![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Draw a sarcomere. What fibres make up which part of it?
|
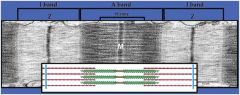
Actin = thin filaments
Myosin = thick filaments (M band) |
|
|
Absolute vs relative refractory period
|
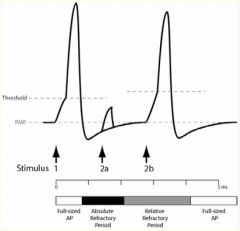
• Absolute refractory period
• Time period when no action potential can be generated. • Due to the fact that.. □ Some Na+ channels are still inactivated □ Some K+ channels are still open, and thus the membrane potential is still hyperpolarized (further away from threshold). • Relative refractory period • Generates an AP. • Requires greater stimulus intensity than usual. |
|
|
States of voltage-gated channels through the phases of an action potential.
|
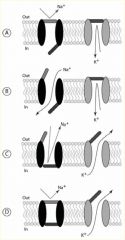
A. Resting state
B. Rising phase C. Falling phase D. Afterhyperpolarization |
|
|
What is the neurotransmitter for excitation at the spinal cord between a sensory Ia afferent neuron, and an alpha motor neuron? What is the neurotransmitter receptor called?
|
Neurotransmitter = glutamate
Receptor = AMPA receptor, which is also a non-specific cation channel. |
|
|
What is the distance that a neuronal membrane depolarization can travel determined by?
|
The distance a depolarization can propagate along a neuron is governed by two factors:
• Axial resistance (Ra) □ Increasing the diameter of the axon = decrease in Ra • Membrane resistance (Rm). □ Rm is increased by myelination Length constant = (Rm/Ra) ^ 1/2 -An increase in Rm, or decrease in Ra, results in longer propagation distance |
|
|
What factors affect the rate, or speed of the action potential propagation?
|
1. Diameter of the neuron.
- the larger the faster. 2. Membrane capacitance. - lower capacitance = less time to charge the membrane, and greater rate of AP propagation. - capacitance is inversely proportional to the distance between the parallel plates. Myelin increases the thickness of the membrane. - capacitance is also proportional to the surface area of the membrane. |
|
|
Sequence of events between myosin and actin filament during a contraction-relaxation cycle
|
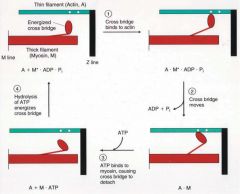
|

