![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
102 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is one purpose of wing flaps?
|
A. To enable the pilot to make steeper approaches to a landing wihtout increasing the airspeed.
B. To relieve the pilot of maintaing continuous pressure on the controls. C. To decrease wing area to vary the lift. |
A. To enable the pilot to make steeper approaches to a landing without increasing the airspeed.
|
|
|
One of the main functions of flaps during approach and landing is to ..
|
A. Decrease the anfle of descent without increasing the airspeed.
B. Permit a touchdown at a higher indicated airspeed. C. Increase the angle of descent without increasing the airspeed. |
C. Increase the angle of descent without increasing the airspeed.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the rudder on an airplane?
|
A. To control yaw.
B. To control overbanking tendency. C. To control roll. |
A. To control yaw.
|
|
|
The four forces acting on an airplane in flight are...
|
A. Lift, weight, thrust and drag.
B. Lift, weight, gravity and thrust. C. Lift, gravity, power and friction. |
A. Lift, weight, thrust and drag.
|
|
|
When are the four forces that act on an airplane in equilebrium?
|
A. During unaccelerated flight.
B. When the aircraft is accellerating. C. When the aircraft is at rest on the ground. |
A. During unaccelerated flight.
|
|
|
What is the relationship of lift, drag, thrust and weight during straight and level flight?
|
A. Lift equals weight and thrust equals drag.
B. Lift, drag and weight equal thrust. C. Lift and weight equal thrust and ddrag. |
A. Lift equals weight and thrust equals drag.
|
|
|
Which statement relates to Bernoillis principle?
|
A. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
B. An additional upward force is generated as the lower surface of the wing deflects air downward. C. Air traveling faster over the curved upper surface of an airfoil causes lower pressure on the top surface. |
A. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
|
|
|
The term "Angle of Attack" is defined as the angle...
|
A. Between the wing chord line and the relative wind.
B. Between the airplane's climb angel and the horizon. C. Formed by the longitudinal axis of the airplane and the chord line of the wing. |
A. Between the wing chord line and the relative wind.
|
|
|
Angle of attack is defined as the angle between the chord line of an airfoil and the
|
A. Direction of relative wind.
B. Pitch angle of an airfoil. C. Rotor plane of rotation. |
A. Direction of relative wind.
|
|
|
The acute angle A is the angle of
|
A. Incidence
B. Attack C. Dihedral |
B. Attack
|
|
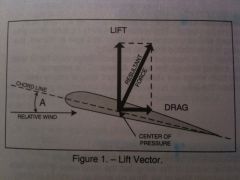
The acute angle A is the angle of...
|
A. Incidence
B. Attack C. Dihedral |
B. Attack
|
|
|
The angle between the chord line of an airfoil and the relative wind is known as the angle of..
|
A. Lift
B. Attack C. Incidence |
A. Lift
|
|
|
The angle of attack at which an airplane wing stalls will..
|
A. Increase if the CG is moved forward.
B. Change with an increase in gross weight. C. Remain the same regardless of gross weight. |
C. Remain the same regardless of gross weight.
|
|
|
As altitude increases, the indicated airspeed at which a given airplane stalls in a particuar configuration will
|
A. Decrease as the true airspeed decreases.
B. Decrease as the true airspeed increases. C. Remain the same regardless of altitude. |
C. Remain the same regardless of altitude.
|
|
|
In what condition must an aircraft be placed in order to spin.
|
A. Partially stalled with one wing low.
B. In a steep diving spiral. C. Stalled. |
C. Stalled.
|
|
|
During a spin to the left, which wings are stalled?
|
A. Both wings are stalled.
