![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is propofol and how is it presented. |
Propofol is a phenolic derivative commonly used in the induction and maintenance of anaesthesia. It is presented as either a 1% or 2% lipid-water emulsion. It has a pKa of 11, therefore unionised at physiological pH. |
|
|
What is the structure of propofol |
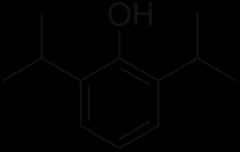
2,6-di(propan-2-yl)phenol |
|
|
What are the dosages of propofol |
Induction: adult - 1.5-2.5 mg/kg (but frequently much larger doses required Child - up to 4mg/kg Maintenance - 4-12 mg/kg/hr (4-8 ug/ml) Sedation in ICU - 0.3-4 mg/kg/hr |
|
|
What are the effects of propofol |
CV - vasodilatation causing decreased SVR Decreased sympathetic activity blunts normal tachycardic reflex, may cause bradycardia (esp. If combined with opiates) Decreased myocardial contractility Resp - respiratory depression leading to apnoea. Cough reflex suppression Layrngospasm rare GI - possibly had some antiemetic effect, ?D2 antagonism CNS - 10% display excitation like movements, thought not true seizure, likely due to impaired subcortical inhibitory: excitatory imbalance. Metabolic - fat overload syndrome, hyperlipidaemia. Pain - can cause pain on injection to small veins Misc - can turn hair and urine green |
|
|
What are the pharmacokinetic properties of propofol, and what are their implications. |
98% protein bound, large (4 L/kg) volume of distribution. This results in short duration of action due to rapidly lowered plasma levels. Metabolised primarily hepatic, but ?some renal extraction. 40% conjugated to glucuronide, 60% metabolised to a quinol. Terminal elimination half life - 5-12 hrs, but can be markedly longer. (Slow release from lipid stores) |
|
|
Discuss toxicity of propofol |
Relatively safe. No adverse effects from iv administration (delayed onset) Safe for most egg allergic pts (different protein used to normal allergin) Implicated in some unexplained paeds deaths where used for long term sedation/maintenance. ? Lipid overload related. Not liscensed for this use in U16s |

