![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the divisions of the nervous system and some vocabulary?
|
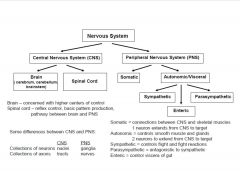
|
|
|
What is the anatomic terminology related to the brain?
|
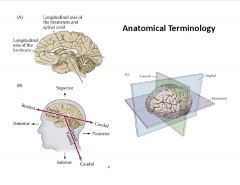
|
|
|
Describe how the nervous system regulates sensory input and output.
|
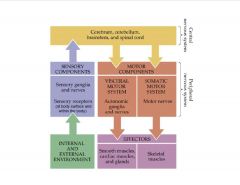
|
|
|
What are the 4 lobes responsible for?
|
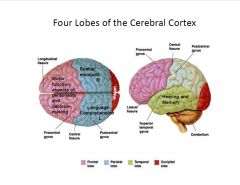
|
|
|
What are the types of movement?
|

|
|
|
Differentiate between upper and lower motor neurons.
|

|
|
|
What is the functional hierarchy of movement control?
|
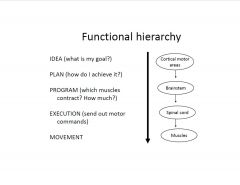
|
|
|
What are the physiological bases of proprioception?
|
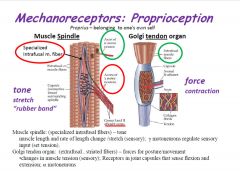
|
|
|
Describe the stretch reflex.
|
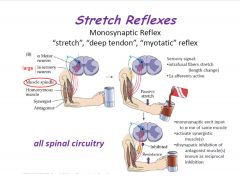
|
|
|
Describe the anatomy of the spinal cord.
|
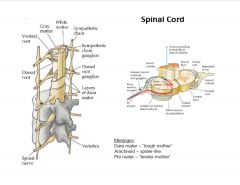
|
|
|
what are the methods of movement correction?
|
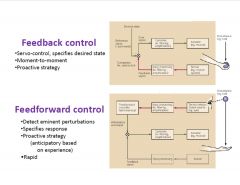
|
|
|
Describe reaction time.
|

|
|
|
What are emotions? Emotional memory?
|

|
|
|
What are the theories on the formation of emotions?
|
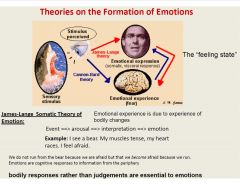
|
|
|
What is another theory of the formation of emotions?
|
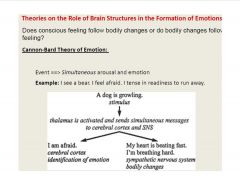
|
|
|
What is the Arnold Cognitive Theory?
|

|
|
|
What are the neural substrates of emotions?
|
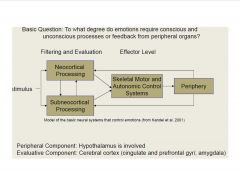
|
|
|
What role does the hypothalamus play in emotional behavior?
|

|
|
|
What does the hypothalamus coordinate in emotional behavior?
|
autonomic and somatic components of emotional states
|
|
|
Contrast behaviors with lesions at different sites of hypothalamus.
|
lateral: animals more placcid
medial: more excitable and aggresive |
|
|
What is the chief parasympathetic nerve?
|
vagus
|
|
|
Where are the parasympathetic preganglionic neurons?
|
sacral segments of the spinal cord
|
|
|
What are the predominant neurotransmitters of the autonomic nervous system?
|
sympathetic: ACh, NE
parasympathetic: ACh |
|
|
Describe the parallel pathways of facial expression and disorders.
|
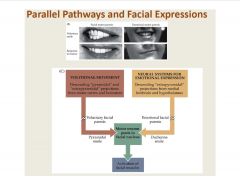
|
|
|
What are the neural systems mediating emotional behavior?
|
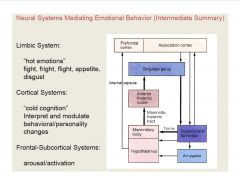
|
|
|
What is the Kluver-Bucy syndrome?
|
-bilateral temporal lobectomy
-lack of affect, visual agnosia, indiscriminate sexual behavior, severe memory loss |
|
|
How do you recapitulate Kluver-Bucy without the memory loss?
|
remove amygdala
|
|
|
What is the amygdala's function?
|
mediates processes that invest sensory experience with emotional significance
|
|
|
In what circuits is the amygdala?
|
inputs: gustatory, visceral, olfactory, auditory, somatosensory, visual, hippocampus, frontal lobes
outputs: ANS, hypothalamus, brainstem motor nuclei |
|
|
What are the functional domains of the amygdala?
|
Lateral amygdala nucleus: sensory interface and key site of plasticity; 2 groups of cells (1 involved in initial learning, the other in memory storage)
Central nucleus: principal output region |
|
|
Define the brain structures implicated in implicit and explicit memories.
|

