![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Water is a compound of? |
Hydrogen and oxygen formed when 2 hydrogen atoms combine with 1 oxygen atom |
167 |
|
|
At what degree does water convert to a solid state of matter, called ice? |
Below 32° |
167 |
|
|
At what degree does water convert to a gas, water vapor or steam? |
212° (boiling point) |
167 |
|
|
Water can not be seen in a vapor form. |
. |
|
|
|
How is Water density or weight per unit of volume measured? |
Pounds per cubic feet |
167 |
|
|
1 gallon of water weighs |
8.3 pounds |
|
|
|
What are a couple ways water may extinguish fires |
Cool or absorb heat from the fire, as well as smother (exclude oxygen from) fires |
168 |
|
|
Water may smother combustible liquids fires if the specific gravity is |

Higher then 1 (heavier then water) |
168 |
|
|
What extinguishment may occur when water converts into steam within a closed space |
Smothering |
168 |
|
|
What are the 3 physical states of matter |
Solid (32°) Liquid (32-212) Gas (invisible water vapor) 212° |
168 |
|
|
Specific gravity of Methylene chloride? What happenes when mixed with water |
1.33 Sinks |
168 |
|
|
Gasoline has a specific gravity of? What happenes when mixed with water? |
.72 - .76 Floats |
168 |
|
|
Water has a specific gravity of |
1.0 |
168 |
|
|
Out of the common extinguishing agents, what agent has the greater heat absorbing capacity |
Water |
169 |
|
|
An advantage of water. amount of heat is required to change water to steam, which then allows |
More heat to be absorbed from the fire |
169 |
|
|
An advantage of water, what happens to heat when a great amount of surface area of water is exposed. |
Heat is more rapidly absorbed. |
169 |
|
|
An advantage of water, the amount of surface area can be increased how when using a handline |
Use of a fog nozzle or deflection of a solid stream off an object |
169 |
|
|
An advantage of water, water converted into steam occupies approximately how many times its original volume |
1700 times It also helps dissipate heat in well a vented room. The ratio is greater the higher the temperature. |
169 |
|
|
A disadvantage of water Water has a high surface tension that makes it difficult to |
Soak into dense materials |
169 |
|
|
A disadvantage of water. Wetting agents may be mixed with water to reduce surface tension and increase its penetrating ability. Water may be reactive with certain fuels, combustible Metals, sodium metal, and triethyl aluminum. Due to low levels of opacity and reflectivity, radiant heat easily passing through water, rendering water curtains ineffective. |
. |
169 |
|
|
What are some safety hazards that may occur in below freezing temperatures. |
Ice dams, frozen pumps, slippery surfaces and frozen hoselines |
169 |
|
|
A disadvantage of water, its a good conductor of electricity |
. |
170 |
|
|
What may be A disadvantage of water with it being relatively heavy. |
An accumulation of water within a structure can lead to an increased potential for structural collapse |
170 |
|
|
What is defined as a force per unit area |
Pressure |
170 |
|
|
What is force per unit area exerted by a liquid or gas measured in pounds per square inch |
Pressure |
170 |
|
|
What is a simple measure of weight usually expressed in pounds or kilograms |
Force |
170 |
|
|
Force in a simple measure of weight and is expressed in pounds. This measurement is directly related to the force of gravity. What is an example of force
If several objects of the same size and weight are placed on a flat surface they all exert the same force on that surface |
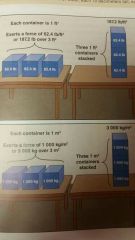
3 Square containers placed next to each other Equal size containing 1 cubic foot of water in weighing 62.4 pounds Each container exerts a force of about 62 pounds per square foot with a total of 187.2 pounds of force over 3 squared foot area If the containers are stacked on top of each other the total force exerted a 187.2 pounds remain the same but the area of contact is reduced to one square foot. The pressure then becomes a 187.2 pounds per square foot |
170 |
|
|
How force is determined |
Force is an influence that causes a change in the speed direction or shape of a substance |
171 |
|
|
Weight of 1 cubic foot of water is approximately how many pounds |
62.4 pounds |
171 |
|
|
What determines the speed when a fluid travels through a hose or pipe? What it is often called? |
The pressure upon that fluid as well as the size of the orifice it is flowing through.
