![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
231 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CT number for blood (fluid, clotted and old)
|
+20 to +100 fluid
+50 to +75 clotted +10 to +15 old |
|
|
What is the purpose of the Gantry?
|
Collects the neccessary attenuation measurements to be sent to the computer for image reconstruction
**Circular device that houses the x-ray tube, DAS and detector array.(Newer CT units house the contiuous slip ring & high voltage generator |
|
|
What is a pixel?
|
Picture element
|
|
|
What is a voxel?
|
Volume element (3D pixel)
|
|
|
What tissue or element has a CT number of zero?
|
water
|
|
|
Absolute contraindications for MRI
|
*Pacemakers
*Ferromagnetic aneurysm clips *Metal fragments in eye *Cochlear implants *Prosthetic heart valves *Internal grug infusion pump *Neurostimulator *Bone-growth stimulator |
|
|
Name three types of magnets
|
*permanent
*Resistant *Super conductive |
|
|
Units for magnetic strength in conventional and standard international.
|
Gaus and Tesla
|
|
|
List three types of gradient coils
|
x, y, and z
|
|
|
Examples of RF coils
|
*Head, limb, TMJ, volume neck, plnanr surface coil (license plate coil), shoulder, wrist, posterior C-spine
|
|
|
list three types of breast tissue
|
Glandular, fibrous and adipose
|
|
|
list a few QC tests for mammo
|
Image of phantom, darkroom, film/screen contact and repeat analysis
|
|
|
what area of the breasts is breast cancer most often found?
|
upper lateral quadrant
|
|
|
Routine views done for mammo?
|
CC cranial caudal &
MLO mediolateral oblique (right & left) |
|
|
Commercial devices to immobilize ped pt
|
pig-o-stat
octogon board |
|
|
what part of the breast holds the breast up?
|
Cooper's ligament
|
|
|
Exams tailored for ped pts?
|
*Bone age
*Club feet series *Scoliosis series *Chest/Abdomen for foreign body |
|
|
age group in pediatrics that has increased vocabulary
|
3-6 years of age
|
|
|
3 things that are the same if positioning an adult or child?
|
positioning (basic)
film critique assessment skills |
|
|
3 things that are different when x-raying adult vs child?
|
approach
views required tools needed |
|
|
Name reasons for a head CT
|
Contusion
Hematomastomas, subdural or epidural hematomas, Cerebral abcess Herpes simplex encephalitis, Meningitis (to check for increased cranial pressure b/4 lumbar puncture), Congenital abnormalities, Intracranial and extracranial tumors |
|
|
Indications for abdominal CT
|
Mestastases in liver,
Mestastases in adrenal glands Cysts Fatty deposits VS tumors Lymph node involvement Chronic pancreatitis Solid pancreatic masses hemangiomas Cirrhotic liver Focal masses in spleen |
|
|
Indications for chest and mediastinum CT
|
Lymphadenopathy,
Bronchogenic carcinoma Lymphoma or other malignancies Medialstinal masses Presence or extent of aneurysms and aortic dissections Pulmonary mestastases Primary lung tumor |
|
|
Indications for spine CT
|
Disk herniation
Spinasl stenosis Spinal infection of disk space or epidural area Trauma or intraspinal tumor |
|
|
Indications for neck or face CT
|
Developmental anomalies
Inflammation or infection Trauma Tumors |
|
|
Define CT
|
process of creating cross-sectional tomographic plane of any part of the body
|
|
|
how is a scan obtained during CT
|
x-ray tube rotating around body part
|
|
|
how is exit radiation measured?
|
by the detector assembly
|
|
|
what does the detector assembly do with this information?
|
sends info or primary data to computer
|
|
|
how does CT eliminate superimposition?
|
By passing a tightly collimated beam through a part at many different angles
|
|
|
how has CT improved contrast resolution?
|
by reducing scatter radiation
|
|
|
Does CT need contrast to demonstrate tissues of similar densities?
|
No! CT has greatly reduced the need for contrast to demonstrate tissues of similar density
|
|
|
where is the digital image displayed?
|
in a matrix
|
|
|
what is a matrix?
|
a grid of rows and columns
|
|
|
what is a pixel?
|
single square or picture element within a matrix
|
|
|
what does slice thickness add to dimension?