B. Beither wing is stalled C. Only the left wing is stalled. |
A. Both wings are stalled.
|
|
|
How will frost on the wings of an airplane affect takeoff performance.
|
A. Frost will disrupt the smooth flow of air over the wing, adversely affecting its lifting capability.
B. Frost will change the camber of the wing, increasing its lifting capability. C. Frost will cause the airplane to become airborne with a higher angle of attack decreasing the stall speed. |
A. Frost will disrupt the smooth flow of air over the wing, adversely affecting its lifting capability.
|
|
|
How does frost affect the lifting surfance of an airplane on takeoff?
|
A. Frost may prevent the airplane from becoming airborne at normal takeoff speed.
B. Frost will change the camber of the wing, increasing lift during takeoff. C. Frost may cause the airplane to become airborne with a lower angle of attack at a lower indicated airspeed. |
A. Frost may prevent the airplane from becoming airborne at normal takeoff speed.
|
|
|
What is ground effect?
|
A. The result of the interference of the surace of the Earth with the airflow patterns about an airplane.
B. The result of an alteration in airflow patterns increasing insuced drag about the wings of an airplane. C. The result of the disruption of the airflow patterns about the wings of an airplane to the point where the wings will no longer support the airplane in flight. |
A. The result of the interference of the surace of the Earth with the airflow patterns about an airplane.
|
|
|
Floating is caused by the phenomenon of ground effect will be most realized during an approach to land and when at ...
|
A. Less than the length of the wingspan above the surface.
B. Twice the length of the wingspan above the surface. C. A Higher than normal angle of attack. |
A. Less than the length of the wingspan above the surface.
|
|
|
What must a pilot be aware of as a result of ground effect?
|
A. Wingtip vortices increase the creating wake turbulence problems for arriving and departing aircraft.
B. Induced drag decreases; therefore any excess speed at the point of flare may cause considerable floating. C. A full stall landing will require less up elecator deflection than would a full stall when done free of ground effect. |
B. Induced drag decreases; therefore any excess speed at the point of flare may cause considerable floating.
|
|
|
Ground effect is most likely to result in which problem?
|
A. Setting to the surface abruptly during landing.
B. Becomine airborne before reaching the recommended takeoff speed. C. Inability to get airborne even though airspeed is sufficient for normal takeoff needs. |
B. Becomine airborne before reaching the recommended takeoff speed.
|
|
|
What force makes an airplane turn?
|
A. The horizontal component of lift.
B. The vertical compnent of lift. C. Centrifugal force. |
A. The horizontal component of lift.
|
|
|
An Airplane said to be inherently stable will...
|
A. Be difficult to stall.
B. Require less effort to control. C. Not spin. |
B. Require less effort to control.
|
|
|
What determines the longitudinal stability of an airplane?
|
A. Location of the CG with respect to the center of lift.
B. The effectiveness of the horiontal stabilizer, rudder, and rudder trim tab. C. The relationship of thrust and lift to weight and drag. C. |
A. Location of the CG with respect to the center of lift.
|
|
|
Changes in the center of pressure of a wing affect the aircrafts
|
A. Lift/Drag ratio
B. Lifting capacity C. Aerodynamic balance and controllability. |
C. Aerodynamic balance and controllability.
|
|
|
An airplane has been loaded in such a manner that the CG is located aft of the aft CG limit. One undesirable flight characteristic a pilot might experience with this airplane would be...
