![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
gram stain pic |
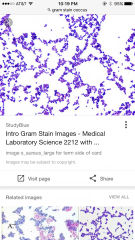
|
|
|
endospores stain pic |

|
|
|
endospores stain pic |
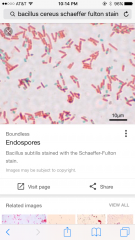
|
|
|
acid-fast stain pic |
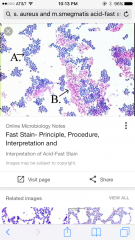
|
|
|
steps in gram staining |
crystal violet-primary gram's iodine-mordant ethyl alcohol wash-differential step/critical step/decolorizer safranin stain |
|
|
purple stain in gram |
crystal violet dark purple |
|
|
mordant in gram |
gram's iodine |
|
|
decolorizer |
ethyl alcohol |
|
|
secondary stain/counter stain |
safranin pink |
|
|
gram positive |
thick peptidoglycan on outside of cell membrane dark purple |
|
|
gram negative |
cell membrane-1 layer of peptidoglycan- membrane pink |
|
|
descriptions of gram stains |
1st: both cocci, little clumps of purple grapes with pink grapes in overall web design 2nd*: looks like blobs of pink rods with couple of purple rods on top (spoons) |
|
|
mixed culture composed of+color of colony |
pseudomonas aeruginosa-greenish escherichia coli-white staphylococcus aureus-yellow |
|
|
two types that produce endospores |
bacillus clostridium |
|
|
vegetative cell |
normal active cell (not a reproductive cell) |
|
|
exoporium |
protein coat that forms a protective barrier around the spore |
|
|
autoclave conditions |
defined by spores 15-20 min @ 121 degrees celsius steam under high pressure |
|
|
schaeffer-fulton method |
endospore staining dont use hot plate use primary stain for 15 minutes this distinguishes components |
|
|
what did we use the schaeffer-fulton method for? (what type of stain is this) |
Bacillus Cereus (endospore) 15 min no steam/heat |
|
|
steps for endospore staining |
malachite green (15 min)-30sec water wash-safranin |
|
|
method used for isolating pure colonies |
method a quadrant streak |
|
|
what color are spores? the vegetative cell? |
clear green and clear pink |
|
|
two types of cells acid-fast distinguish from |
cell-walls with high lipid content (mycolic acid) ---cells that appear waxy versus cells that lack the above |
|
|
acid-fast cells? |
alcohol cannot remove the primary stain of carbol fuchsim from the mycolic acid |
|
|
non acid-fast cells |
alcohol removes the primary stain no mycolic acid |
|
|
acid-fast counter stain |
methylene blue |
|
|
colors of mycolic acid cells adn non mycolic cells |
"dark" pink "dark" blue |
|
|
what did we use as a acid-fast example shape color |
Mycobacterium smegmatis "dark" pink short rods (bacilli) |
|
|
what did we use for non-acid fast example |
staphylococcus aureus "dark" blue spheres (cocci) |
|
|
description of spore staining |
cottoncandy in lattice overall shape the rods are LIGHT pink and lined in ^shape the rods are pink and there are little circle light blue ones(supposed to be green) in clumps around them (could be inside them) this is a lot bigger than other slides |
|
|
description of acid-fast stain |
tiny pink and blue dots that are so small cant tell the pink are rods, the colors are intermixed -more concentrated than gram dots, more like holes than clumps |
|
|
parfocal microscope |
focus lengths of lenses are the same so dont need to refocus |
|
|
oculars |
lens in eye pieces (10X) |
|
|
objective lenses |
4X- 10X- low power 40X- high-dry 100X- oil immersion |
|
|
ubiquity |
everywhere |
|
|
coccus (combos) |
sphere streptococcus (chain) staphylococcus (grapes) |
|
|
bacilli |
rod shaped |
|
|
sprilla |
"spiraled" actually look like curved rods |
|
|
description of bacilli |
pink. rods, lining up like trains, piled up in places |
|
|
description of coccus |
pink balls in clumps (roughly triangle) that look like grapes, some of the clumps hold hands |
|
|
spirilla description |
pink squiggles on top of eachother (thin) |
|
|
binocular eyepiece versus focusing eyepiece |

