![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the normal anatomy of the prostate. |
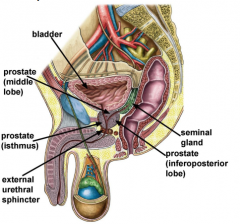
Approximately 3cm long, 4 |
|
|
What are the 3 zones of the prostate? |
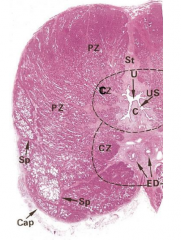
3 glandular regions |
|
|
What is the aetiology of BPH? |
– Advancing age |
|
|
What are the symptoms of BPH? |
– Weak or interrupted flow of urine |
|
|
What is the epidemiology of BPH? |
All men over the age of 40: |
|
|
What is the diagnosis of BPH? |
• History |
|
|
What is standard treatment for BPH? |
• Pharmacotherapy |
|
|
What surgery is possible for BPH? |
Transurethral resection of the prostate: – Failed voiding trials
Open prostatectomy: – For very large prostates ALSO: |
|
|
What are the differences between direct and indirect inguinal hernias? |
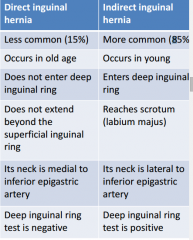
|
|
|
What are the types of hernias? |
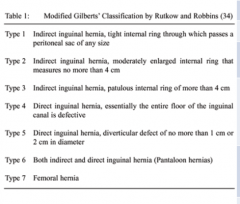
|
|
|
What is the anatomy of the inguinal rings? |
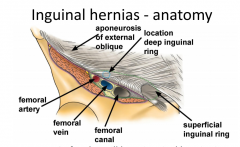
|
|
|
What is the epidemiology of inguinal hernias? |
Approx 25% of males will have inguinal hernias in |
|
|
What is the anatomy of direct inguinal herniass? |
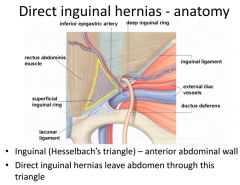
|
|
|
What is the treatment for direct inguinal hernias? |
Treatment |
|
|
What is an indirect inguinal hernia? |
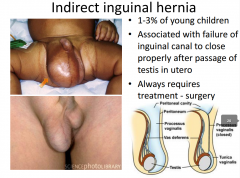
|
|
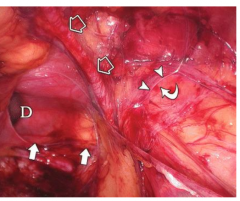
Describe this laparoscopic view of a right direct inguinal hernia. |

|
|
|
Give a summary of the characteristics of direct and indirect hernias. |
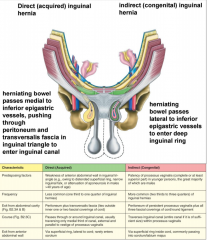
|
|
|
What is erectile dysfunction and when is it seen? |
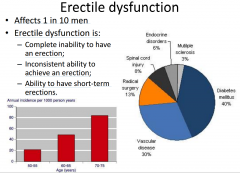
|
|
|
Describe the anatomy of the penis. |
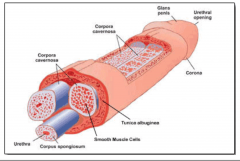
|
|
|
Describe the penile vascular anatomy when erect. |
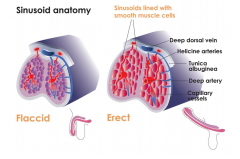
|
|
|
What happens to the lacunar space during erection? |
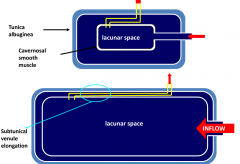
|
|
|
What 4 things can centrally control erection? |
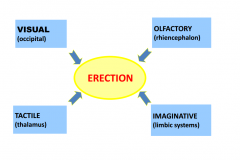
|
|
|
What is the effect of sympathetic and parasympathetic activation of smooth muscle nerve terminals of the penis? |
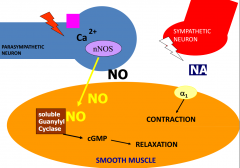
|
|
|
What is the role of NO in ED? |
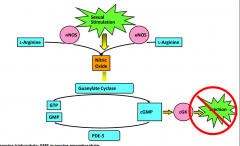
|
|
|
What is the treatment of ED? |
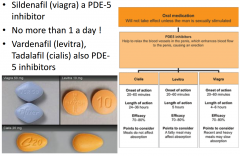
+ penile prosthesis. |