|
A. Longer takeoff run.
B. Difficulty in recovering from a stalled condition. C. Stalling at a higher-than-normal airspeed. |
B. Difficulty in recovering from a stalled condition.
|
|
|
What causes an airplane (except a T-Tail) to pitch nosedown when the power is reduced and controls are not adjusted?
|
A. The CG shifts forward when the thrust and drag are reduced.
B. The downwash on the elevators from the propeller slipstream is reduced and elevator effectiveness is reduced. C. When thrust is recuded to less than weight, lift is also reduced and the wings can no longer support the weight. |
B. The downwash on the elevators from the propeller slipstream is reduced and elevator effectiveness is reduced.
|
|
|
Loading an airplane to the most aft CG will cause the airplane to be...
|
A. Less stable at all speeds.
B. Less stable at slow speeds, but more stable at high speeds. C. Less stable at high speeds, but more stable at low speeds. |
A. Less stable at all speeds.
|
|
|
In what flight condition is torque effect the greatest in a single engine airplane?
|
A. Low airspeed, high power, high angle of attack.
B. Low airspeed, low power, low angle of attack. C. High airspeed, high power, and high angle of attack. |
A. Low airspeed, high power, high angle of attack.
|
|
|
The left turning tendency of an airplane caused by P-Factor is the result of the...
|
A. Clockwise rotation of the engine and the propeller turning the airplane counterclockwise.
B. Propeller blade descending on the right, producing more thrust than the ascending blade on the left. C. Gyroscopic forces applied to the rotating propeller bladers acting 90 degress in advance of the point where force was applied. |
B. Propeller blade descending on the right, producing more thrust than the ascending blade on the left.
|
|
|
When does P-Factor cause the airplane to yaw to the left?
|
1. When at low angles of attack.
2. When at high angles of attack. 3. When at high airspeeds. |
2. When at high angles of attack.
|
|
|
The amount of excess load that can be imposed on the wing of an airplane depends upon the ....
|
A. Position of the CG
B. Speed of the airplane. C. Abruptmness at which the load is applied. |
B. Speed of the airplane.
|
|
|
Which basic flight maneuver increases the load factor on an airplane as compared the straight and lebel flight?
|
A. Climbs
B. Turns C. Stalls |
B. Turns
|
|
|
During an approach to a stall, an increased load factor will cause the aircraft to...
|
A. Stall at a higher airspeed
B. Have a tendency to spin. C. Be more difficult to control |
A. Stall at a higher airspeed
|
|
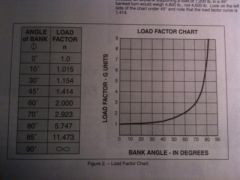
If an airplane weighs 3300 pounds, what approximate weight would the airplane structure be required to support during a 30 degree banked turn while maintaining altitude?
|
A. 1200 pounds
B. 3100 Pounds C. 3960 Pounds. |
C. 3960 Pounds.
|
|
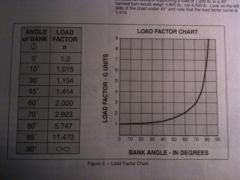
If an airplane weighs 4500 pounds, what approximate weight would the airplane structure be required to support during a 45 degree banked turn while maintaining altitude?
|
A. 4500 Pounds
B. 6750 Pounds C. 7200 Pounds |
B. 6750 Pounds
|
|
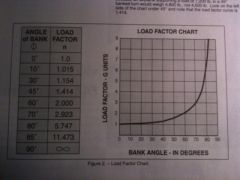
If an airplane weighs 2300 pounds, what approximate weight would the airplane structure be required to support during a 60 degree banked turn while maintaing altitude?
|
A. 2300 Pounds
B. 3400 Pounds C. 4600 Pounds |
C. 4600 Pounds
|
|
|
In the Northern Hemisphere, a magnetic compass will normally indicate a turn toward the north if
|
A. An aircraft is decelerated while on an east or west heading.
B. A left turn is entered from a west heading. C. An aircraft is accelerated while on an east or west heading. |