|
|
|
what do you use to squish the eye pieces together |
interpupillary adjustment |
|
|
, iris diaphragm, field diaphragm, condenser centering screw, substage condenser |

|
|
|
where do you put your top hand when carrying the micro? where do you put your bottom hand? |
top: arm bottom: base |
|
|
where do you put ur slide |
mechanical stage |
|
|
how do you move slide |
stage controls |
|
|
what secures your slide |
stage clip |
|
|
whats the turny thing |
revolving nosepiece |
|
|
lens that come off of turny thing |
objective lenses |
|
|
eye pieces are also called |
eye tubes |
|
|
want to move the slide up alot? |
coarse adjustment |
|
|
want to move slide up a little |
fine adjustment |
|
|
brightfield microscope |
light goes directly in eye w/o being interfered |
|
|
diopter adjustment ring |
on left eye piece to make both right and left eyes see sharp images |
|
|
Kinyoun acid-fast method |
acid-fast method |
|
|
what produce spores |
bacillus and clostridia |
|
|
endospores |
dehydrated the less water the more heat resistant |
|
|
sporulation |
reduces water content to 10-30% of orig |
|
|
how decrease volume in endospore |
calciumdipicolinate and spore specific proteins make cytoplasmic gel this controls the amount of water that can go in |
|
|
acid-fast disease |
mycobacterium tuberculosis mycobacterium leprae (Hansen's Disease/leprosy) |
|
|
acid fast method with heat |
ziehl-Neelsen |
|
|
primary stain in acid fast |
carbol fuchsin and phenol |
|
|
mordant in acid fast |
heat allows penetration |
|
|
non-acid fast example |
staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
what did we use in acid-fast |
mycobacterium smegmatis (soil/genitalia/non pathogenic) staphylococcus aureus (opportunist pathogen) |
|
|
insoluble complex formed in gram staining |
crystal violet-iodide complex |
|
|
strength of bac cell wall |
peptidoglycan |
|
|
how decolorizer works in gram |
decolorizer dissolves lipids in outer membrane of gram negative so complex can escape through thin peptidoglycan layer |
|
|
isolating techneques |
streak plate and pour plate to get pure colony |
|
|
smear goals |
get cells to adhere to glass not distort cells (shink) thin |
|
|
bacterium with polyphosphate granules |
corynebacterium diptheriae |
|
|
what were grams origninal goals |
differentiate bacteri cells from eukaryotic nuclei from diseased lung |
|
|
differential stains |
gram and acid-fast |
|
|
acid-fast staining |
carbol fuchsin-10 min methylene blue |
|
|
endospore cortex |
thick layer forms around endospore and contracts (decrease volume) |
|
|
mordant for spore stain |
heat |
|
|
acid-fast types |
mycobacterium and nocardia |
|
|
mycolic acid |
cell wall lipids fatty acids+fatty alcohols+hydrocarbon chain (80) |
|
|
danger of leaving cells too long for gram staining? |
gram + can decay into gram - (not other way tho) |
|
|
what do endospores do in gram stain |
look pink/clear |
|
|
type of streak plate |
method a quadrant streak plate |
|
|
condensation on plate |
can spread bacteria (ruin pure colonies) |
|
|
parcentral |
stay centered between flips |
|
|
bacteria to us |
10x more bacteria |
|
|
colony |
visible massof cells more than 1 bilion could be the division of 1 cell but also could be a streptococcus |
|
|
frau hesse |
wife of koch coworker figured out algae could be used as solidifying agent (agar-agar) this wasnt degraded by pathogenic bacteria |
|
|
dont contaminate stuff or let stuff contanimate |
aseptic technique |

