![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
126 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
State three facts about the difference between Active and Passive Transport.
|
Active Transport
- Against the concentration gradient - uses ATP - Always trans-membranes protein Passive Transport - Along its conentration gradient - Only use kinetic energy - Simple osmosis |
|
|
|
Foramen
|
Round or oval opening through a bone.
|
|
|
|
Condyle
|
Rounded articular projection.
|
|
|
|
Osteon
|
Haversian System
Lamella - weight bearing, support for the bone Haversian of central canal - contains all the blood vessels and nerves located in the center of the osteon. Volkman's canal - perpendicular to the central or Haversian canal. |
|
|
|
What happens when bones are exposed to heat?
|
the bones become calcified and begin to flake and crumble.
|
|
|
|
Bones of the skull
|
Pest of 6
P - Parietal Bone E - Ethmoid Bone (eye cavity) S - Sphenoid Bone (temples and eye cavity) T - Temporal Bone O - Occipital Bone F - Frontal Bone 6 - Six bones in the skull |
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelial
|
Cuboidal looking cell when not under pressure, when under pressure it looks like squamous cells. (urinary tract)
|
|
|
|
Squamous
|
wide, flatten nuclei that are used for protection and transporting materials.
|
|
|
|
Cuboidal
|
tall as they are wide, nuclei are symetrical and round. Secretion and absorption.
|
|
|
|
Columnar
|
Taller than they are wide, nuclei is oval and elongated.
Absorption and secreation. |
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|
striations and the nucleus are on the side.
|
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|
Striations, intercalated discs, nucleus are in the center.
|
|
|
|
Smooth Muscle
|
No Striations
|
|
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton
|
Consists of 126 bones and includes the free appendages and their attachments. The free appendages are the upper and lower extremites, or limbs and their attachments which are called girdles.
|
|
|
|
Axial Skeleton
|
Consists of 80 bones. They include the bones of the head, vertebral column, ribs and breastbone or sternum.
|
|
|
|
Irregular Bones
|
are spongy bone that is covered with a thin layher of compact bone.
Found in the vertebra and some fo the bones in the skull. |
|
|
|
Flat Bones
|
are thin, flattened, and usually curved.
Found in the cranium and the sternum. |
|
|
|
Short Bones
|
are roughly cube shaped with vertical and horizontal dimensions approximately equal.
Found in the wrist and ankle. |
|
|
|
Long Bones
|
Bones that are longer than they are wide.
Found in the thigh, leg, arm and forearm. |
|
|
|
Psedostratified Columnar
|
ciliated can be non-ciliated (GI-system), heavily evangenated with goblet cells.
Goblet cells secrete mucus out. |
|
|
|
Simple
|
all cells are at the basement membrane
|
|
|
|
Stratified
|
There is multiple cell layers - look at the most apical cells.
|
|
|
|
What are the two type of skin that is very rarely seen?
|
Stratified Columnar and Cuboidal.
|
|
|
|
Who wrote this quote: "Give me a lever long enough and a fulcrum on which to place it and I shall move the world"
|
Archimedes
|
|
|
|
Microscope:
Arm |
Connects the base and head, used for carrying the microscope
|
|
|
|
Microscope:
Condenser |
Concentrates light
|
|
|
|
Microscope:
Base |
Supports the microscope
|
|
|
|
Microscope:
Fine Adjustment Knob |
Precise Focusing
|
|
|
|
Microscope:
Nosepiece |
Holds the objective lens
|
|
|
|
Microscope:
Stage |
Supports the glass slide
|
|
|
|
Working Distance
|
is the distance betwee the objective lens and the specimen.
At low magnification the working distance is relatively long, at high the working distance is short. |
|
|
|
Total Magnification
|
Power of the ocular lens * Power of the Objective Lens
|
|
|
|
Integumentary System
|
Skin, hair, and nails
Function: Protection |
|
|
|
Skeletal System
|
Bones
Function: Support/Protection |
|
|
|
Nervous System
|
Brain, spinal cord, nerves
Function: Receive/Transmit Impulses |
|
|
|
Muscular System
|
Muscles
Function: Movement |
|
|
|
Endocrine System
|
Thyroid, Parathyroid, Adrenal and Pituitary glands; pancreas, stomach, pineal gland, ovaries and testes.
Function: Metabolism/Homeostasis |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular System
|
Heart, blood, blood vessels
Function: Transport |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System
|
Thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoracic duct, spleen and lymph nodes.
Function: Transport/Cleanses blood. |
|
|
|
Respiratory System
|
Nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs.
Function: Gas Exchange |
|
|
|
Digestive System
|
Mouth, Esphagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum, anus, liver, gall bladder, Pancreas adn appendix.
Function: Breakdown and absorption of foods |
|
|
|
Urinary System
|
Kidneys, ureters, bladder adn urethra
Function: Waste processing and elimination |
|
|
|
Mitosis
|
is a comples process which allows the cells to give identical copies of its DNA to each of the daughter cells.