C. An aircraft is accelerated while on an east or west heading.
|
|
|
During flight, when are the indications of a magentic compass accurate?
|
A. Only in straight and level unaccelerated flight.
B. As long as the airspeed is constant. c. During turns if the bank does not exceed 18 degrees. |
A. Only in straight and level unaccelerated flight.
|
|
|
Deviation in a magnetic compass is caused by the ...
|
A. Presence of flaws in the permanent magnets of the compass.
B. Difference in the location between true north and magnetic north. C. Magnetic fields within the aircraft distorting the lines of magnetic force. |
C. Magnetic fields within the aircraft distorting the lines of magnetic force.
|
|
|
In the Northern Hemisphere, if an aircraft is accelerated or decelerated, the magnetic compass will normally indicate...
|
A. A turn momentarily.
B. Correctly when on a north or south heading. C. A turn toward the south. |
B. Correctly when on a north or south heading.
|
|
|
In the Northern Hemisphere, a magnetic compass will normally indicate initially a turn toward the west if...
|
A. A left turn is entered from a north heading.
B. A rght turn is entered from a north heading. C. An aircraft is accelerated while on a north heading. |
B. A rght turn is entered from a north heading.
|
|
|
In the Northern Hemisphere, the magnetic compass will normally indicate a turn toward the south when...
|
A. A left turn is entered from an east heading.
B. A right turn is entered from a west heading. C. The aircraft is decelerated while on a west heading. |
C. The aircraft is decelerated while on a west heading.
|
|
|
In the Northern Hemisphere, a magnetic compass will normally indicate initially a turn toward the east if ...
|
A. An aircraft is decelerated while on a south heading.
B. An aircraft is accelerated while on a north heading. C. A left turn is entered from a north heading. |
C. A left turn is entered from a north heading.
|
|
|
What should be the indication on the magnetic compass as you roll into a standard rate turn to the right from a south heading in the Northern Hemisphere?
|
A. The compass will inistially indicate a turn to the left.
B. The compass will indicate a turn to the right, but at a faster rate than is actually occurring. C. The compass will remain on south for a short time, then gradually catch up to the magnetic heading of the airplane. |
B. The compass will indicate a turn to the right, but at a faster rate than is actually occurring.
|
|
|
The pitot system provides impact pressure for which instrument?
|
A. Altimeter
B. Vertical speed indicator. C. Airspeed indicator. |
C. Airspeed indicator.
|
|
|
Which instrument will become inoperative if the pitot tube becomes clogged?
|
A. Altimeter
B. Vertical speed. C. Airspeed. |
C. Airspeed.
|
|
|
If the pitot tube and outside static vents become clogged, what instruments would be affected?
|
A. The altimeter, airspeed indicator, and turn and slip indicator.
B. The altimiter, airspeed indicator and vertical speed indicator. C. The altimiter, attitude indicator, and turn and slip indicator. |
B. The altimiter, airspeed indicator and vertical speed indicator.
|
|
|
Which instruments will become inoperative if the static vents become clogged?
|
A. Airspeed only.
B. Altimeter Only C. Airspeed, Altimiter and Vertical Speed |
C. Airspeed, Altimiter and Vertical Speed
|
|
|
What does the red line on an airspeed indicator represent?
|
A. Maneuvering Speed.
B. Turbulent or rough air speed. C. Never exceed speed. |
C. Never exceed speed.
|
|
|
What is an important airspeed limitation that is not color cided on airspeed indicators?
|
A. Never-Exceed speed.
B. Maximum structural cruising speed. C. Meaneuvering Speed. |
C. Meaneuvering Speed.
|
|