|
volume
|
|
|
what is a voxel?
|
volume element of matrix
|
|
|
what is a voxel a product of?
|
pixel area and slice thickness
|
|
|
field of view? (FOV)
|
determines the amount of data displayed on monitor
|
|
|
how is each pixel assigned?
|
to a number that is related to the linear attenuation coefficient of the tissue with in each voxel
|
|
|
what are numbers called in CT
|
CT numbers or Hounsfield units
|
|
|
CT numbers equal?
|
relative comparison of x-ray attenuation of a voxel of tissue to an equal volume of water
|
|
|
water is a reference b/c (2 reasons)
|
ABUNDANT IN THE BODY AND HAS UNIFORM DENSITY
|
|
|
what number is water asinned?
|
zero
|
|
|
what are positive CT numbers?
|
tissues that denser than water
|
|
|
what are negative CT numbers?
|
tissues less dense than water
|
|
|
what is the scale range for numbers in CT?
|
-1000 (air) to +14,000 (dense bone)
|
|
|
In CT the grey level on display corresponds to?
|
Data converted into gray-scale image
(number for that pixel) The brightness values of the grey-scale image correspond to the pixels and CT numbers of the digital data they represent |
|
|
name the three system components for CT
|
*computer and operators console
*gantry *patient table |
|
|
what is the computers function?
|
links technologist and other components of imaging system
|
|
|
four basic functions of computer in CT
|
*control data and acquisition
*image reconstruction *storage of image data *image display |
|
|
3 functions of the gantry
|
*can tilt to compensate for body angle
*aperture =opening in center of gantry ~28" wide *Pt table advances thru apeture |
|
|
Operators console function
|
point from which the technologist controls the scanner
|
|
|
what is the operator's console equipped with?
|
Keyboard, graphic monitor, other input devices (mouse and touch screen)
|
|
|
operator's console scan parameters that are controlled at the console are?
|
technique factors, slice thickness, table index and reconstruction algorithm
|
|
|
windowing technique allows viewer to alter contrast of displayed image by adjusting ?
|
window width and window level
|
|
|
what is window width? (2)
|
WINDOW WIDTH CONTROLS CONTRAST (shades of grey)
Narrow=fewer shades=high contrast Wide=more shades=longer scale **Range of CT numbers used to map signals into shades of gray **Establishes the number of grey levels displayed |
|
|
what does "narrow window" refer to?
|
fewer shades of grey or high contrast
|
|
|
what does wide window refer to?
|
greater shades of grey or longer scale of contrast
|
|
|
what is window level?
(3 things) |
*sets the midpoint of range of grey levels displayed
*used to set the center CT number within the range of grey levels used to display image *should be set to CT number of the tissue of interest |
|
|
what are the most common procedures for CT
|
head chest abdomen
|
|
|
what was CT originally used for?
|
neurological disorders
|
|
|
how is contrast media used in CT(2 things)
|
*helps distinguish normal anatomy from pathology
*increases visibility of diseased processes |
|
|
how is contrast administered in CT?
|
IV, orally and rectally
|
|
|
2 main things contrast used for
|
enhance tumors in brain, visualize vascular structures
|
|
|
what type of contrast is required for abdominal CT
|
oral contrast
|
|
|
what does the contrast of the abdomin differentiate between?
|
Between bowel and other structures
|
|
|
how can rectal contrast be used?
|
as part of abdominal or pelvic protocol
|
|
|
special features of CT
|
dynamic screening, spiral/helical CT, multi-slice spiral/ helical CT, CT angiography, 3D imaging, radiation treatment planning.
|
|
|
what demonstrates bone better CT or MR?
|
CT
|
|
|
What displays soft tissue better CT or MRI?
