![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Rostral is |
The nose |
|
|
Caudal is |
The tail |
|
|
Anterior is |
The front |
|
|
Posterior is |
The back |
|
|
Dorsal is |
The top (for humans dorsal and posterior are the same) |
|
|
Ventral is |
below (for humans ventral and anterior are the same) |
|
|
Medial is |
Middle |
|
|
Lateral is |
Moving away from the middle |
|
|
The caudal of the brain would be |
The brain stem |
|
|
What are planes |
A term used to describe how something is sectioned.
|
|
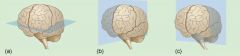
Which of the following displays a Horizontal Plane? A. B. |
A. |
|
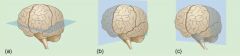
Which of the following displays a sagittal plane? A. B. C. |
B. |
|
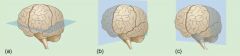
Which of the following displays a coronal plane? A. B. C. |
C. |
|
|
Gray matter chiefly consists of what type of cells? |
Neuron cells |
|
|
White matter consists of what? |
1 Neuron cell body projections (axons) 2. Oligodendrocytes |
|
|
Why does white matter appear white? |
White matter is surrounded by a fatty layer called myelin |
|
|
What types of genes are responsible for producing segmented body structures? |
Hox Genes |
|
|
Why are Hox genes important? |
They are used for patterning symmetry in the embryo thereby producing segmentation |
|
|
Peripheral nervous system is composed of what two main systems |
1. Somatic nervous system (which contains the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system) 2. Autonomic nervous system |
|
|
Which nervous system transmits sensation and produces movement? |
Somatic nervous system |
|
|
Which nervous system is responsible for arousal? |
Sympathetic nervous system |
|
|
Which nervous system is responsible for calming? |
Parasympathetic nervous system |
|
|
Which nervous system is responsible for maintaining balance of internal functions? |
Autonomic nervous system |
|
|
The autonomic nervous system is composed of |
The cranial and spinal nerves |
|
|
T/F: Afferent relays information out while efferent relays information in |
False. Afferent relays information in and efferent relays information out. |
|
|
Define "Dermatomes" |
A portion of the body represented by a spinal cord segment |
|
|
describe Bell-Magendie Law |
Proposed that the dorsal roots are sensory (afferent) while the ventral roots are motor (Efferent) |
|
|
Damage to a dermatome can result in |
A loss of sensation to a specific region of the body associated to that spinal cord. |
|
|
Based on Bell-Magendie Law which of the following is false? A. Sensory = Afferent B. Dorsal = Afferent C. Motor = Ventral D. Efferent = Motor E. Sensory = Motor |
E. Sensory = Motor |
|
|
In the spinal cord, grey matter can be easily recognized due to its shape. What is this shape? |
Butterfly |
|
|
T/F: In the spine, grey matter is medial relative to white matter
|
True |
|
|
What are the main functions of the spinal cord? |
1. Relay body info to brain 2. Relay brain info to muscles 3. Spinal cord behaviors (reflex) |
|
|
Who first described the reflexes of the spinal cord? |
Charles Scott Sherrington |
|
|
Describe a simple spinal cord circuit |
1. Sensory information from sensory receptors is taken through the dorsal root 2. information is processed 3. Motor information is sent to the ventral root to carry out movement |
|
|
What is an example of a stretch reflex? |
Patellar reflex |
|
|
What are four types of reflexes? |
1. Stretch 2. Stepping 3. Placing 4. Scratch |
|
|
Describe the Babinski Sign |
A test in which scratching/tickling the underside of the foot elicits a curling response. This is used to test the central nervous system. If the toes curl up than that could indicate damage to the spinal cord. If the toes curl down than the spine is normal |
|
|
Define "Paralysis" |
Loss of movement and sensation |
|
|
Define "Quadraplegia" |
Paralysis in four limbs |
|
|
Define "Paraplegia" |
Paralysis in the lower limbs |
|
|
T/F: paralysis always results from the initial blow/trauma |
False. It can also result from damage after the initial trauma. I.e. the vertebrae is pressed against the spinal cord) |
|
|
What is NOGO |
A chemical secreted in the adult spinal cord that prevents modifications due to sprouting neurons. |
|
|
Why would it be important for the brain to have a chemical like NOGO? |
NOGO helps to control the amount of new growth of neurons in the brain. Without NOGO, it would be possible for uncontrollable production of neurons to occur resulting in cancer. |
|
|
The simplest behavior circuit wise is: A. A stepping response B. A scratch reflex C. A stretch reflex D. A placing response |
C. A stretch reflex |
|
|