What is the caution range of this airplane?
|
A. 0-60
B. 100-165 C.165 - 208 |
C.165 - 208 |
|
|
What is the maximum speed at which the airplane can be operated in smooth air?
|
A. 100MPH
B. 165 MPH C. 208 MPH |
C. 208 MPH
|
|

What is the maximum speed at which the airplane can be operated in smooth air?
|
A. 100MPH
B. 165 MPH C. 208 MPH |
C. 208 MPH
|
|

What is the full flap operating range for the airplane?
|
A. 60-100 MPH
B. 60 - 208 MPH C. 65 - 165 MPH |
A. 60-100 MPH
|
|

Which color identifies the never exceed speed?
|
A. Lower limit of the yellow arc.
B. Upper limit of the white arc. C. The radial line. |
C. The radial line.
|
|

Which color identifies the power off stalling speed in a specified configuration?
|
A. Upper limit of the green arc.
B. Upper limit of the white arc. C. Lower limit of the green arc. |
C. Lower limit of the green arc.
|
|

What is the maximum flaps extended range?
|
A. 65 MPH
B.100 MPH C. 165 MPH |
B.100 MPH
|
|

Which color identifies the power off stalling speed in a specified configuration?
|
A. The upper limit of the green arc?
B. The upper limit of the white arc? C. Lower limit of the green arc? |
C. Lower limit of the green arc?
|
|

What is the maximum flaps extended speed?
|
A. 65 MPH
B. 100 MPH C. 165 MPH |
B. 100 MPH
|
|

Which color identifies the normal flap operating range?
|
A. The lower limit of the white arc to the upper limit of the green arc.
B. The green arc C. The white arc. |
C. The white arc. |
|

Which color identifies the power off stalling speed with wing flaps and landing gear in the landing configuration?
|
A. The limit of the green arc.
B. Upper limit of the white arc. C. Lower limit of the white arc. |
C. Lower limit of the white arc.
|
|

What is the maximum structural cruising speed?
|
A. 100 MPH
B. 165 MPH C. 208 MPH |
B. 165 MPH
|
|
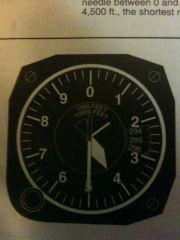
Altimeter 2 indicates
|
A. 1500 feet.
B. 4500 feet. C. 14500 feet. |
C. 14500 feet.
|
|

This altimeter indicates
|
A. 500 feet.
B. 1500 feet. C. 10500 feet. |
C. 10500 feet.
|
|