|
MRI
|
|
|
Name 5 advantages of spiral CT
|
*scan time less
*interscans are minimized *one single exposure and one breadth allows complete coverage of anotomic area *patient motion artifacts are reduced *shifting of anatomic structures position reduced |
|
|
name 3 limitations of spiral CT
|
*tubes with improved cooling and higher capacity (more power)
*reconstruction time (interpolational algorithm applied to all collected data) *unshapen images from partial volume averaging |
|
|
CT exam brain width and center
|
width 190
center 50 |
|
|
CT exam skull width and center
|
width 3500
center 500 |
|
|
CT exam orbits width and center
|
width 1200
center 50 |
|
|
CT exam abdomen width and center
|
width 400
center 35 |
|
|
CT exam liver width and center
|
width 175
center 45 |
|
|
CT exam mediastinum width and center
|
width 325
center 50 |
|
|
CT exam lung width and center
|
width 2000
center -500 |
|
|
CT exam spinal cord width and center
|
width 400
center 50 |
|
|
CT exam spine center and width
|
width 2200
center 400 |
|
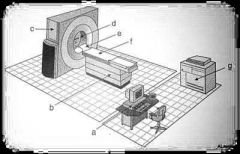
|
a. Operator console
b. Adjustable table c. Gantry d. Apeture e. Head holder f. patient couch g. laser imager |
|
|
Positive CT numbers are?
|
DENSER than water (lighter)
|
|
|
NEGATIVE CT numbers are?
|
LESS DENSE than water (darker)
|
|
|
Scale numbers for CT are
|
-1000 (air) to +14,000 (dense bone)
|
|
|
Hounsfield unit for air
|
-1000
|
|
|
Hounsfield unit for lungs
|
-250 to -850
|
|
|
Housfield units for fat?
|
-100
|
|
|
Hounsfield units for orbits?
|
-25
|
|
|
Hounsfield units for water?
|
ZERO!!
|
|
|
Hounsfield unit for cysts?
|
-5 to +10
|
|
|
Hounsfield unit for fluid?
|
Zero to +25
|
|
|
Hounsfield unit for tumor?
|
+25 to +100
|
|
|
Hounsfield unit for blood?
*Fluid *Clotted *Old |
Fluid : +25 to +50
Clotted: +50 to +75 Old: +10 to +15 |
|
|
Hounsfield unit for brain?
|
+20 to +40
|
|
|
Hounsfield unit for muscle?
|
+35 to +50
|
|
|
Hounsfield unit for gallbladder?
|
+5 to +30
|
|
|
Hounsfield unit for liver?
|
+40 to +70
|
|
|
Hounsfield units for aorta?
|
+35 to +50
|
|
|
Hounsfield units for bone?
|
+150 to +1000
|
|
|
Hounsfield units for metal?
|
+2000 to +4000
|
|
|
What is the reference point for CT and why?
|
Water because
*It is abundant in the body *It has uniform density *Has value of zero |
|
|
What are the most common CT procedures?
|
Head
Chest Abdomen |
|
|
When CT of head is done what is imaged and what is the scout?
|
Vertex to base is imaged and the scout is usually lateral.
|
|
|
When doing a CT of the abdomen what is imaged and what is the scout?
|
Diaphram to pubic symphysis is imaged and the scout is an AP.
|
|
|
When doing a CT of just the chest or mediastinum area what must be changed to obtain an accurate picture and what scout is done?
|
Since the lungs have air in them the window level/width must be changed to match lungs and the scout is an AP.
|
|
|
What does a thin CT slice do to patient dose?
|
Increases patient dose
|
|
|
What will a thick CT slice do to patient dose?
|
Thick slice will decrease patient dose but can miss something.
|
|
|
An axial CT means?
|
Top to bottom CT
|
|
|
Coronal CT means?
|
Front to back CT
|
|
|
Sagittal CT means?
|
Side to side CT
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for CT?
|
There are NO contraindications for CT!!
|
|
|
What is a "window level " for in CT?
|
A "centering point" for choosing density which is chosen by Hounsfield number of the anatomy in the study.
|
|
|
CT vs. MRI (4)
|
*Patients with metal in thier body
*Useful for claustrophobic patient or cannot tolerate longer MRI scans *Less costly exam than MRI *Visualize bone better |
|
|
Special CT features?