This speed is often called velocity |
172 |
|
|
What is the first principle that determines the action or pressure on fluids |
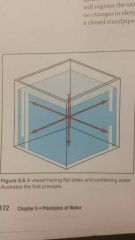
Fluid is perpendicular to any surface. A vessel with flat sides, pressure exerted by the weight of water is perpendicular to walls. If pressure is exerted in any other direction, the water would begin to move downward along the sides and rise at the corners |
|
|
|
What is the 2nd principle that determines the action or pressure on fluids |
Pressure applied to a confined fluid (fluid at rest) is transmitted equally in all directions.
This principle is used in hydrostatic testing. |
172 |
|
|
What is the 3rd principle that determines the action or pressure on fluids |

Pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions
A sphere filled with water and pressure applied by the pump, multiple gages with no change in elevation will all read the same pressure. |
172 |
|
|
Due to increasing water pressure requirements necessary for the height of the building what is installed in standpipe systems that serve high rise buildings |
Pressure regulating devices |
173 |
|
|
What do pressure regulating devices on standpipes do |
Allow hose lines on Lower floors to be more easily controlled while allowing high pressures required to access upper floors |
173 |
|
|
What is the 4th principle that determines the action or pressure on fluids |

The pressure of a liquid in an open vessel is proportional to its depth (weight)
Ex. Three open vessels with water each one foot bigger than the other. bigger the vessel, more water, more weight |
173 |
|
|
What is the 5th principle that determines the action or pressure on fluids |
Pressure of a liquid in an open vessel is proportional to the density of the liquid 1 inch of mercury creates that same pressure as 13.55 inches of water at the bottom |
173 |
|
|
What is the 6th principle that determines the action or pressure on fluids |
The pressure of liquid at the bottom of a vessel is independent of the shape of the vessel |
174 |
|
|
Pressure that surrounds the earth, has depth and density, exerting pressure on everything |
Atmospheric pressure |
174 |
|
|
What is the atmospheric pressure at sea level |
14.7 psi Greatest at low altitudes and least at high |
174 |
|
|
Atmospheric pressure reading is |
Pounds per square inch absolute. (Psi above a perfect vacuum is absolute zero) |
174 |
|
|
Any pressure less than atmospheric is called? Absolute zero pressure is called? |
Vacuum Perfect vacuum |
175 |
|
|
Alternate term for pressure, especially pressure due to elevation. |
Head pressure. Every 1 ft increase in elevation .434 psi is gained |
176 |
|
|
What pressure refers to the height of the water supply above the discharge orifice. |
Head pressure
Ex. Water supply 100 ft above the hydrant discharge opening is referred to as 100 ft of head. That elevated water supply creates the head pressure. |
175 |
|
|
Water flow definition of What pressure is stored potential energy available to force water through pipes, fittings, hose, and adapters. |
Static pressure
At rest or without motion |
175 |
|
|
Pressure in a system before it flows from a hydrant is considered |
Static pressure |
175 |
|
|
Water pressure may be produced by |
Elevated water supply, atmospheric pressure or pump |
175 |
|
|
What pressure found in a water distribution system during normal consumption |
Normal operating pressure |
176 |
|
|
What pressure is the portion of the total available pressure not used to overcome friction loss or gravity while forcing water through pipes fittings hoses or adapters |
Residual pressure
Remainder of the pressure not being used. |
176 |
|
|
Pressure at the test hydrant while water is flowing Pressure remaining in the water supply system while the test water is flowing and is part of the total pressure that is not used to overcome forcing water through fire hose pipes fittings and adapters |
Residual |
176 |
|
|
Water is flowing from discharge opening, the forward velocity pressure is called |
Flow pressure |
176 |
|
|
How to measure the forward velocity of flow pressure |
Pilot tube and gauge |
176 |
|
|
What refers to the center line of the pump or bottom of a static water supply Source above or below ground level |
Elevation
Height of a point above sea level or some other reference point vertical distance between the local surface of the Earth and global sea level. The local surface of the Earth will be either "land or water surface". |
176 |
|
|
What is altitude |
Geographic Position of an object in relation to sea level. The location may be above below or at sea level vertical distance between an object and the local surface of the Earth. |