|
|
|
Summarize the emotional pathway.
|
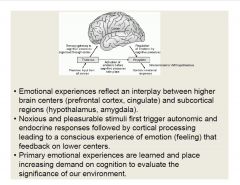
|
|
|
What role does OFC play in the emotional process?
|

|
|
|
What role does the OFC play in decision-making?
|

|
|
|
Describe the neural mechanisms underlying decision-making in the PFC.
|
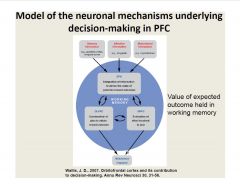
|
|
|
What region does the OFC regulate and which is implicated in OCD pathologies?
|
nucleus accumbens
|
|
|
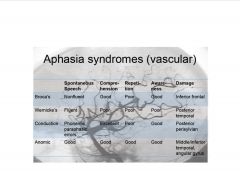
Compare and contrast the various types of aphasia.
|
|
|
|
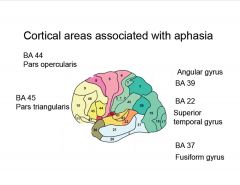
What cortical areas are associated with aphasia?
|
|
|
|
According to Davis et al, what is Broca's area responsible for?
|
-maintaining the serial order of phonemes, graphemes and other linguistic elements.
|
|
|
Which Brodmann's areas are responsible for naming and comprehension, naming but not comprehension, or purely semantic errors in oral naming with no errors in word comprehension?
|
BA 22, superior temporale
BA 37, inferior temporal/fusiform BA 37, fusiform gyrus (critical for accessing lexica representations of output) |
|
|
Which BA is responsible for purely semantic errors in oral naming w/or w/o errors in word comprehension?
|
BA 39, angular gyrus
|
|
|
What is BA 22 responsible for?
|
links lexical representations to a distributed set of semantic reatures that collectively comprise the meaning of the word.
|
|
|
What are the areas in front of and behind the central sulccus responsible for?
|
anterior: selecting responses
posterior: mapping the environment |
|
|
What are the dorsal and ventral streams responsible for?
|
dorsal: "how to"
ventral: "what" |
|
|
What are the functional specializations of each hemisphere?
|
left: fine temporal resolution-->digital, fast, automatic
right: spatial remapping, analog, slow |
|
|
What is the typical proportion of sylvian fissure branches in the left hemisphere?
|
planum temporale=long
planum parietele=short |
|
|
Describe the 2 circuit model of cortical organization of speech.
|
left hemisphere: dorsal stream translates auditory, visual, and kinsthetic codes into speech
bilateral ventral stream associates these codes with the lexicon and distributed semantic system |
|
|
What area of the brain was affected in the KE family (mutation in FoxP2 gene).
|
caudate nucleus was smaller (gene product interferes with normal formation of caudate nucleus and possible other motor systems, impairing procedural learning).
FoxP2 is a highly conserved transcription factor polymorphisms assoc. with behavioral marker of specific language impairment and autism: non-word repetition |
|
|
Summarize the speech pathway.
|

|
|
|
What are the basal ganglia structures?
|
caudate
• putamen • globus pallidus (2 parts: GPi and GPe) • substantia nigra, pars reticulata (the non-pigmented part) • Substantia nigra, pars compacta (pigmented DA neurons) • Subthalamic nucleus • Associated thalamic nuclei for “indirect pathway” |
|
|
Describe the organization/compartmentalization of the basal ganglia.
|
Caudate- receives input from frontal eye fields and multimodal association cortices
• Putamen- receives input from primary and secondary motor and somatosensory cortices as well as visual and auditory association areas. * this somatotopic organization is maintained throughout the other BG nuclei, such that cortical feedback loops from throughout the neocortex run in parallel with each other on their course through the nuclei. |
|
|
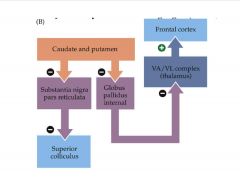
Describe the functional organization of the intrinsic circuitry of the basal ganglia.
|
|
|
|
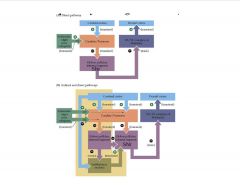
Describe disinhibition of the direct and indirect pathways via the basal ganglia.
|
|

