![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Positioning goal |
Allow optimal surgical access while minimizing potential risk to patient |
|
|
Surgical team work |
Knowledge, teamwork, timing, communication closed loop |
|
|
Factors contributing to physiological changes |
Surgical position. Length of time. Patty and positioning devices. Types of anesthesia. Surgical procedure. |
|
|
Use of sequential compression devices SCD |
Improve venous return. Prevent venous pooling in dependant areas |
|
|
Consequences of general anesthesia |
Myocardial depression and vasodilation leads to decreased cardiac output decreased blood pressure leads to blood pools independent body areas leads to decreased preload decrease stroke volume |
|
|
Cardiac Consequences of neuromuscular blockade |
Decrease venous return due to lack of muscle tone |
|
|
What is blunted by general anesthesia? |
Compensatory mechanisms such as increased heart rate increased systemic vascular resistance to counteract hypotension |
|
|
Cardiac consequences of prone position |
Increase in your CVP. Increase intrathoracic pressure. Decreased left ventricular volume. decrease venous return. Increase or decrease cardiac index |
|
|
Cardiac effects of lateral decubitus position kidney rest elevated |
Decrease blood pressure due to dependent leg position. Decrease venous return due to extreme flexion. Kidney rest, compresses the great vessels. Should lie under the dependent iliac crest |
|
|
Cardiovascular effect of opioids |
Slow heart rate. Decreased cardiac output. Decrease blood pressure. |
|
|
Cardiovascular effects on seated position |
Decreased cardiac index. Decreased CVP. Decrease pulmonary capillary wedge pressure. Increased svr. The higher the head is elevated during hypotension will increase risk of ischemia + hypoperfusion. Cardiac output decrease the more patient is raised |
|
|
What positions cause minimal hemodynamic changes |
Supine and lateral |
|
|
Cardiac effects of sitting, prone, flexed lateral position. |
Cardiac output and blood pressure decrease |
|
|
Regions elevated above the heart in the head up, sitting, and lithotomy positions may be at risk for? |
Hypoperfusion, hypotension, ischemia, |
|
|
Change in height between heart does what to mean arterial pressure |
Increases or decreases by 2 mm of mercury for every 1 in |
|
|
Describe cerebral pressures in relation to map in sitting position |
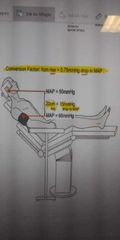
If arm map is 65 and cerebrum map is 50. For every 20 cm arrives there will be a 15 millimeters of mercury drop-in map |
|
|
When are hemodynamic changes minimal? |
When the patient is placed in a 45-degree, head up sitting position |
|
|
What happens to cardiac output when the patient is raised to 90° and why? |
Cardiac output decreases 20% if the patient is raised to 90° because venous blood pools in the extremities |
|
|
What are the effects of venous congestion in intracranial structures? |
Decrease cerebral blood flow |
|
|
How to prevent facial edema in the prone position? |
Position the head level or higher than the heart to minimize venous outflow obstruction |
|
|
What is the effect of combination of lithotomy and head down tilt |
Increase in myocardial function and oxygen demand, causing increase in CVP, pulmonary artery pressure, pcwp, and a decrease in cardiac output in patients with coronary artery disease and heart failure |
|
|
What happens to individuals with peripheral artery disease when lower extremities are elevated above the heart |
At risk for ischemia because of relative state of hypoperfusion. They are at higher risk for compartment syndrome |
|
|
What type of monitoring should be in place in procedures where the head is elevated and cerebral perfusion is a concern |
Invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring with transducer placed at the level of The Circle of Willis |
|
|
Cardiovascular effects of Trendelenburg position |
Increase in myocardial work as per Frank Starling curve |
|
|
Frank Starling mechanism |
Increase in end-diastolic volume, preload will increase cardiac contractility, will increase stroke volume. Increase contractility will make the curve higher |
|
|
