![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are arteries otherwise known as? |
Resistance vessels |
|
|
What are capillaries otherwise known as? |
Exchange vessels |
|
|
What is the source of energy that propels the blood? |
Muscular contraction |
|
|
What are veins otherwise known as? |
Capacitance vessels |
|
|
How is flow restricted to one direction only? |
Valves at the inflow and outflow points of the ventricles |
|
|
How is the pump refilled after contraction? |
By the atria passively leaking blood, and then actively squeezing blood, into the ventricles |
|
|
How are the layers of myocardium arranged? |
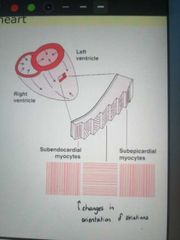
Sub endocardial myocytes are arranged in a superior-interior orientation. As you go up the layers, the myocytes twist 180 degrees, ending up at sup-inf again at the subepicardial myocytes |
|
|
Which mechanism couples electricity and tension in the heart? |
Excitation contraction coupling |
|
|
Write the equation relating tension and pressure |

Laplaces law |
|
|
Why is laplaces law different in the ventricles to in the vessels? |
Because the ventricles are a different shape to the vessels (cone vs rod) |
|
|
What is the vicious cycle of maladaptive hypertrophy? |
If a ventricle grows, it's radius increases. According to laplaces law, this will require a corresponding increase in tension to maintain the pressure. To increase tension, the heart grows more, further increasing radius and starting the cycle again |
|
|
How are pressure and flow related? |
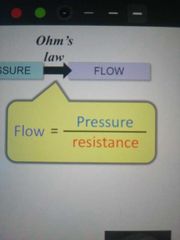
Ohms law |
|
|
What provides resistance in the heart? |
Valves |
|
|
What is an incompetent valve? |
A valve that won't fully close, which may cause some blood to leak backwards |
|
|
What is a stenosed valve? |
A valve that won't fully open, leading to increased resistance and a corresponding higher pressure to maintain flow |
|
|
What is the isovolumetric phase? |
The phases of the cardiac cycle where both valves of a ventricle are closed, so the volume remains constant |
|
|
What is the purpose of the isovolumetric phase? |
To ensure that the AV valve is closed before the semi lunar valve opens, to prevent backflow |
|
|
True or false - atrial systole takes place within ventricular diastole? |
True |
|
|
During atrial contraction, which valves are open? |
AV only |
|
|
During ventricular systole, which valves are open? |
Semilunar only |
|
|
What is the first phase of ventricular diastole? |
Isovolumetric relaxation - the ventricular pressure is between aortic and atrial pressure, so all valves are closed. The ventricle pressure decreases without a change in volume |
|
|
When do isovolumetric phases occur with relation to pressure? |
When ventricular pressure is between arterial and atrial pressure |
|
|
What is the second phase of ventricular diastole? |
The filling phase, where ventricular pressure drops so low it sucks blood in through the AV valve. This is called passive recoil |
|
|
What is the first phase of ventricular systole? |
Isovolumetric contraction - the ventricle pressure increases without an accompanying change in volume |
|
|
What is the second phase of ventricular systole? |
Ejection into the aorta |
|
|
When do the two heart sounds occur? |
When the valves close at the start of the isovolumetric phases |
|
|
Which is lub and which is dub? |
Lub is AV closure at the start of isovolumetric contraction Dub is semilunar closure at the start of isovolumetric relaxation |
|
|
How much do the atria contribute to ventricular filling in young people? |
10-20% |
|
|
How much do the atria contribute to ventricular filling in the elderly? |
50% |
|
|
Why is atrial fibrillation a more dangerous condition in the elderly than young people? |
Because as you get older, your recoil and passive ventricular filling decrease so the atria contribute more to ventricular filling |
|
|
Draw a diagram of changing ventricular pressure during the cardiac cycle |
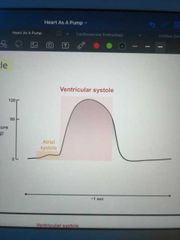
|
|
|
Draw a diagram of changing ventricular volume during the cardiac cycle |
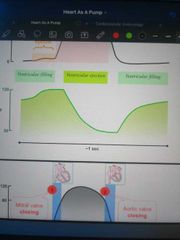
|
|
|
What causes central venous pressure to rise? |
Atrial contraction A-V valve closure Atrial filling |
|
|
What causes CVP to fall during the cardiac cycle? |
Atrial relaxation AV valve opening |
|
|
Why is CVP linked to atrial pressure? |
Because there is no valve linking vena cavae to RA |
|
|
Draw a labelled diagram to show jugular venous pressure in response to the cardiac cycle |
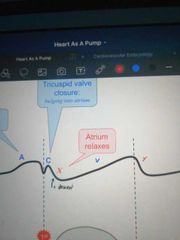
|
|
|
What causes the A wave on a JVP curve? |
Atrial systole |
|
|
What causes the C wave on a jugular pressure graph? |
Closure of the tricuspid valve - can hear the lub at this point |
|
|
What causes the X descent? |
Atrial relaxation |
|
|
What causes the V ascent? |
Atrial filling during ventricular systole |
|
|
What causes the Y descent on a JVP graph? |
The opening of the tricuspid valve |

