![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two basic types of prosthetic heart valves? |
1) tissue ( stented/stentless, homografts, autografts) 2) mechanical |
|
|
What is the flow pattern for bioprosthetic valves? |
1) trileaflet open to circular orifice 2) similar to native valve 3) laminar flow with blunted profile 4) small amount of regurgitation likely 5) inflow stream directed towards septum |
|
|
What are the available stented bioprosthetic valves? |
1) carpentier 2) St. Jude 3) Medtronic 4) Mitroflow |
|
|
What are the advantages of stentless bioprosthetic valves? |
1) improved hemodynamics 2) easier to implant (Only used in aorta so far) |
|
|
What is the echo appearance of stentless bioprosthetic valves? |
1) mimics normal aortic valve 2) increased echogenicity 3) dilation of root often improves following procedure |
|
|
What are the available stentless bioprosthetic valves? |
Old generation 1) Medtronic F. 2) Toronto 3) Prima-Edwards New generation 4) Shelhigh 5) Sorin (Newer generation easier to implant due to less sutures) |
|
|
What are the advantages of sutureless bioprosthetic valves? |
1) designed to replace valve 2) uses a minimally invasive open-heart surgery |
|
|
What are the types of sutureless bioprosthetic valves? |
1) Perceval 2) 3F 3) Intuity |
|
|
A bioprosthetic valve that uses a cyropreserved human aortic valve is called: |
A homograft |
|
|
What are features of the homograft? |
1) no stents needed 2) aortic or pulmonic position 3) rarely seen in AV valves 4) valve failure usually result of regurgitation |
|
|
What are the fluid dynamics of homografts? |
1) similar to native valve 2) flow velocities slightly higher 3) valve areas slightly smaller |
|
|
A bioprosthetic valve that uses a patients own pulmonary valve and places it in aortic position, usually only done in children, is called: |
An autograft |
|
|
Repair of the native valve using a flexible ring sewn into the annulus position is called: |
Annuloplasty ring ( Carpentier-edwards most common) |
|
|
What are the characteristics of mechanical valves? |
all have a sewing ring, moving component, and cage/strut |
|

A mechanical valve with a spherical occluder and mechanical cage, no longer implanted these days, is called: |
Ball and cage |
|
|
What are the types of ball and cage valves? |
1) Star-Edwards (most common) 2) Smeloff 3) Braunwald 4) Magovern 5) Magover 6) Harken 7) DeBakey 8) Hufnagel |
|
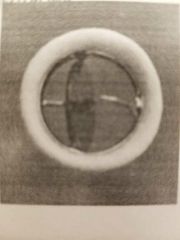
A mechanical valve with a circular disc that opens at an angle, controlled by a central strut or slot, is called: |
Tilting disc valve |
|
|
Types of tilting disc mechanical valves include: |
1) Bjork (most common) 2) Medtronic (most common) 3) Lillehei 4) Hall 5) Wada 6) Omiscience and Omnicarbon |
|

What are the characteristics of the bileaflet valve? |
1) Two semicircular disks that open to form two large orifices 2) st. Jude most frequently used |
|
|
What are the three mechanisms of failure in prosthetic mechanical valves? |
1) structural 2) thromboembolic complications 3) endocarditis |
|
|
A rupture of one or more sutures that anchor the sewing ring is called: |
Dehiscence |
|
|
What are the echo features of dehiscence? |
1) exaggerated motion of valve 2) rocking motion as sewing ring prolapses (in extreme cases) |
|
|
What are the incidental findings of mechanical valves? |
1) spontaneous contrast 2) abnormal position |
|
|
Cardiac dysfunction due to an implant being too small or too large is called: |
Pseudo-prosthetic dysfunction |
|
|
What are the normal values for prosthetic regurgitation? |
1) MR jet area <2 cm squared 2) MR jet length <2.5 cm 3) AI jet area <1 cm 4) AI jet length <1.5 cm |
|
|
Signs of severe aortic regurgitation in prosthetic valves is: |
1) PHT of 250 milliseconds or lower 2) holodiastolic reversal in descending aorta 3) 55% or higher reguritant fraction |
|
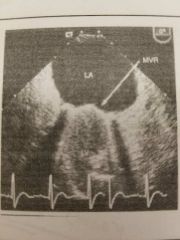
Blood flow through three orifices is a profile for which mechanical valve? |
Bileaflet |
|
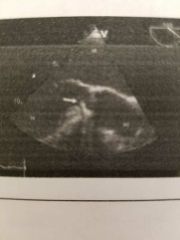
Newly formed vascular tissue around a valve is called: |
Pannus growth |
|
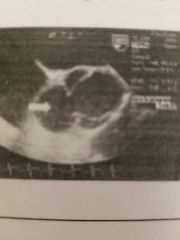
This is the 2D appearance for: |
Aortic ring abscess |
|
|
About how long do bioprosthetic valves last before failing to open/close? |
10 yrs + |
|
|
What are the complications associated with bioprosthetic valves? |
1) calcification / degeneration 2) endocarditis 3) perivalvular leak 4) dehiscence 5) stenosis 6) regurgitation 7) thrombus |
|
|
What are the complications associated with mechanical valves? |
1) thrombus 2) stenosis 3) dehiscence 4) endocarditis 5) hemolysis 6) mechanical failure 7) heart-valve mismatch 8) LVOT obstruction 9) pannus growth 10) regurgitation |

