![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
types of pricing method |
1. economic pricing 2. cost based (full or MC) 3. competition based (going rate - undifferentiable so set prices and price wars drive down) or competitive bidding (lots of demand so customers bid price up) 4. market based pricing (takes into account PQ heuristic, point in life cycle, product line pricing, value to customers, distributor mark up) |
|
|
how do you choose an initial price for product |
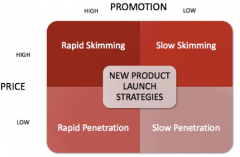
|
|
|
how do you justify a high price |
high value to customer consumer not the customer lack of competition (captive market) excess demand high switching costs customers under high pressure to buy |
|
|
why might you want a low price |
loss leader (complementary products) objective is penetration or domination economies of scale barrier to entry predatory pricing |
|
|
how does PLC affect price |
intro - low price or free samples growth - increase as much as demand allows to cover high marketing costs maturity - price levels off as costs reduce decline - either change product (reposition) or harvest profits while you still can (e.g.. discounts) |
|
|
Which prices methods are ethically wrong |
price fixing - colluding predatory pricing - running at loss so small firms go bust deceptive pricing - advertising flight for £90 but then adding tax luggage etc penetration when entering market may lead to predatory |