Respiratory effects on the Supine position |
Decreased Force residual capacity and decreased total lung capacity |
|
|
Respiratory effects in prone position |
Improve VQ matching and oxygenation |
|
|
Respiratory effects in the lateral decubitus position 4 spontaneously breathing patients |
Ventilation and perfusion are greater in the dependent lung then in the non dependent lung in awake patients |
|
|
Respiratory effects in the lateral decubitus position for anesthetize patients |
Abdominal contents shift cephalad moving the hemidiaphragm of the dependent lung upward, decreasing ventilation in the dependent lung and reducing its compliance. Non dependent lung better |
|
|
Respiratory effects in the sitting position |
More favorable for ventilation. Less effect on lung volumes. Rib cage increases ventilation |
|
|
Respiratory effects in the Trendelenburg position |
Exacerbates effects of various positions. Increase Trendelenburg decreases Force residual capacity |
|
|
Respiratory effects in the lithotomy position |
Viscera shift cephalad limiting diaphragmatic movement, impacting oxygenation |
|
|
Perioperative peripheral nerve injuries are frequently attributed to what |
Incorrect surgical positioning |
|
|
Common component of all peripheral nerve injuries is |
Ischemia. Intraneural blood flow may be compromised by Stretch, compression, transection , kinking |
|
|
Patient factors attributed to perioperative peripheral nerve injury |
Advanced age, gender, extremes and body habitus, pre-existing conditions |
|
|
Perioperative occurrences related to ppni |
Positioning devices, prolong surgical procedure, and aesthetic of technique |
|
|
Intraoperative occurrences related to ppni |
Hypovolemia, hypotension, hypothermia, hypoxia, electrolyte imbalance |
|
|
Primary mechanisms of nerve injuries |
Transaction, compression, traction and stretch, kinking |
|
|
Nerve injury caused by improperly placing legs in candy cane stirrups |
Peroneal nerve injury |
|
|
Contributing factors to nerve injury |
Incorrect surgical positioning, positioning devices, surgical duration, patient characteristics, malfunctioning equipment |
|
|
What is considered prolonged surgical procedure in terms of time |
Greater than 4 hours |
|
|
What nerve injuries can be caused by positioning devices |
Brachial plexus injury if the onboard Falls or if using shoulder straps. Improper placement of axillary roll compressors neural and vascular structures and can cause compartment syndrome |
|
|
How do muscle relaxants contribute to nerve injury |
May contribute to stretch injury by allowing increased mobility of joints |
|
|
What injuries are caused with neuro axial and nerve block techniques |
Hematoma and needle trauma |
|
|
Underweight patient with a BMI of less than 22 is at risk for what type of nerve injury |
Ulnar neuropathy |
|
|
Patient with muscular physique is at risk for? |
Compartment syndrome |
|
|
Effects of obesity |
Large tissue masses Place increase pressure on dependent body part adipose tissue is poorly perfused |
|
|
Most common injured nerve |
Ulnar nerve |
|
|
Presentation and symptoms of ulnar nerve injury |
Claw hand, ring and Little Finger hyper-extended. Loss of abduction and adduction of fingers and flexion. Pain and numbness |
|
|
Actual Contributing factors to ulnar neuropathy |
Surgical positioning. Age greater than 50. Pre-existing disease. TOURNIQUET. Gender. Has a delayed onset of approximately 3 days |
|
|
What position do you put the arms in to prevent nerve injury |
Pad bony prominences. Supinating the arms in Supine position. Abduct arms less than 90 degrees when not tucked |
|
|
What type of nerve injury is a risk for almost all surgical positions |
Brachial plexus nerve injury |
|
|
How to avoid brachial plexus nerve injury |
Avoid head rotation away from abducted arms. Arm adduction less than 90 degrees. Avoid shoulder braces. Head in midline. |
|
|
Nerve Roots affected by brachial plexus injury |
C8, T1. Nerve may be compressed between first rib and clavicle |
|
|
Type of spinal cord injury |
Mid cervical flexion myelopathy with temporary or permanent quadriplegia |
|
|
Factors contributing to spinal cord injury |
