrane reduces the release of glutamate this depolarizes the bipolar cell, which leads to increased glutamate release causing it to increase rate of firing
|
|
|
receptive fields in ganglion cells are tested how?
|
- micro electrodes are used to record the electrical activities of a single neurone
- investigator can shine light in various locations while recording - if light in a spot excites the neurone the it is part of the excitatory receptive field (on firing) - if it inhibits activity then it is an inhibitory receptive field (off firing) |
|
|
Retina Geniculate Pathway (primary visual Pathway)
|
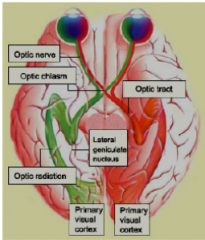
- optic nerves join at base of brain at optic chasm
- the axons from ganglion on inner side near nose cross thru chasm and ascend to LG of opposite side of brain - axons from ganglion on outer side remain on same side of brain |
|
|
primary Visual cortex also called...
|
striate cortex, V1
|
|
|
V1 sends info to...
|
V2, V3, V4, MT (V5) of extrastriate cortex
|
|
|
inferior temporal cortex contains...
|
v4: area TEO (colour discrimination), area TE
|
|
|
pronatopia, deuternanopia, tritanopia
|
-red n green confused- red cones filled with green opsin
-" - green cones filled with red opsin - rare, lack blue cons, see world in green and red |
|
|
what types of stripes are in v2? where do the dorsal and ventral streams begin?
|
thin and thick (receive info concerning colour) pale (receive info concerning spatial frequency, orientation)
- the ventral stream begins at the pale and thin stripes and the dorsal stream begins at the thick stripes |
|
|
in the posterior parietal cortex, there is the INTRAPARIETAL SULCUS. WHat are the parts of this and their functions?
|
LIP and VIP involved in visual attention and saccades
MIP involved in reaching/pointing AIP involved in grasping and manipulating CIP involved in depth |

