![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1 85% of prostatic adenocarcinoma located? |
1 peripheral gland (why they can be palpated rectally) |
|
|
|
1 What is gleason score? |
1 Predominant gleason grade added with secondary grade |
|
|
|
1 List variants of prostatic adenocarcinoma? (7) |
1 (all of these are very rare, like <1% and most have bad prognosis except the first one) basaloid (adenoid cystic like), prostatic duct, adenosquamous, squamous cell, signet-ring, with neuroendocrine features, mucinous |
|
|
|
1 To dx mucinous variant must have ? % mucin? 2 What % of carcinomas have neuroendocrine features ? NE cells resembele ? and stain with ? 3 SCC, prognosis? PSA levels? Tx? 4 Adenosquamous is associated with? 5 What do squamous and adenosquamous have in common? 6 histo of basaloid carcinoma? prognosis? |
1 >25%, very uncommon (<1%) 2 10-30%, Paneth cells (eosinophilic cytoplasmic granules); stain wht PSA & chromogranin 3 very poor porgnosis, normal PSA levels even with metstases, do not respond to hormone terapy 4 prior radiation or homotherapy for conventional carcinoma 5 they have poor prognoses, not graded and are negative for PSA and PASP 6 resembles adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary gland and is less agressive than the restL |
|
|
|
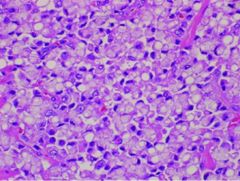
1 To dx signet ring cell carcinoma what % must be present? 2 graded as? Tumor behavior? |
1 25% 2 gleason 5, very agressive |
|
|
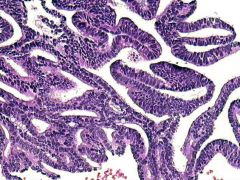
Prostatic duct carcinoma 1. Histo? 2 Typical location? 3 often mixed with?
|
1 Columnar pseudostratified epithelium with amphophilic cytoplasm often with comdeonecrosis and prominent atypia. Growth often papillary with occasional cribriforming (resembeles endometrioud CA) 2 Periurethral! unlike the others wich are peripheral! 3 conventional acinar carcinoma |
|
|
1 List differential diagnoses for prostatic adenocarcinoma? (7) |
1 Atrophy, partial atrophy, seminal vesicle, squamous metplasia, basal cell hyperplasia, adenosis and high grade PIN |
|
|

|
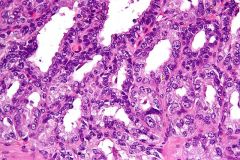
Atrophy 1 micro description? |
1 basophilic glands with open lumen lned by cells with high n/c ration +/- prominent nucleoli but cells maintain lobular architercture separated by fibroti stroma and BM is preserved (with P63 stain, though may be fragmented). With sclerosis may become angulated though |
|
|
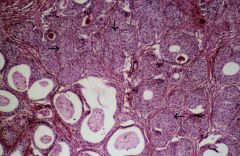
Seminal vescicle epithelium 1 histo? 2 pertinent negative stain? |
1 Cytoplasm with yellow/brown lipofuschin granules and columnar cells may show hyperchromasia or atypia but no mitoses; PSAP negative! |
|
|
Squamous metaplasia 1 due to? |
1 infarcts, s/p TURP, estrogen therapy, anti-estrogen therapy or radiation therapy |
|

|
Basal cell hyperplasia 1 histo? 2 Location? usually accompanies?
|
1 small solid nests of large stratified hyperchromatic epithelial cells with clear cytoplasm and prominent nucleoli 2 Peripheral zone; nodular hyperplasia |
|
|
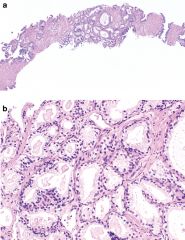
Adenosis (there is also a sclerosing version) 1 histo? 2 Found almost exclusively in? 3 strong association with? 4 AKA? |
1 numerous crowded small pale glands (sizes can vary) usually in lobular configuration with nearby transition to normal glands; oftern contain copora amylacea but NOT blue mucin and at least some staining with basal cell markers. 2 Transition zone 3 nodular hyperplasia (86%) 4 atypical adenomatous hyperplasia |
|
|
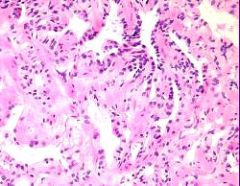
partial atrophy 1 histo?
|
1 Stellate undlated glands with pale cytoplasm and crinkled nuclei mixed with complete atrophy, usually lack atypia and patchy presence of basal cells |
|