Altimeter indicates
|
A. 9500 feet
B. 10950 feet C. 15940 feet |
B. 10950 feet |
|
|
What is absolute altitude?
|
A. The altitude read directly from the altimeter.
B. The vertical distance of the aircraft above the surface. C. The height above the standard datum plane. |
B. The vertical distance of the aircraft above the surface.
|
|
|
What is true altitude?
|
A. The vertical distance of the aircraft above sea level.
B. Te vertical distance of the aircraft above the surface. C. The height above the standard datum plane. |
A. The vertical distance of the aircraft above sea level.
|
|
|
What is density altitude?
|
A. The height above the standard datum plane.
B. The pressure altitude corrected for nonstandard temperature. C. The altitude read directly from the altimeter |
B. The pressure altitude corrected for nonstandard temperature.
|
|
|
Under what condition is pressure altitude and density altitude the same value?
|
A. At sea level, when the temperature is 0 degrees.
B. When the altimeter has no installation error. C. At standard temperature. |
C. At standard temperature.
|
|
|
Under what condition is indicated altitude the same as true altitude?
|
A. If the altimeter has no mechanical error.
B. When at sea level under standard conditions. C. When at 18,000 feet MSL with the altimeter set at 29.92 |
B. When at sea level under standard conditions.
|
|
|
What is pressure altitude?
|
A. The indicated altitude corrected for position and installation error.
B. The altitude indicated when the barometric pressure scale is set to 29.92 C. The indicated altitude corrected for nonstandard temperature and pressure |
B. The altitude indicated when the barometric pressure scale is set to 29.92 |
|
|
Altimeter setting is the value to which the barometric pressure scale of the altimeter is set so the altimeter indicates...
|
A. Calibrated altitude at field level.
B. Absolute altitude at field elevation. C. True altitude at field elevation. |
C. True altitude at field elevation.
|
|
|
If it is necessary to set the altimeter from 29.15 to 29.85, what changes occur?
|
A. 70 foot increase in indicated altitude.
B. 70 foot increase in density altitude. C. 700 foot increase in indicated altitude. |
C. 700 foot increase in indicated altitude.
|
|
|
If a pilot changes the altimeter setting from 30.11 to 29.96, what is the appropriate change in indication?
|
A. Altimeter will indicate .15" hg higher
B. Altimeter will indicate 150 feet higher. C. Altimeter will indicate 150 feet lower. |
C. Altimeter will indicate 150 feet lower.
|
|
|
If a flight is made from an area of lower pressure into an area of high pressure without the altimeter setting being adjusted, the altimeter will indicate
|
A. The actual altitude above sea level.
B. Higher than the actual altitude above sea level. C. Lower than the actual altitude above sea level. |
C. Lower than the actual altitude above sea level.
|
|
|
If a flight is made from an area of high pressure into an area of lower pressure without the altimeter being adjusted, the altimeter will indicate
|
A. Lower then the actual altitude above sea level.
B. Higher than the actual altitude above sea level. C. Actual altitude above sea level. |
B. Higher than the actual altitude above sea level.
|
|
|
Which condition would cause the altimeter to indicate a lower altitude than true altitude?
|
A. Air temerature lower than standard.
B. Atmospheric pressure lower than standard. C. Air temperature warmer than standard. |
C. Air temperature warmer than standard. |
|
|
Under what condition will true altitude be lower than indicated altitude?
|
A. In colder than standard air temperature.
B. In warmer than standard air temperature. C. When density altitude is higher than indicated altitude. |
A. In colder than standard air temperature.
|
|
|
How do variations in temperature affect the altimeter?
|
A. Pressure levels are raised on warm days and the indicate altitude is lower than true altitude.
B. Higher temperatures expand the pressure levels and the indicated altitude is higher than true altitude. C. Lower temperatures lower the pressure levels and the indicated altitude is lower than true altitude. |
A. Pressure levels are raised on warm days and the indicate altitude is lower than true altitude.
|
|
|
The proper adjustment to make on the attitude indicator during level flight is to align the
|
A. Horizon bar to the level flight indication.
B. Horizon bar to the miniature airplane C. Miniature airplane to the horizon bar. |
C. Miniature airplane to the horizon bar. |
|
|
How should a pilot determine the direction of bank from an attitude indicator?
|
A. By the direction of deflection of the banking scale.
B. By the direction of the horizon bar. C. By the relationship of the mini airplane to the deflected horizon bar. |
C. By the relationship of the mini airplane to the deflected horizon bar.
|
|
|
A turn coordinator provides an indication of the
|
A. Movement of the aircraft about to yaw and roll axes.
B. Angle of bank up to but not exceeding 30 degrees. C. Attitude of the aircraft with reference to the longitudinal axis. |
A. Movement of the aircraft about to yaw and roll axes.
|
|
|
To receive accurate indications during flight from a heading indicator, the instrument must be
|
A. Set prior to flight on a known heading.
B. Calibrated on a compass rose at regular intervals. C. Periodically realigned with the magnetic compass as the gyroo precesses. |
