![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
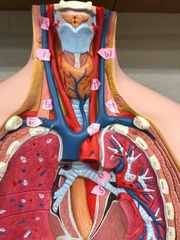
A |
right common carotid artery |
|
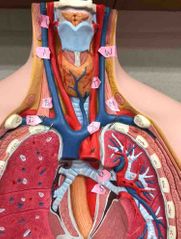
B |
right internal jugular vein |
|
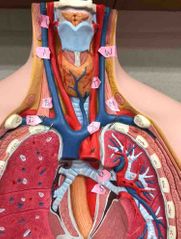
C |
right superior thyroid artery |
|
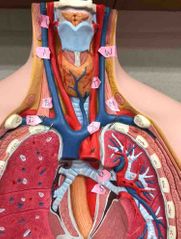
D |
right subclavian vein |
|
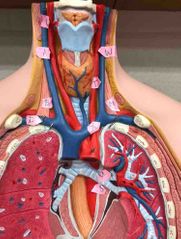
W |
left common carotid artery |
|
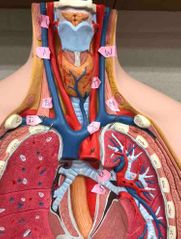
X |
left brachiocephalic vein |
|

T |
left internal jugular vein |
|
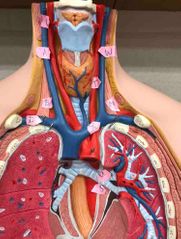
M |
left subclavian artery |
|
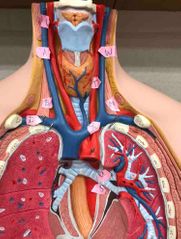
U |
superior left pulmonary vein |
|

S |
thoracic part of aorta |
|

E |
celiac trunk |
|

F |
abdominal aorta |
|
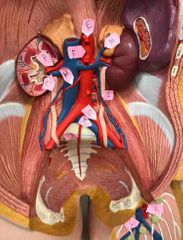
P |
renal artery |
|

O |
renal vein |
|

H |
right testicular artery |
|
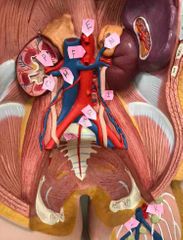
N |
left suprarenal vein |
|

I |
left testicular vein |
|

Q |
left common iliac artery |
|
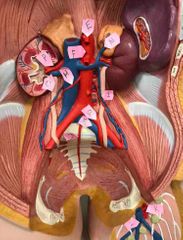
R |
left common iliac vein |
|

J |
median sacral artery |
|
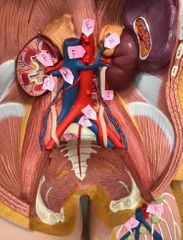
K |
femoral artery |
|

L |
great saphenous vein |
|

top burned part |
effects of smoking, discolored thicker tissue |
|

superior lobe pathology |
abscess from pneumonia |
|

middle lobe pathology |
granuloma from tuberculosis |
|

inferior lobe pathology |
lesions from tuberculosis |
|

white mass |
cancerous tumor |
|

death of an artery |
-clear artery -0% blockage |
|

death of an artery |
buildup begins -less than 50% blockage -plaque deposits form as cholesterol, fat, and calcium |
|

death of an artery |
reduced flow -50%-69% -artery continues to narrow, reducing the amount of blood and oxygen reaching the heart |
|

death of an artery |
high risk -more than 70% blockage -may experience chest pain |
|
death of an artery |
damage occurs -100% blockage -artery is completely blocked, can lead to heart attack |
|
|
pathology indicated by a thicker myocardium |
congestive heart failure |
|
|
pathology indicated by thinner myocardium |
myocardial infarction |
|
|
vital capacity equation |
vital capacity = TV + IRV + ERV |
|
|
Tidal Volume |
- 500 ml - amount of air moved in every breath |
|
|
Inspiratory Reserve Volume |
- IRV - Amount of air that can be forcibly inhaled - 2100-2300 ml |
|
|
Expiratory Reserve Volume |
- 1200 ml - amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled |
|
|
Residual volume |
- amount of air that remains in the lungs - 1200 ml |
|
|
functional volume |
- amount of air that reaches the respiratory zone - 350 ml |
|
|
anatomical dead space volume |
- amount of air that remains in the conducting zone - 150 ml |