|
*Dynamic scanning
*Spiral/helical CT *Multi-slice spiral/hlical CT *CT angiography *3D imaging *Radiation treatment planning (to pinpoint where to go in for treatment) |
|
|
Advantages of spiral CT
|
*Less than 60 seconds scan time
*One consistent scan (better for contrast media flow studies and physiology of organ studies *One exposure (one breath hold) *Motion artifacts are reduced *Reduction of anantomy shifting caused by breathing |
|
|
Disadvantages of CT vs. X-ray
|
*CT needs more power to operate b/c the need for more cooling
*Takes longer for image to appear(algorithm applied to reduce streak artifacts) *Unshapen images due to partial volume averaging |
|
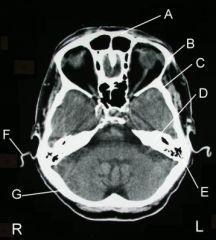
|
a. Frontal bone
b. Zygoma c. temporal bone d. Petrous ridge e. Mastoid air cells f. Cartilage g. Occipital bone |
|
|
Define MRI
|
The use of a magnetic field and radio waves to obtain a mathematically reconstructed image.
|
|
|
Absolute contraindications for MRI
|
8Pacemakers
*Ferromagnetic anuerysm clips *Cochlear implants *Prosthetic heart valves *Internal drug infusion pumps *Nuerostimulators *Bone-growth stimulators |
|
|
What is the patient prep for an MRI exam?
|
*Screen for all contraindications
*Remove ALL metal *Explain exam (NO movement from patient & noise from machine) *Ensure patient comfort |
|
|
Name the five components of an MRI system.
|
*Magnet
*Gradient coils *RF (radio frequency) coils *Electronic support system *Computer & display |
|
|
Name the KEY components of MRI imaging system to produce an image
|
**Magnetic field
**Pulsed radio waves **Nuclei of hydrogen atoms in the body |
|
|
Name how magnets are measures in strength in conventional and standard international units.
|
Conventional is Gauss
Standard international is Tesla |
|
|
What are the three types of magnets?
|
*Resistive
*Permanent *Superconducting |
|
|
How many Tesla for resistive magnet?
|
0.3 Tesla
**requires large amount of electric power |
|
|
How many Tesla for permanent magnet?
|
0.3 to 3.0 Tesla
**This magnet CANNOT be turned off |
|
|
How many Tesla for a superconducting magnet?
|
2 to 3 Tesla
**requires cryogenic materrial to keep cool (liquid nitrogen or liquid helium) **can come in short bore or open (short bore is a little longer than a CT gantry and open MRI has no sides only a top & bottom) |
|
|
What are gradient coils?
|
coils that carry electrical current to produce a desired gradient magnetic field (causes precession)
|
|
|
Name three types of gradient coils.
|
X,Y, & Z
|
|
|
Name some types of RF (radio frequency) coils.
|
*Limb/ extremity
*Volume neck *Breast *Plantar (License plate) *Head *TMJ *Shoulder *wrist *Posterior C-spine |
|
|
What does "T" stand for in T1 and T2 weighted images?
|
"T" stands for the time it takes for nuclei to relax back to its natural state
|
|
|
How is the time determined for MRI (T1 & T2)?
|
Time is determined by the type of tissue .
|
|
|
What is T1 in MRI?
|
Longitudinal relaxation time in MRI
|
|
|
What is T2 in MRI?
|
Transverse relaxation time in MRI
|
|
|
What does the electrical support system do in MRI?
|
Provides power to
*Gradient coils *Cooling system *Magnet *Computer and display |
|
|
What does the tech do at the computer & display?
|
sets all the parameters for
*scan time *slice thickness *Image acquisition |
|
|
Appearance of T1 & T2 weighted images of cortical bone?
|
T1 is dark
T2 is dark |
|
|
Appearance of T1 & T2 image of Red bone marrow?
|
Red bone marrow
T1 light grey T2 dark grey |
|
|
Appearance of T1 & T2 images of air?
|
Air is dark in T1 & T2
|
|
|
Appearance of T1 & T2 images of white brain matter?
|
White brain matter is
T1 light grey T2 dark grey |
|
|
Appearance of T1 & T2 images of fat?
|
Fat is
T1 bright T2 Dark grey |
|
|
Appearances of T1 & T2 images of grey matter?
|
Grey brain matter
T1 dark grey T2 light grey |
|
|
Appearance of T1 & T2 images of CSF/water?
|
CSF/water
T1 is dark T2 is bright |
|
|
Appearance of T1 & T2 images of muscle?
|
Muscle is
T1 dark grey T2 Dark grey |
|
|
Appearance of T1 & T 2 images vessels?