Phases: 1) Prophase 2) Early Metaphase 3) Metaphase 4) Early Anaphase 5) Late Anaphase 6) Early Telophase 7) Late Telophase 8) Interphase |
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
Tiny spherical bodies composed of RNA and protein, floating free or attached to the rough ER.
Site of Protein Synthesis |
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
|
Rough ER - provides an area for storage and transport
Smooth ER - no function in protein sythesis. (Membranous Tubules) |
|
|
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
stack of flattened sacs with bulbous ends and associated small vesicles found close to the nucleus; new proteins are made.
(Protein Packaging) |
|
|
|
Lysosomes
|
Various sized membranous sacs containing digestive enzymes.
(Digestion) |
|
|
|
Peroixosmes
|
Small lysosome-like membranous sacs containing oxidase enzymes that detoxify alchohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals.
(Detoxification) |
|
|
|
Mitochondria
|
Rod shaped bodies with a double-membran wall; powerhouse.
(ATP Production) |
|
|
|
Centrioles
|
Paired, cylindrical bodies lie at right angles to each other, close to the nucleus, form the bases of cilia and flagella.
|
|
|
|
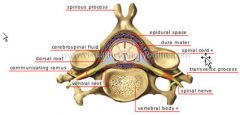
Spinous Process
|
is the protrusion on the center of the back of a vertebral body. It is the site for the attachement of many spiral muscles.
|
|
|
|
Transverse Process
|
is a protrusion extending out from either side of a vertebral body and provides the point of articulation for the ribs.
|
|
|
|
Verterbral Foramen
|
is for the passage of the spinal chord.
|
|
|
|
What are the sutures of the skull and what make them up?
|
Coronel suture - Frontal and parietal bones
Lambdoidal Suture - parietal and ocipital bone Squamous - parietal and temporarl Sagital - between the two parietal bones. |
|
|
|
Occipital Condyles
|
a protrusion on teh occipital boen of the skull that forms a joint with the first cervical vertebra, enabling the head to move relative to the neck.
|
|
|
|
What are the effects of soaking bones in acid?
|
the acid dissolves the minerals in the bones matrix.
|
|
|
|
Fontanels
|
(Soft Spot) are indentations between the bones of a fetal skull and are fibrous membranes.
|
|
|
|
Calcaneus
|
The quadrangular bone at the back of the tarsus. Also called a heel bone.
|
|
|
|
Lesser Trochanter
|
of the femur is a conical eminence, which varies in size in different subjects. Projects from the lower and back part of the base of the femur neck.
|
|
|
|
Lateral Malleolus
|
is the name for the bony prominence on each side of the ankle.
|
|
|
|
31 Spinal Nerves
|
Cervical (c1-c8)
Thoracic (T1-T12) Lumber (L1-L5) Sacrum (S1-S5) Coccyx - 1 |
|
|
|
Sesamoid bone
|
are bones that form within tendons.
|
|
|
|
Prophase
|
The first and longest phase of mitosis. Chromosomes become more coiled and can be viewed under a light microscope. Each duplicated chromosome is seen as a pair of sister chromatids joined by the duplicated but un-separated centromere. The nucleolus disappears. In the cytoplasm, the mitotic spindle, consisting of microtubules and other proteins, forms between the two pairs of centrioles as they migrate to opposite poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope disappears at the end of prophase. This signals the beginning of the substage called prometaphase. DNA becomes visible strands.
|
|
|
|
Metaphase
|
Spindle fibers align the chromosomes along the middle of the cell nucleus. This line is referred to as the metaphase plate. This organization helps to ensure that in the next phase, when the chromosomes are separated, each new nucleus will receive one copy of each chromosome
|
|
|
|
Anaphase
|
Third state of mitosis, begins when the sister chromatids break and each chromatid (now called a chromosome) moves toward an opposite end of the cell. Bye the end of anaphase, the chromosomes are at opposite ends of the cell.
|
|
|
|
Telophase
|
Spindle fibers break apart, two new nuclear membranes begin to form, and the chromosomes disperse into chromatin.
|
|
|
|
Cytokinesis
|
is the division of the cytoplasm, photosynthesis is the process by which a cell produces its own food
|
|
|
|
Endocytosis
|
is how a cell ungulfs large food particles.
|
|
|
|
Atlas (C1)
|
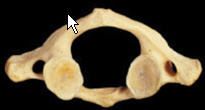
|
|
|
|
Axis (C2)
|
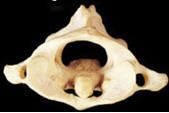
|
|
|
|
Quadrants of the abdomen
|
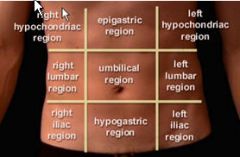
|
|
|
|
Meissner's Corpuscle
|
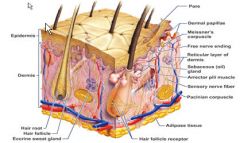
|
are egg-shaped receptors consisting of a mass of intertwined fibres. They are located between the dermis and epidermis that inform the brain exactly where the skin is touched.
