![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Proteins |
-Enzymes are proteins - Proteins are made up of amino acids -the amino acid is a particular enzyme in sequence - proteins can act up as °structural components of tissue- muscles °hormones- insulin is a protein that works up as hormones °antibodies- they lock onto antibodies to kill invading cells ° catalyst- enzymes -all enzyme are proteins -Amino acids can fold up to the 3d shape which is the proteins. |
|
|
Enzymes |
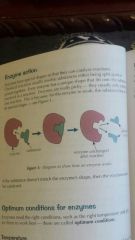
-Enzymes are made of proteins -living things produce enzymes that act as biological catalysts
-Catalysts- a substance that increases the speed of chemical reception without being changed or being used in the reaction
-Enzymes have special shapes do they can catalyst reactions
-The reason why proteins are it's unique shape is the folding of long chains of amino acids, to give each protein a special shape. it's held together by bonds that's why it's given a unique shape.
-The proteins special shape to allow other molecules to fit into it letting the protein do its job.
-Enzymes only catalysts to one reaction because every enzyme has their own unique shapes to fit onto in a reaction. -The proteins special shape to allow other molecules to fit into it letting the protein do its job. ♤The enzyme and the substrate lock and key. (They have to fit each other if it the substrate doesn't match the enzymes shape, the reaction won't be catalysed) ♤if they fit, it's enzymes/substrate complex ♤After the reaction. Enzyme is unchanged as the substrate is split as it's made into product. -IF THE ENZYME IS INVOLVED IN SPEEDING UP AN REACTION IT'S CALLED ENZYME CATALYSED REACTION |
|
|
Optimum conditions for enzymes |
-Enzymes need the right temperature and pH. This is called optimum conditions
÷TEMPERATURE
-Charging the temperature changes the rate of an enzyme catalyst reaction some of the enzymes will break. If could break the enzymes shape making it not work anymore. This means denatured.
-Denatures- enzyme shape changes -Enzymes in the human body work best at 37°C
-The substrate and enzymes lock and key as if it's too hot above 40°C it will become denatured.
÷PH -it affects enzymes -A low pH means acidic and A High pH means alkaline -if the pH is too high or low. It interferes with the bonds. -it changes the shape and denatures the enzymes. - 7.5 -All Enzymes have a pH that they work best at this called optimum pH. |
|
|
Uses of enzymes |
-Biological detergents- contains protease and lipase (breaks down protein and fats and oils in stains) they are more effective working at low temperature in 30°. -Baby food- protease (it pre-digests proteins for the baby ) -Diet food- Glucose syrup is converted into fructose syrup by using isomerase enzyme. It's sweeter than glucose that's why it's used in swimming and food and drink. |
|
|
Digestive enzymes |
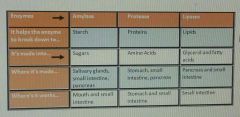
Food is broken down by two ways -By digestive system -By enzymes -They produced by specialised cells in the glands and they are released into the guts to mix with food molecules -Starch and proteins and fats are large molecules. They are too big to go through the walls of the digestive system Sugar and amino acids and glycerol are such smaller molecules So they can easily pass through the digestive system -The digestive catalyst breaks down the large molecules to small molecules. -Different enzymes help to break them to different types of food |
|
|
The table of digestive system |
|