|
Vessels are
T1 dark T2 dark |
|
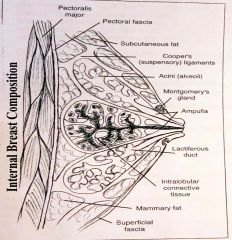
|
a. pectoralis major
b. pectoral fascia c. subcutaneous fat d. Coopr's ligament (suspensory e. acini (alveoli) f. Montgomery's gland g. ampula h. lactiferous duct i. intralobular connective tissue j. mammary fat k. superficial fascia |
|
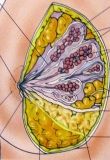
|
a. ducts
b.nipple c. areola d. ampulla e. subcutaneous fat f. Interlobular connective tissue g. lobe h. mammary fat i. Cooper's (suspensory) ligament j. alveoli |
|
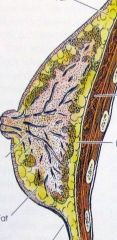
|
a. fat
b. nipple c. lactiferous duct d. inframammary crease e. retromammary fat f. pectoralis major |
|
|
Define screening mammography.
|
Routine exam with no issues. (asymptomatic)
**Craniocaudal (CC) **Mediolateral oblique (MLO) RIGHT & LEFT |
|
|
Define diagnostic mammography.
|
A specific reason to do more tests. Suspect cancer is present or patient is known to have past breast cancer.
CC & MLO with any of the other 11 projections are done |
|
|
Where is breast cancer predominantly found?
|
Upper outer quadrant
|
|
|
Name some of the breast cancer.
|
**Ductal carcinoma incitu
**Infiltrating ductal **Medullary carcinoma **Infiltrating lobular |
|
|
What is patient prep for mammography?
|
-No deoderant
-No powder -Nolotion/oils -Wipe down *(These steps help prevent a false positive) |
|
|
Which muscle should be seen on image?
|
Pectoralis major (white part on image near chest wall)
|
|
|
what is another name for the craniocaudal with implant displaced?
|
Pinch and pull
|
|
|
What is a must for quality for film-screen mammography?
|
Taut compression
**Applied compression immediately before exposure and release immediatelyt after. |
|
|
Should direct pressure be applied to implants? And who stated whether yes or no?
|
NO per Dr. G.W. Eklund
|
|
|
What does compression decrease in mammography?
|
**Radiation dose by decreasing breast thickness
**geometric blurring by decreasing object to image distance **Variation in radiographic density of the breast by increasing uniformity of breast thickness |
|
|
Compression in mammography increases ?
|
**Image contrast by decreasing scatter radiation
**Image resolution by decressing motion through immobilization **Separation of breast tissue by decreasing breast tissue overlap (spreads out tissue) |
|
|
What is key to compression cooperation?
|
Patient education
|
|
|
Fibro-Glandular breast classification? (4)
|
-15 to 30 years of age (and childless females over age 30)
-Pregnant or lactating females -Radiographically dense -Very little fat |
|
|
Fibro-Fatty breast classification?(4)
|
-30 to 50 years of age
--young women with 3 or more pregnancies -Average density radiographically -50% fat and 50% fibro-glandular |
|
|
Fatty-breast classification (4)
|
-50 years and over
-Postmenopausal -Minimal density radiographically -breasts of children and males |
|
|
What MUST be present on film to have a properly positioned mammogram?
|
Pectoralis major muscle
|
|
|
Most common type of breast cancer?
|
Ductal carcinoma
|
|
|
What is essential to success with pediatric patients?
|
**understanding children are not small adults
**appreciating thier need to be approached on their level |
|
|
When dealing with pediatric patients who is the second patient?
|
The parent
|
|
|
if the child is old enough to understnad should you speak directly to them?
|
YES!
|
|
|
When/if you speak directly to a child what are 2 things to keep in mind?
|
**use age appropriate language at thier eye level
**PARENT WILL LISTEN AND APPRECIATE SPECIAL ATTENTION GIVEN TO CHILD |
|
|
when child is too young who should the exam be explained to?
|
The parent
|
|
|
what three things to remember when talking to parents of the pediatric patient
|
**use lay terms and simple sentences
**Parents are often stressed and distracted **simple instructions will aid understanding |
|
|
when dealing with aggitated parent of pediatric patient remember (6)
|
-fear causes aggitation
-remain calm -use soothing tones -introduce yourself and escort parent & patient to private area(avoid upsetting others) -listen with concern w/o interuption -provide explanation and comfort - |
|
|
Parent participation depends upon ?