Congestion in the veins draining the spinal cord with hypertension may result in decreased spinal cord perfusion. Avoid hyperflexion of the head and neck |
|
|
Effect of Trendelenburg and reverse Trendelenburg positions |
Increased CVP. Increased intraocular pressure. Increased ICP. Edema to the face, tongue, oropharyx and eyes. Decreased perfusion pressure to brain |
|
|
How to avoid common peroneal injury in the lithotomy position |
Both legs should be elevated and lowered simultaneously. To avoid common peroneal injury |
|
|
Effects of common peroneal nerve injury |
Foot drop |
|
|
Effects of straight legs in lithotomy position |
Kinking injury leading to stretch of the sciatic nerve |
|
|
Things to check when patient is in lateral decubitus position |
Ensure dependent ear and eye are free of pressure. Assess perfusion to dependent arm with cap refill check |
|
|
What does the auxiliary role do |
Please. Dependent side slightly caught up to the excella. Relieves pressure exerted on the shoulder, auxiliary vessels and brachial plexus. |
|
|
What position is preferable for intracranial procedures |
Prone position to avoid the risky sitting position |
|
|
Perioperative vision loss is associated with what kind of surgery |
Spine, orthopedic joint and cardiac surgery. Effects can range from decreased visual Acuity to complete vision loss |
|
|
Contributing factors to perioperative vision loss |
Duration in prone position. I compression. Increased intraocular pressure. Hypoperfusion. Anemia |
|
|
Causes of perioperative vision loss |
Ischemic optic neuropathy. Central retinal artery occlusion. Cortical blindness. Glycine toxicity. |
|
|
How does ischemic optic neuropathy occur |
Decreased perfusion to the optic nerve due to decreased blood flow in the internal carotid artery. I o n after prone spinal surgery is very common |
|
|
Ischemic optic nerve injury contributing factors |
Spinal surgery. Prone position. Large blood loss. Wilson frame usage. |
|
|
Most common causes of i o n |
Hypoperfusion and elevated intraocular pressure |
|
|
Ocular perfusion pressure equals |
Map - intraocular pressure |
|
|
Ocular perfusion pressure decreases caused by |
General anesthesia. Anything that lowers map. Hypertension. Hemorrhage. Hypovolemia |
|
|
What position will affect intraocular pressure |
Steep Trendelenburg where the head position is lower than the heart increases intraocular pressure |
|
|
What is the least preferred head support technique in prone position |
Horseshoe adapter in prone position |
|
|
Central retinal artery occlusion when is recovery of vision possible |
If blood flow is restored within 4 hours |
|
|
Risk factors for c r a o |
Hypertension. Cardiovascular disease. Increased BMI. Open-angle glaucoma. Sickle cell anemia |
|
|
What is compartment syndrome |
Tissue swelling as a result have increased pressure and decreased tissue perfusion in muscles with tight faccia borders |
|
|
What can happen with compartment syndrome |
Systemic hypotension. Vascular obstruction of major extremity vessels cuz by intrapelvic retractors. External compression of elevated extremity. Swollen muscle compresses nerves and blood vessels |
|
|
Positions at risk for compartment syndrome |
Trendelenburg and lithotomy. Legs should be periodically lowered to the level of the body if the procedure lasts more than two to three hours |
|
|
What causes venous air embolism |
Negative pressure sucks air from the incision into the right side of the heart, decreases gas exchange and causes a VQ mismatch. |
|
|
What causes venous air embolism |
Any position where there is a negative pressure gradient between the right atrium and veins at the operative site |
|
|
How to detect venous air embolism |
End-tidal CO2 will drop. Presence of end-tidal nitrogen. Mill wheel murmur heard through esophageal stethoscope. |
|
|
Gold standard for detection of venous air embolism |
Transesophageal echocardiogram |
|
|
Who's at risk for paradoxical air embolism. What happens in paradoxical air embolism |
Patience with patent foramen ovale. Right atrial pressure is greater than left atrial pressure and air enters systemic circulation |
|
|
Alternative to TEE |
Transcranial Doppler |