176 |
|
|
What is elevation pressure |
Gain or loss of pressure in a hoseline due to change in elevation Nozzle above pump, pressure loss. Nozzle below pump, pressure gain. |
176 |
|
|
How does altitude impact the production of fire streams |
Atmospheric pressure drops as height above sea level increase. Levels of little consequence between sea level and 2000 ft |
176 |
|
|
Above sea level atmospheric pressure decreases how much psi |
0.5 psi for every 1000ft
Above 2000 ft pumpers work hard to get a draft. It effects the atmospheric lift |
176 |
|
|
What is loss of pressure created by turbulence of water moving against the interior walls of the hose or pipe |
Friction loss Fire service definition - total pressure loss forcing water through pipe fittings fire hose and adapters |
177 |
|
|
Causes of friction loss in a fire hose |
Movement of water molecules against each other Lining of fire hose Kinks Change in hose size Couplings Improper gasket Adapters Adapters |
177 |
|
|
Friction loss in older hose may be what percent greater the new hose |
50% |
177 |
|
|
What is referred to as the coefficient of friction of a pipe |
Rough inner surface of the pipe |
177 |
|
|
In a pipe the rougher the inner surface the greater the what |
Greater the friction loss will be |
177 |
|
|
Friction loss can be measured by inserting what in a hose or pipe |
In line gauges |
177 |
|
|
The difference in residual pressure between two gauges placed a distance apart in the same diameter hose or pipe when water is Flowing is the friction loss for that distance |
Example - the difference in pressure between a nozzle and Pumper |
178 |
|
|
Pressures Residual - the pressure that is left in the system. Hydrant 1's pressure is open (not flowing). Flow pressure - from a discharge opening. hydrant 2s pressure open and flowing |
. |
|
|
|
First basic principle for friction loss |
all considerations are the same. Friction loss varies directly with the length of hose or pipe. example. gpm is the same but 2 different lines are pumped with different lengths the figure out the different psi.. |
178 |
|
|
The second basic principle for friction loss |
When hoses are the same size, friction loss varies approximately with the "square" of the increase in the velocity of the flow. friction loss develops faster then the change in velocity.
Example flowing from 200 GPM doubled to 400 gpm, friction loss increased 4 times from 3.2 (squared) psi to 12.8 |
178 |
|
|
What is the third principle for friction loss |
When the flow remains consistent the friction loss in a hose will decrease when the diameter of the hose is increased
Bigger the hose less the friction loss . 76% reduction in friction loss, using 4 inch instead of 3 inch. |
|
|
|
The fourth principal to friction loss |
For a given velocity friction loss is approximately the same regardless of the pressure on the water |
179 |
|
|
Water being virtually incompressible a pressure of 30000 PSI is required to reduce its volume by what percent |
1% |
179 |
|
|
With water being incompressible the same volume of water supplied into a fire hose under pressure at one end will be discharged at the other end |
. |
179 |
|
|
What determines the velocity for a given volume of water |
The diameter of the hose The smaller the hose the greater the velocity needed to deliver the same volume |
179 |
|
|
Where is flow pressure the greatest and lowest |
Greatest near the source of Supply lowest at the furthest point |
180 |
|
|
If the velocity is increased beyond the practical limits a stream can travel, friction becomes so great the entire system is agitated by resistance. The agitation causes a degree of turbulence known as? |
Critical velocity |
181 |
|
|
Hose lengths of various diameters have a specific hose length at which the reduction in flow makes their use undesirable. Beyond this point what is necessary to do to increase flow and reduce friction |
Use parallel lines or siamese lines |
181 |
|
|
What characteristics in a hose layout will affect friction loss |
Hose lengths Hose diameter Kinks |
181 |
|
|
To reduce the friction loss due to hose lengths or diameter you need to? |
Reduce the length of the lay and increase the diameter of the hose |
181 |
|
|
How to reduce friction loss due to hose diameter. |
Use larger diameter, hose may be reduced from LDH to an appropriate size capable of handling. |
181 |
|
|
How may hose kinks be minimized |
Proper hose handling techniques |
181 |
|
|
In a large fire operation where large volume of water is needed the Fire department should make a request to |