|
-department philosophy or protocols
-wishes of parent and patient -laws of provence or sate -better if only one parent (avoids overcrowdingf) |
|
|
advantages to parent participation (4)
|
-can watch child
-tech can leave room -assist with immobilization -parent can witness to professional conduct |
|
|
Pediatric patients that are infant to 6 months old only require (3)
|
*warmth
*security *nurishment |
|
|
What should be remembered when dealing with infant to 6 month old patients?
|
-they do not distinguish between caregivers
-startled by loud noises -comforted by pacifiers and familiar objects |
|
|
Pediatric patients 6 months to 2 years have 3 major problem areas (FEARS)
|
-pain
-separation from parent -limitation in movement |
|
|
What do ped pt from 6 months to 2 years of age require?
|
**Most assertive immobilization technique (better than several adults in lead aprons)
**parent participation |
|
|
ped pt age group 2 to 4 years have 4 positives
|
-very curious
-enjoy fantasy -cooperate if treated like a game -respond to praise |
|
|
what will an agitated child respond to?
|
NOTHING!!!
|
|
|
Pediatric patients that are infant to 6 months old only require (3)
|
*warmth
*security *nurishment |
|
|
What should be remembered when dealing with infant to 6 month old patients?
|
-they do not distinguish between caregivers
-startled by loud noises -comforted by pacifiers and familiar objects |
|
|
Pediatric patients 6 months to 2 years have 3 major problem areas (FEARS)
|
-pain
-separation from parent -limitation in movement |
|
|
What do ped pt from 6 months to 2 years of age require?
|
**Most assertive immobilization technique (better than several adults in lead aprons)
**parent participation |
|
|
ped pt age group 2 to 4 years have 4 positives
|
-very curious
-enjoy fantasy -cooperate if treated like a game -respond to praise |
|
|
what will an agitated child respond to?
|
NOTHING!!!
|
|
|
5 year old ped pt. vary from
|
confident to clingy
|
|
|
6 to 8 year olds are ideal for inexperienced rad techs for (3) reasons
|
-eager to please
-easy to communicate with -very modest |
|
|
Preteens and adolescents are able to understandbut still require (4) things
|
-worried about recovery
-need clear explanation and questions answered -possibility of pregnancy -a female tech should ask if pt. possibly pregnant |
|
|
Immobilization for ped pt should (3) things
|
*never be traumatic, tortuous event for child
*never cause harm *good communication stategy required |
|
|
3 tools regularly used to immobilize ped pts.
|
-Velcro compression band (called Bucky or body band)
-strip of reusable Velcro -"bookends" |
|
|
Commercial devices used in ped immobilization
|
**Pigg-o-stat
**Octagonal immobilizer |
|
|
Name common pediatric exams
|
-chest
-hip -abdomen -GI & GU procedures |
|
|
Does the pediatric patient have to be awake for CXR?
What are 3 signals for good time to take x-ray |
YES!!
-at end of cry child will gasp -abdomen extends on inspiration - ribs are outlined on inspiration |
|
|
Why are hip x-rays ordered for ped pts.
|
-Legg-Calve'-Perthes disease
-Congenital hip dislocation -Nonspecific hip pain |
|
|
What is usually done when examining the hip?
|
BOTH sides are examined for comparison
|
|
|
What projection is needed of the peds pt if foreign object or stones are suspected?
|
AP abdomen
|
|
|
For an obstruction or abdominal pain in a peds pt what projection should be done?
|
An upright or left lateral decubitus with supine film
|
|
|
What projection is done for peds pt for a trauma?
|
Cross-table lateral to detect free air
|
|
|
GI & GU procedures useful tool for peds pts is
|
octagonal immobilizer or modified
'bunny" wrap |
|
|
Unique exams to pediatrics
|
-Bone age
-Foreign bodies (aspirated or ingested) -Scoliosis -Scanogram -Shunt series |
|
|
Why is a bone age exam done? what is the standard exam?
|
-to evaluate degree of Skeletal maturation
-PA of left hand and wrist (protocols for 1-2 year olds often include AP of knee) |
|
|
Foreign bodies aspirated for pediatric patients is common cause for respiratory distress in children b/t ?
