![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Suborder Pleurodira |
"side-neck," bending neck laterally, family Chelidae and Pelomedusidae |
|
|
Family Chelidae |

webbed feet, reduced shell, Austro-South American |
|
|
Family Pelomedusidae |

Afro-South American, no cervical scutes, understudied |
|
|
Suborder Cryptodira |
Bend neck sagitally (S shape) |
|
|
Family Emydidae |
box and water turtles, largest and diverse group, well developed shells, 24 marginal scutes and 12 plastral scutes, males have concave plastron for breeding. |
|
|
Family Cheloniidae |
Sea turtles, streamlined shells, head and limbs cannot retract |
|
|
Family Dermochelyidae |
Leatherback, largest extant, longest ranging ecotherm, feeds exclusively on jellyfish |
|
|
Family Trionychidae |
Softshell turtles, lack peripheral bones and no scutes on carapace. |
|
|
Family Testudindae |
Tortoises, |
|
|
Family Kinosternidae |
musky secretions from glands below carapace, 22 , marginal scutes and cervical scutes, fleshy barbels on chins. |
|
|
Family Chelydridae |
Snapping turtles, 24 marginal scutes, widely separated ventral scutes. 3 knobby keels and small plastron. |
|
|
Acrodont teeth |
fused to outer surface of bones in jaws, squamate families
|
|
|
Pleurodont teeth |
Supported by shelf of bone along tooth, snakes and other squamates |
|
|
Theocodont teeth |
Set in sockets of bone, mammals and archosaurs. |
|
|
Anapsids |
Lacks temporal fenestration or temporal bars, ancestral. Testudines |
|
|
Synapsids |
Have one temporal fenestration or temporal bar, mammalia |
|
|
Diapsida |
Have two fenestrations or temporal bars, lepidosaurs and archosaurs |
|
|
Carapace=Top Plastron=Bottom |
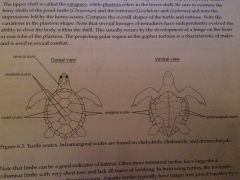
|
|
|
Review Turtle Skull and skeleton |
pg 77-78 |
|
|
Turtle Respiration |
Active respiration, muscles contract to move organs against, lungs to exhale, aquatic turtles can also respire through skin and cloaca. |
|
|
Testudinata Phylogeny |
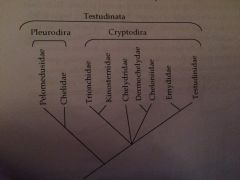
|