The spinal cord connects with sensory receptors on the body via the _________________________________ A. Autonomic Nervous System B. Somatic Nervous System C. Peripheral Nervous System D. Sympathetic Nervous System |
C. Peripheral Nervous System |
|
|
Who proposed three divisions of the brain |
Paul D. MacLean |
|
|
Paul D. MacLean proposed that the brain was divided into three parts. What are these three divisions? |
1. Neo-cortex 2. Limbic system 3. Reptillian |
|
|
The _______________________ is the main brain of a fish, amphibian, or reptile |
Brainstem |
|
|
T/F: The brainstem has centers for coordinating movememnt, controlling regulatory functions, and for hearing and vision but no real provision for conscious control of behavior |
True |
|
|
The brainstem can be separated by a ventricle into two parts. The _______________ part which is above the ventricle is responsible for sensory function while the _____________ part which is below the ventricle is responsible for motor funciton |
Dorsal (Tectum); Ventral (Tegmentum) |
|
|
There are three main divisions of the brain stem. What are they? |
1. diencephalon 2. mesencephelon (midbrain) 3. Cerebellum |
|
|
Diencephalon translates into |
The rooms |
|
|
What are three components of the diencephalon? |
1. Epithalamus 2. Thalamus 3. Hypothalamus |
|
|
This component of the diencephalon is responsible for seasonal rhythms such as hibernation |
Epithalamus |
|
|
The epithalamus is controlled by what gland? |
Pineal Gland |
|
|
this component of the diencephalon is considered a cortical relay system |
Thalamus |
|
|
This component of the diencephalon regulates behavior |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
Imagine that your body temperature has been extremely irradic over the past few weeks. Which body part would you say is likely to be malfuncitoning? A. Hypothalamus B. Thalamus C. Epithalamus D. Cerebellum |
A. Hypothalamus |
|
|
Name 2 behaviors in which the hypothalamus regulates. |
1. Drinking 2. Eating 3. Temperature Regulation 4. Sleep 5. Salt regulation 6. Sexual motiviation 7. sexual behavior 8. stress |
|
|
What is the normal function of the Lateral Hypothalamuc Nucleus (LHN)? |
Healthy LHN sends signals to encourage hunger and eating |
|
|
What would likely happen to the function of a damaged LHN? |
Damaged LHN would not be able to sends signals to promote hunger. Therefore, you would not be hungry |
|
|
What is the normal function of the Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus (VHN) |
Normal VHN sends signals to stop eating. |
|
|
What would happen to the function of a damaged VHN? |
a damaged VHN would not be able to send signals to stop eating. Therefore, you would over eat. |
|
|
The Tectum and the Tegmentum can be found |
in the mesencephalon (Midbrain) |
|
|
The _________________ also known as the roof is responsible for sensory fnction
|
Tectum |
|
|
The _______________ also known as the floor is responsible for motor functions |
Tegmentum |
|
|
The Tectum is divided into two parts |
1. Superior Colliculus 2. Inferior Colliculus |
|
|
The superior colliculus is responsible for |
Visual control |
|
|
The inferior colliculus is responsible for |
auditor control |
|
|
The Tegmentum is composed of |
Substantia Nigra |
|
|
What is the functional role of the substantia nigra |
Reward, addiction, and movement |
|
|
Damage to the ___________ appears to result in parkinsons |
Substantia Nigra |
|
|
Substantia Nigra is black because |
it contains melanin |
|
|
Parkinsons was once known as |
Shakin Palsy |
|
|
Tegmentum is comprised of |
1. substantia nigra 2. The reticular formation |
|
|
What is the reticular formation involved in? |
Sleep, arousal, attention, movement and some reflexes |
|
|
Describe the "little net" |
loosely clustered neurons amidst white matter in the tegmentum. |
|
|
What is the function of the reticular activating system? |
1. filters and prioritizes sensory information 2. Helps the brain to focus and remain alert 3. consciousness |
|
|
What would result if damage to the Reticular activating system occured |
Damaged RAS could lead to a coma.
|
|
|
The Cerebellum is responsible for |
Motor behavior and motor skill learning |
|
|
The cerebellum is __________ in agile animals than less agile animals |
Larger |
|
|
Birds that are strong fliers have a larger lobule _____ |
VI |
|
|
Birds with adept beaks have a larger/longer lobule _____________ |
VI, VII, and VIII |
|
|
THe dinecephalic nucleus that suppresses weigh gain is: A. Lateral Hypothalamus B. Ventromedial C. Dorsolateral D. Ventrolateral |
B. Ventromedial |
|
|
The function of the tectum is to: A. Map visual space B. Map auditory space C. Map visual and auditory space D. Catch mice |
C. Map visual and auditory space. |
|
|
The brainstem connects what two components? |
1. forebrain 2. Spinal cord |