|
6 months and 3 years of age
|
|
|
When a pediatric pt has aspirated a radiolucent object what exam is usually done?
|
Esophageal study
- lateral soft tissue neck (image obtained better with mc Infant head & neck immobilizer) -PA chest taken on inspiration and expiration to check if object lodged in bronchus -lateral chest is also taken for location |
|
|
what is a common foreign body that is ingested and what are the images taken?
|
Coins are commonly ingested and images are the neck, chest and abdomen to locate
|
|
|
Define scoliosis
|
the presence of one or more lateral-rotary curvatures of spine
|
|
|
What are the usual projections for scoliosis for children?
|
PA or AP of entire spine on single IR in upright, recumbent, lateral bending position can be used
|
|
|
when should you use shielding in pediatrics?
|
Always!!! As long as it will not comprimise the x-ray.
|
|
|
What is a scanogram for and the projections used?
|
Used to determine the length descrepancy (if any) of bones in both lower extremities.
3 projections are **AP hips, **AP knees, **AP ankles with radiographic ruler down the middle of legs OR along side of either leg is used. |
|
|
Shunt series indications are?
|
Hydrocephalus or acquired hydrocephalus (build up of excess fluid in the brain - not draining properly)
|
|
|
What are the two types of shunts done?
|
VP shunt - ventriculoperitoneal (releases fluid into peritoneum)
OR VA shunt - ventriculoatrial (releases fluid into atrium of heart) |
|
|
Bone age for pediatric pts under 2 years of age projections are
|
ALL the joints on the left side of body. (PA hand and wrist, lateral knee)
|
|
|
Myelomeningocele - define
|
Congenital defect characterized by cystic protrusion of the meniges, spinal cord tissue and fluid.
|
|
|
Myelomeningocele occurs as a result of
|
spina bifida
|
|
|
Define spina bifida and what does it cause?
|
cleft in neural arches of vertebra and causes various degrees of paralysis and hydrocephalus
|
|
|
How should the procedure be performed on pediatric patient for a myelomeningocele?
|
PRONE!! If done supine use the donut!
|
|
|
What is intussusception?
|
The prolapse of one part of the intestineinto the lumen of an immediately adjoining part.
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of intestinal obstruction in infancy and when does it occur?
|
Intussusception and will usually occur in the first year of life.
|
|
|
What procedure can intussusception be reduced?
|
It can be reduced under fluoroscopy with any contrast but air is preferred.
|
|
|
What is osteogenesis?
|
Brittle bone disease. (OI) - children prone to spontaneous fractures or fractures with minimal trauma.
|
|
|
What approach is best used when handling a child with osteogenesis?
|
**The team approach along with the primary care giver. (PRIMARY CARE GIVER KNOWS HOW TO MOVE PATIENT SAFELYT)
**Perform procedure in bed or stretcher **Technical factors need to be reduced (check technical factors after first exposure b/4 preceeding with remaining images) |
|
|
Is there a universal agreed-upon definition of child abuse?
|
NO!
Child abuse is described as "the involvement of physical injury, sexual abuse, or deprivation of nutrision, care, or affection in circumstances which indicared that the injury or deprivation may not be accidentalor may have occurred from neglect" |
|
|
Is it manditory to report suspected child abuse?
|
Yes! Tech should report any suspected case to radiologist or physician
|
|
|
What are some classic indications or x-ray indicators of child abuse?
|
-posterior rib fracture
-corner fractures -"bucket-handle" fractures of limbs |
|
|
What must ALWAYS be used when taking x-rays of suspected child abuse?
|
MARKERS!!!!
**Makes the x-ray a legal document that can be used in court!!!! |
|
|
What exam should be avoided if child abuse is suspected and why? What is recomended instead?
|
"Babygram"
**Reduced diagnostic quality. **Skeletal survey is recommended with each part centered accurately |
|
|
What are the recommended images for a suspected child abuse case.
|
AP & lateral skull
AP & lateral complete spine AP both humeri AP both forearms AP pelvis AP both femora AP both fibulae and tibiae AP both feet AP & lateral ribs |
|
|
What does pediatric radiography require?
|
Experience and practice to obtain confidence and competence
|
|
|
What is another term for child abuse?
|
Non-accidental trauma
|

