![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
adadfg
|
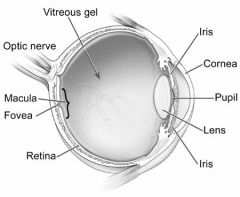
Name parts of the eye
|
|
|
What are sensory receptor cells?
|
Each organ of sense (hear, taste, touch, smell, touch) has sensory receptor cells which transform sensation physical energy to neural information
|
|
|
Definition of sensation?
|
Stimulation of the sensory organs with sensory information (and relaying info to brain
|
|
|
What is definition of perception?
|
When our brain organizes and interprets sensations
|
|
|
What is cornea?
|
The window to the eye. Captures light wave bouncing around to bend or direct into eye
|
|
|
What is a problem assoc w cornea?
|
When the cornea is mis-shaped which causes light to be distorted
|
|
|
What is the aqueous humor?
|
Nourishes the cornea and the lens.
|
|
|
Wht is a problem assoc w aqueous humor?
|
glaucoma Produced on excess or when a drainage problem causes the water to build up. Pressure causes intensely blurred vision
|
|
|
What is fx of the iris and pupil?
|
Pupil is back center of the eye. Iris is colored part of eye. Works together to regulate the amount of light that actually enters the eye
I.e. bright light → pupil contracts and iris expands I.e. low light → pupil dilates and iris becomes smaller |
|
|
What is the lens?
|
Focus image on the retina by accommodating light. Made of protein fiber and is flexible. Like a camera lens, extends itself (becomes thicker) or flattens itself depending on how far the object is to be focused
|
|
|
What are 2 problems assoc with the lens?
|
Cataract
Presbyopia |
|
|
Def Cataract?
|
Opaque cloud that forms over the eye, caused by extensive exposure to radiation and sun
|
|
|
Def of presbyopia?
|
Disease of the lens
Protein fiber becomes less flexible w/ an inability to focus |
|
|
What is vitreous humor?
|
Clear thick fluid filling interior eye chamber. Maintains optimum eye shape
|
|
|
name 3 problems assoc w vitreous humor?
|
1 mypia
2 hyperopia 3 floaters |
|
|
What is myopia?
|
Near sighted (able to see close). Eyeball becomes elongated horizontally causing lens and retinal distance too great
|
|
|
What is hyperopia?
|
Far sighted (able to see far). Distance btwn lens and retina too short
|
|
|
What are floaters?
|
Debris that makes their way to vitreous humor and blocks passage of light to retina
|
|
|
What is the retina?
|
Very back layer of eye (innermost) contains photoreceptor cells (rods and cones)
|
|
|
What are Rods?
Where are they most concentrated? |
Shaped like a rod. Along periphery of retina. Help to see in dim light
|
|
|
What are cones?
Where are they most concentrated? |
Shaped like a cone. Aid in visual acuity, seeing in lighted conditions and colors.
At the fovea (best place to see) |
|
|
What does optic nerve do?
|
The point that rod and cones attach to optic nerve. Transforms this physical energy (light) to neural energy and carries back to brain for processing
|
|
|
What are 2 types of cues for depth perception?
|
Oculomotor and visual
|
|
|
Whats is an oculomotor cue?
|
Kinesthetic cues for depth derived from sensation of muscular contraction of the extra ocular muscles and the lens. The actual physical movement of the eye muscles and lens communicate depth perception to the brain
|
|
|
Name 2 types of oculomotor cues?
|
accommodation and vergence
|
|
|
Definition of accomodation?
|
When the lens of the eye adjust their thickness in order to focus on an object. Depending on how much the lens adjusts the movement communicates information about the distance btwn the object and the viewer
|
|
|
Definition of vergence?
|
When the eyes move in the opposite direction either inward (convergence) or outward (divergence). In order to focus on an object and communicates depth to brain. When eye moves inward (closer object) and when moves outward (farther away).
|
|
|
name 2 types of visual cues?
|
binocular and monocular cues
|
|
|
What is the difference btwn binocular and monocular cue?
|
Need precense of one or both eyes to detect difference
|
|
|
WHAT IS RETINAL DiSPARITY?
|
Retinal disparity is when the each eye host an image based on what it has perceived in its field of vision. Each eye sees a different version of the vision b/c of the unique angle in which they sit. The difference in lateral separation communicates to our brain depth
|
|
|
2 Types of monocular cues?
|
Static and non static
|
|
|
Difference btwn static and non static cue?
|
One is stationary and other is done while moving
|
|
|
3 types of static cues?
|
1 interposition
2 perspective cue 3 texture perspctive |
|
|
What is interposition?
What type of cue is this? |
When 2 things take up space in our vision we assume that the larger is closer to us.
Static |
|
|
perspective cue?
What type of cue is this? give example |
Linear perspective is when we look at something from a distance.
Static Cue I.e. when you stand on a railroad track and the father away the track the farther the tracks are apart. |
|
|
What is texture perspective?
What type of cue is this? give example |
When the texture of an object provides depth information
Monocular I.e. when looking at carpet the carpet farther away appears smoother |
|
|
Whzt is an example of a non static cue?
|
Motion Parralax
|
|
|
What is a motion parralax?
|
A non static cue. Whe you are moving and things that are closer to you go by faster than those that are farther away.
ie when you are drving and things in your peripheral vision move by faster that those that are in front of you |
|
|
3 major components of hearing system?
|
outer, inner, and middle ear
|
|
|
Where is outer ear and what does it do?
|
Extend outward from the head and tries to capture as many sound waves as possible
|
|
|
Where are the parts of the middle ear and what does it do?
|
The parts are the hammer, anvil, and stirrup. Their function is vibrating and transmitting the sound waves further into the ear. Function of middle ear is to amplify sound waves.
|
|
|
Where are the parts of the inner ear
|
cochlea and organ of corti
From the Middle ear (hammer, anvil, stirrup)transmits info to the cochlea |
|
|
What does the cochlea do?
|
Bony tube (resembling a snail) and contains the basilar membrane and conduct sound to the organ or corti.
|
|
|
What does the organ of corti do?
|
Ogan of corti contains hair like receptor cells responsible for converting physical sound waves to neural impulses and sent back to brain via the auditory nerve
|
|
|
What are taste buds?
|
Receptors for taste are located in the taste buds and located in structures called pappillae
|
|
|
What are pappillae?
How many are there? Where are they? |
Taste sensory organs.
10,000 of them. Located on tongue, roof of mouth and back of throat. Human taste system can only detect 4 sensation; sweet, sour, bitter, and salty. Each taste bud only responds to only one or 2 of these categories |