|
High grade PIN (small focus of carcinoma in photo) 1 histology? how to DX? 2 Accompanying carcinoma in ? %?
|
1 multilayering of enlarged crowded plemorphic nuclei with prominent nucleoli; dx at low power 2 30%
|
|

|
Cowpers glands 1 aka? 2 histo? |
1 bulbourethral gland 2 Well demarcated lobules of small, compact tubuloalveolar glands resembling minor salivary glands radiating from a duct and trapped in muscle fascicles |
|

|
Nephrogenic adenoma/metaplasia (listed below in bladder metaplasias) 1 histo? 2 pathogenesis? 3 Positive IHC? |
1 Tubules composed of single layer of cuboidal cells with clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm usually near urothelium extending into muscle with accompanying inflammation. 2 assocated with urothelial injury such as intravesicle BCG treatment or transplant. 3 AMACR + |
|

|
Prostatic nodular hyperplasia 1 patient population? 2 Location and histology? 3 two associations? |
1 Men, incrases with age 45-50% in 5th decade, 75% in 8th decade 2 peri-urethral, a proliferation of stroma (first) and glands in which the stroma has increased smooth muscle and the glands are lined by flat to columnar etihleium with pale cytoplsm and recular centrally located nuclei with intact basal layer, may be very cystic and contain corpora amylacea 3 Squamous metaplasia and infarction |
|
|
1 List 3 types of bladder metaplasia? 2 List the subtypes, patient population and cuases of the first one? |
1 squamous, intestinal and nephrogenic (see above card)
|
|
|

|
Squamous metaplasia 1 List 2 subtypes, patient population, causes and associations of each? |
1vaginal: women, nonkeratinizing, regarded as normal because so common in bladder trigone
keritinizing: men, aka leukoplakia due to chronic irritation has an association with SCC of bladder |
|

|
Intestinal metaplasa 1 aka? 2 Due to? 3 what is the sequence of progression of this lesion? |
1 cystitis glandularis 2 chronic inflammationand mucosal irritation 3 von Brunn's nests (invaginations of urothelium) --> cystitis cystica (central cystic area filled with mucin) --> cystitis glandularis (glands acquire colonic like mucinous epithelium) |
|
|
1 List bladder neoplastic bladder lesions? (6) 2 Patient population? 3 Western association? middle eastern association? location? 4 Serum beta-HCG?
|
1 Flat dysplasia, Flat CIS, papilloma, PUNLMP, LG papillary urotheilial carcinoma, HG papillary urlthelial carcinoma 2 M>W (3:1), White>black, ages 50-70 3 smoking; Schistosoma haematobium --> SCC; trigone 4 10-30% of patents with HG urothelial carcinoma and 50% with mets
|
|
|
|
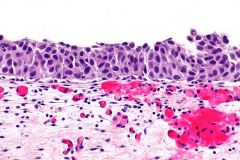
Flat dysplasia 1 Almost always seen in? 2 histo? (large interobsever variability even amongst experts) |
1 patients with carcinoma 2 Enlarged disorganized nuclei that overlap, dont mature but are normal thickness of urothelium, even chromatin with no nucleoli (b/w reactive and CIS) |
|
|
|
Urothilial carcinoma in situ 1 list 4 variants? 2 histology? |
1 lare cell, small cell, clinging (denuding), pagetoid 2 Pleomorphic hyperchromatic cells resembling high grade carcinoma but confined to the epithlium, often lack cellular cohesion |
|

|
PUNLMP 1 stands for? 2 histo?
|
1 papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential 2 Papillae with orderly arrangement of cells with minimal architectural and nuclear atypia; urothelium thicker than papilloma with larger nuclei |
|

|
low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma 1 histology? 2 ? % of urothelial neoplasms? |
1papillary with densly packed uniform overlapping nuclei that are more round and pleomphic that usual with irregular nuclear borders 2 15-30% |
|

|
high grade urothelial carcinoma 1 Represent ? % of urothelial neoplasms? 2 Histology? 3 List 5 variants? 4 List positive IHC? 5 Explain CK20 staining? |
1 50-60% 2 infiltrating tumor cells in sheets nests or cords with marked pleomorphism, large nucleoli and many abnormal mitoses 3 pseudoglandular, nested, sarcomatoid, mixed histology, small cell neuroendocrine 4 postiive for Leu-M1 (CD15), p63, CK7, CK20 5 CK20 normally stains umbrella cells but shows full thickness stainin in dysplasia |
|

|
papilloma 1 list two types? 2 histo? |
1 inverted, exophytic 2 both have mature elongated bland urothelial cells that are perpendicularly oriented but the exophytic has central stroma and the inverted has central epithleium. |