C. Periodically realigned with the magnetic compass as the gyroo precesses.
|
|
|
An abnormally high engine temperature indication may be caused by
|
A. The oil level being too low.
B. Operating with a too high viscosity oil. C. Operating with an excessively rich mixture. |
A. The oil level being too low.
|
|
|
Excessively high engine temperatures will
|
A. cause damage to heat conducting hoses and warping of the cylinder cooling fins.
B. cause loss of power, excessive oil consumption, and possible permanent internal engine damage. C. not appreciably affect an aircraft engine. |
B. cause loss of power, excessive oil consumption, and possible permanent internal engine damage.
|
|
|
Excessively high engine temperatures either in the air or on the ground, will
|
A. increase fuel consumption and may increase power due to increased heat.
B. Result in damage to heat conducting hoses and warping of cylinder cooling fans. C. cause loss of power, excessive oil consumption, and possible permanent internal engine damage. |
C. cause loss of power, excessive oil consumption, and possible permanent internal engine damage.
|
|
|
For internal cooling, air cooled engines are especially dependent on
|
A. A properly functioning thermostat.
B. Air flowing over the exhaust manifold. C. The circulation of lubricating oil. |
C. The circulation of lubricating oil.
|
|
|
If the engine oil temperature and cylinder head temperature gauges have exceeded their normal operating range, the pilot may have been operating with
|
A. The mixture set too rich.
B. Higher than normal oil pressure. C. Too much power and wit the mixture set too lean. |
C. Too much power and wit the mixture set too lean.
|
|
|
What action can a pilot take to aid in cooling an engine that is overheating during a climb?
|
A. Reduce rate of climb and increase airspeed.
B. Reduce climb speed and increase RPM. C. Increase climb speed and increase RPM |
A. Reduce rate of climb and increase airspeed.
|
|
|
What is one procedure to aid in cooling an engine that is overheating?
|
A. Enrich the fuel mixture.
B. Increase the RPM C. Reduce the airspeed. |
A. Enrich the fuel mixture.
|
|
|
How is the engine controlled on an engine equipped with a constant speed propeller?
|
A, The throttle controls power output as registered on the manifold pressure gauge and the propeller control regulates the RPM.
B. The throttle controls power output as registered on the manifold pressure gauge and the propeller control regulate a constant blade angle. C. The throttle control engine RPM as registered on the tachometer and mixture control regulates the power output. |
A, The throttle controls power output as registered on the manifold pressure gauge and the propeller control regulates the RPM.
|
|
|
A precaution for the operation of an engine equipped with a constant speed propeller is to
|
A. avoid high RPM settings with high manifold pressure.
B. Avoid high manifold pressure settings with low RPM. C. Always use a rich mixture with high RPM. |
B. Avoid high manifold pressure settings with low RPM.
|
|
|
What is the advantage of a constant speed propeller?
|
A. Permits the pilot to select and maintain a desired cruising speed.
B. Permits the pilot to select the blade angle for the most efficient performance. C. Provides a smoother operation with stable RPM and eliminates vibrations. |
B. Permits the pilot to select the blade angle for the most efficient performance.
|
|
|
One purpose of the dual ignition system on an aircraft engine is to provide for
|
A. Improved engine performance.
B. Uniform heat distribution. C. Balance cylinder head pressure. |
A. Improved engine performance.
|
|
|
If the ignition switch ground wire becomes disconnected from the circuit, the magneto
|
A. Will not operate because the battery is disconnected from the circuit.
B. May continue to fire. C. Will not operate. |
B. May continue to fire.
|
|
|
With regard to carburetor ice, float type carburetor systems in comparison to fuel engine systems are generally considered to be
|
A. More susceptible to icing.
B. Equally susceptible to icing. C. Susceptible to icing only when visible moisture is present. |
A. More susceptible to icing.
|
|
|
Which condition is most favorable to the development of carburetor icing?
|
A. Any temperature below freezing and a relative humidity of less than 50%.
B. Temperature between 32F and 50F and low humidity. C. Temperature between 20F and 70F and high humidity. |
C. Temperature between 20F and 70F and high humidity.
|
|
|
The possibility of carburetor icing exists even when the ambient air temperature is as
|
A. high as 70F and the relative humidity is high.
B. high as 95F and there is visible moisture. C. Low as 0F and the relative humidity is high. |
A. high as 70F and the relative humidity is high.
|
|
|
If an aircraft is equipped with a fixed pitch propeller and a float type carburetor, the first indication of carburetor ice would be..
|
A. A drop in oil temperature and cylinder head temperature.
B. Engine roughness. C. Loss of RPM |
A. A drop in oil temperature and cylinder head temperature.
|
|
|
The operating principle of float type carburetors is based on the
|
A. Automatic metering f air at the venturi as the aircraft gains altitude.
B. Difference in air pressure at the venturi throat and the air inlet. C. Increase in air velocity in the throat of a venturi causing an increase in pressure. |
B. Difference in air pressure at the venturi throat and the air inlet.
|