|
|
|
Epiphyseal Fracture
|
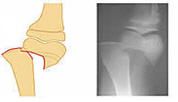
|
Epiphysis separates from the diaphysis along the epiphyseal plate.
|
|
|
Compression Fracture
|
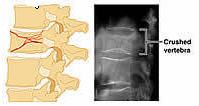
|
Bone is crushed
|
|
|
Depressed Fracture
|
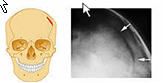
|
Broken bone portion is pressed inward.
|
|
|
Greenstick Fracture
|
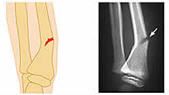
|
Bone breaks incompletely. Only one side of the shaft breaks.
|
|
|
Comminuted Fracture
|
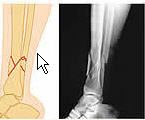
|
Bone fragments into three or more pieces.
|
|
|
Spiral Fracture
|
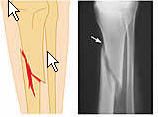
|
Ragged break occurs when excessive twisting forces are applied to a bone.
|
|
|
Zygomatic Process
|
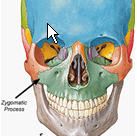
|
Any of several bony processes that articulate with the zygomatic bone.
|
|
|
Mandibular Fossa
|
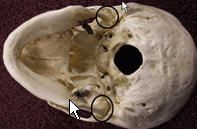
|
A deep concavity in the temporal bone at the root of the zygomatic arch that receives the condyle of the mandible.
|
|
|
Thoracis Vertebra
|
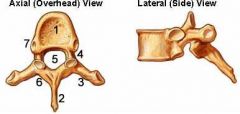
|
T1 - T12
|
|
|
Lumbar Vertebra
|
|
L1 - L5
|
|
|
Sacral Verterbra
|
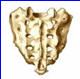
|
S1 - S5
|
|
|
Concentric Layer of the bone
|
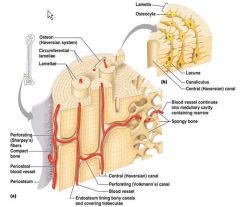
|
|
|
|
Bones of the Body (Anterior)
|
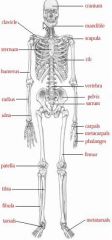
|
|
|
|
Bones of the body (Posterior)
|
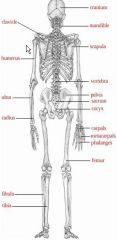
|
|
|
|
Skull Bones
|
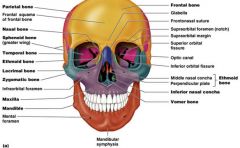
|
|
|
|
Parietal Bones
|
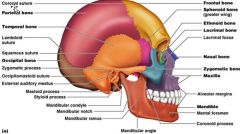
|
|
|
|
What are the statins used with a microscope?
|
Physilogic saline - a sterile solution of sodium chloride that is isotonic to body fluids.
Methlylene Blue Stain - stains cells to a violent blue, making organelles easier to identify. |
|
|
|
What are the steps to prepare a wet mount slide?
|
1. Apply the cells to the slide
2. Add a drop of stain 3. Lower the cover slip 4. View the slide |
|
|
|
Cephalic
|
Head
|
|
|
|
Frontal
|
Forehead
|
|
|
|
Nasal
|
Nose
|
|
|
|
Orbital
|
eye
|
|
|
|
Buccal
|
Cheek
|
|
|
|
Oral
|
Mouth
|
|
|
|
Cervical
|
Neck
|
|
|
|
Mental
|
chin
|
|
|
|
Acromial
|
Shoulder
|
|
|
|
Sternal
|
Breast bone
|
|
|
|
Axillary
|
Armpit
|
|
|
|
Thoracic
|
Chest
|
|
|
|
Mammary
|
breast
|
|
|
|
Brachial
|
Arm
|
|
|
|
Antecubital
|
Front Elbow
|
|
|
|
Popliteal
|
posterior knee
|
|
|
|
Sural
|
calf
|
|
|
|
Carpal
|
Wrist
|
|
|
|
Palmar
|
Palm
|
|
|
|
Pollex
|
Thumb
|
|
|
|
Digital
|
Fingers/toes
|
|
|
|
Pubic
|
Genital
|
|
|
|
Patellar
|
anterior knee
|
|
|
|
Crural
|
Leg
|
|
|
|
Tarsal
|
Ankle
|
|
|
|
Hallux
|
Big Toe
|
|
|
|
Occipital
|
base of the skull
|
|
|
|
Vertebral
|
Spinal
|
|
|
|
Scapular
|
Shoulder Blade
|
|
|
|
Dorsum
|
Back
|
|
|
|
Lumbar
|
lower back
|
|
|
|
Sacral
|
between hips
|
|
|
|
Perineal
|
between anus and genitalia
|
|
|
|
Femoral
|
Thigh
|
|
|
|
Calcaneal
|
Heel
|
|
|
|
Plantar
|
Sole
|
|