Water utility department to increase the pressure |
182 |
|
|
What are the inaccurate components of a water systems |
Source of water supply Means of moving water Water treatment or processing facilities Water distribution system |
182 |
|
|
Example of primary surface water supply |
Rivers and lakes |
|
|
|
Source of Ground water supply |
Wells or water producing system |
|
|
|
What are the means of moving water |
Direct pumping system Gravity system Combination system |
183 |
|
|
Moving water system uses 1 or more pumps that takes water from a primary source and discharges it through a filtration and treatment system |
Direct pumping system |
183 |
|
|
Uses a primary water source located at a higher elevation then the distribution system. |
Gravity system Usually only sufficient when located several 100 ft above distribution system |
183 |
|
|
Wster System that uses direct pumping and distribution. |
Combination system |
|
|
|
Most communities use what system of moving water |
Combination system |
183 |
|
|
What tanks are served as emergency storage and provide adequate pressure through the use of gravity |
Elevated storage tanks |
183 |
|
|
What are the main concerns the fire department face with water treatment facilities and why |
Maintenance failure, natural disaster, loss of power supply, or a fire could disable the pumping stations or severely hamper the purification process Those would reduce the volume of water pressure |
184 |
|
|
What part of the overall water supply system receives the water from the pumping station and delivers it throughout the area served |
Distribution system |
184 |
|
|
When a hydrant receives water from 2 or more directions it is said to have a? |
Circulating feed or Loop line |
184 |
|
|
A distribution system that provides circulating feed from several mains constitutes as? |
Grid system
(Lateral feeders for improved distribution) |
|
|
|
In a grid system what is a Large main that convey large quantities of water to various points of the system for local distribution to the smaller mains |
Primary feeders |
184 |
|
|
In a grid system what uses intermediate sized pipes that reinforce the grid within the various loops of the primary feeder system and aid the concentration of the required fire flow at any point |
Secondary feeder |
184 |
|
|
In a grid system what is the grid arrangement of smaller mains serving individual fire hydrants and blocks of consumers |
Distributors |
185 |
|
|
Where are larger mains found |
Industrial and business districts, principal streets connected to smaller mains serving specific neighborhoods or development |
185 |
|
|
In a water distribution system what provides the means for controlling the flow of water through distribution piping |
Valve |
185 |
|
|
Where should valves be placed in a distribution system |
Frequent intervals so small districts are cut off if it were necessary to stop flow at specific points |
186 |
|
|
What is one of the most important factors of a water supply system |
The water departments ability to promptly operate the valves during an emergency |
186 |
|
|
What kind of valve shows whether the gate valve seat is open, closed or partially closed. |
Indicating valve |
186 |
|
|
What are 2 common indicating valves |
Post indicating and os&y Found on sprinklers and some water distribution system applications |
186 |
|
|
On the os&y system if the thread portion is outside the yoke then the system is |
Open |
186 |
|
|
One of the most common type of valve used on public water distribution systems normally found in manholes or in valve boxes |
Non indicating |
186 |
|
|
A below grade valve can be operated aboveground by |
Using a socket wrench on a reach rod |
187 |
|
|
When opening non indicating valves sometimes they are clockwise or counter |
. |
|
|
|
Control valves in public water distribution systems are normally gate valves. If a valve resists turning it usually means? |
Dabris or obstruction |
187 |
|
|
The average daily consumption in a water system capacity means |
Average amount of water per day used in a year |
|
|
|
Maximum daily consumption in a water system capacity means |
Maximum amount of water used in a 24 hour interval within a 3 year period |
188 |
|
|
The peak hour consumption in a water system capacity means |
Maximum amount of water used in a 1 hours interval over the course of the day |
188 |
|
|
Private water supply systems exists for one of the following purposes |
To provide water for sanitary and fire protection purposes, to provide water for Fire Protection in manufacturing process. Sometimes for residential |
|

