![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Psychology |
The science of behaviour and mental processes. |
|
|
|
Neuroscience |
How the body and brain enable emotions, memory, and sensory experiences |
Perspective |
|
|
Evolutionary |
How the natural selection of traits has promoted the survival of genes |
Perspective |
|
|
Psychodynamic |
How behaviour springs from unconscious drives and conflicts |
Perspective |
|
|
Behaviour genetics |
How our genes and environment influence our individual differences |
Perspective |
|
|
Behavioural |
How we learn observable responses |
Perspective |
|
|
Cognative |
How we encode,process,store, and retrieve information |
Perspective |
|
|
Social cultural |
How behaviour and thinking vary across situations and cultures |
Perspective |
|
|
Wilhelm wundt |
Established the first psyc lab in uni. Of leipzig, ger. 1879 after ecperiment on reaction and perception |
Person... Structuralist |
|
|
Edward bradford titchener |
Used introspection to search for the minds structural elements and aimed to discover the minds structure |
Person.. Structuralist |
|
|
William james |
Considered the evolved functions of our thoughts and feelings. Why it did these things... Adaptive |
Person. Functionalist |
|
|
Mary whintin calkins |
Mentored by william james. Memory researcher and first woman to be president of the american psychological association |
Person.. Functionalist |
|
|
Margaret floy washburn |
First (official) female psyc ph.d and second female apa pres 1921 Synthesized animal research Wrote books on it |
Person |
|
|
John b. Watson |
Worked with rosalie rayner Championed psyc as the science of behaviour |
Person |
|
|
B.f skinner |
Rejected introspection and studied how consequences shape behaviour |
Person... Founder of behaviorism |
|
|
Sigmund freud |
Emphasized the ways our unconscious thought processes and our emotional responses to childhood experience affect our behaviour. Controversial ideas Influenced humanities self understanding |
Famous |
|
|
Carl Rogers and Abraham maslow |
How current environmental influences can nurture or limit our growth potential and the importance of having our needs for love and acceptance satisfied |
People ... Humanists |
|
|
Structuralism |
Used introspection to define the minds make up |
Wilhelm wundt and edward titchener |
|
|
Functionalism |
Focused on how mental processes enable us to survive and flourish |
William james and mary calkins |
|
|
Behaviourism |
Cannot observe a sensation but can observe the behaviour as one responds Believes Psyc is objective |
B.f skinner |
|
|
Humanistic psyc |
Current environment influence can nurture or limit growth Importance of having needs for love and acceptance met |
Carl rogers and abraham maslow |
|
|
Cognitive neuroscience |
Study of the brain activity linked with cognition (perception thinking memory and language) understanding of the brain activity underlying mental activity |
|
|
|
Statistics |
A branch of mathematics that is used for analyzing research data |
|
|
|
Descriptive stats |
Used mearly to describe a set of data |
|
|
|
Inferential stats |
Making inferences about a population |
|
|
|
Behaviour genetics |
The study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behaviour. Weigh the effects and interplay of heredity and environment |
|
|
|
Environment |
Every nongenetic influence from prenatal nutrition to the people and things around us |
|
|
|
Chromosomes |
Threadlike structures made of dna molecules that contain the genes |
|
|
|
Dna |
A complex molecule containing the genetic i formation that makes up the chomosomes |
|
|
|
Genes |
The biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes A segment of dna capable of synthesizing a protein |
|
|
|
Genome |
The complete instructions for making an organism Consisting of all the genetic material in that organisms chromosomes |
|
|
|
Identical twins |
Develops from a single egg split in two |
|
|
|
Fraternal twins |
Develop from separate fertilized eggs |
|
|
|
Twin adoption studies |
Used to tease apart the influence of environment and heredity on behaviour |
|
|
|
Variable |
A characteristic or quality that can take on two or more values |
|
|
|
Independent variable |
The variable that is manipulated The researcher manipulates the iv to see its effect on the dv It is the variable that is controlled |
|
|
|
Dependant variable |
The variable that is measured It may change in response to a response to a manipulation |
|
|
|
Operational definition |
Defining variable in terms of how they are measured or manipulated |
|
|
|
Population |
The whole group you want to study or describe |
|
|
|
Sample |
Your set of observations A subset of the population |
|
|
|
Random sample |
A sample that fairly represents a population Because each member has an equal chance if inclusion |
|
|
|
Representative sample |
A subset of a statistical population that accurately reflects the members of an entire population |
|
|
|
Generalizable |
The ability to say that the results obtained with your sample are also true of the population |
|
|
|
External validity |
The extent to which the results of a study can be generalized to other situations and to other people |
|
|
|
Replication |
Repeating a study to see if the results are reliable enough to be duplicated |
|
|
|
Random assignment |
Assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance to minimize preexisting differences between those different groups |
|
|
|
Hypothesis |
A testable prediction often implied by a theory |
|
|
|
Theory |
An explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviours or events |
|
|
|
Scientific method |
A self correcting process for asking questions and observing natures answers |
|
|
|
Mode |
Most common value in a data set |
|
|
|
Median |
The middle score in a data set when they are arranged in numerical order |
|
|
|
Mean (def.) |
The average score Sum of all scored decided by the number of observations |
|
|
|
Mean (equation) |
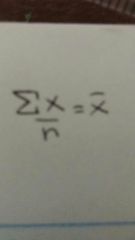
|
|
|
|
Sample size |
(n) number of observations that make up a data set |
|
|
|
Measures of central tendancy |
A single value that describes the typical or central score in a data set |
|
|
|
Measures of variability |
A single value that describes the spread in the data set How similar or diverse the scored are |
|
|
|
Range |
The difference between the lowest and highest scores |
|

