![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Amino acid - a simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (—COOH) and an amino (—NH₂) group. |
Peptide - a compound consisting of two or more amino acids linked in a chain, the carboxyl group of each acid being joined to the amino group of the next by a bond of the type -OC-NH-. |
|
|
Polypeptide - a linear organic polymer consisting of a large number of amino-acid residues bonded together in a chain, forming part of (or the whole of) a protein molecule. |
Protein - any of a class of nitrogenous organic compounds which have large molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids and are an essential part of all living organisms, especially as structural components of body tissues such as muscle, hair, etc. and as enzymes and antibodies. |
|
|
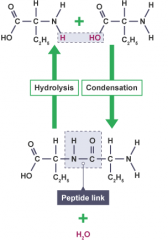
Two amino acids can undergo a condensation reaction to form a di-peptide. Further condensation reactions result in a polypeptide. The amino acid units are linked by peptide bonds (sometimes called peptide links). |
Protein structure The sequence of amino acids in a protein is called its primary structure. Within a chain the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. Each protein has its own characteristic sequence of amino acids.Three types of bonding can happen within a protein molecule (intramolecular bonding) and between protein molecules (intermolecular bonding): Hydrogen bonds, Covalent bonds and Ionic bonds |
|
|
Primary - Covalent bond (amide/peptide bond) |
Secondary - Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
Tertiary - Ionic bonds, disulfide bonds, hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding |
Quaternary - Ionic bonds, disulfide bonds, hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding |
|
|
Protein test - Proteins are detected using Buret reagent. This turns a mauve or purple colour when mixed with protein. |

