![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
204 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What four aspects does Human Factors encompass |
-medical aspects -psychological aspects -ergonomical aspects -engineering aspects |
|
|
What percent of accidents involve some form of Human Factors |
75% |
|
|
What are the three terms that are located at the bottom of the Airmanship Model from bottom up |
Discipline, Skill, Proficiency |
|
|
What are the 5 pillars of knowledge |
Self, Aircraft, Team, Environment, Risk |
|
|
What are the two terms that fulfil the upper part of the Airmanship model |
Situational Awareness, Judgement |
|
|
Human Factors is the interaction between what three things |
People, machines and the environment |
|
|
Research in the late ___s found what |
Late 1970s. Found majority of crashes were failures of communication, decision making and leadership |
|
|
What is the make up of the gases in the atmosphere |
78% Nitrogen 21% Oxygen 1% Other |
|
|
Why does an increase in altitude mean a ____ in air pressure |
Decrease. Because there are less molecules at greater altitudes |
|
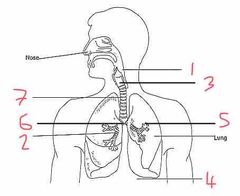
Name number 1 and their use |
Pharynx - determines if contents are food or air |
|
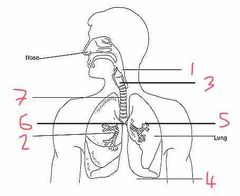
Name number 2 and their use |
Bronchioles - supply O2 to alveoli |
|
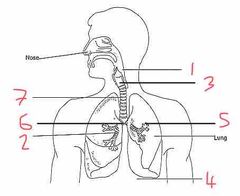
Name number 3 and their use |
Larynx - voice box |
|
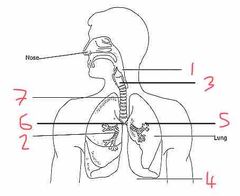
Name number 4 and their use |
Diaphragm - allows for breathing by expanding (breath out) or contracting (breath in) |
|
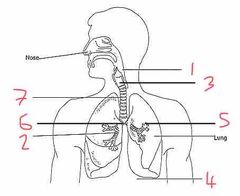
Name number 5 and their use |
Alveoli - diffusion of O2 into the blood stream |
|
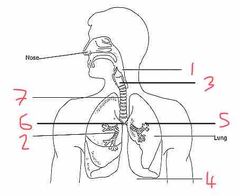
Name number 6 and their use |
Bronchi - separates O2 evenly between the lungs |
|
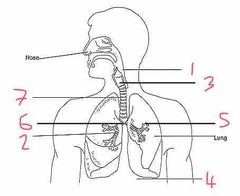
Name number 7 and their use |
Trachea - wind pipe (ribs of cartilage to stop it from collapsing) |
|
|
What is the use of the circulatory system |
Circulation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood throughout the body |
|
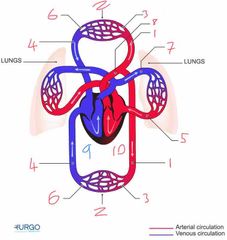
Name number 1 and it’s use |
Artery - carry oxygenated blood away from heart to capillaries/arterioles |
|
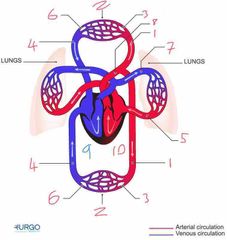
Name number 2 and it’s use |
Tissue Capillary - supply muscles with oxygen from red blood cells |
|
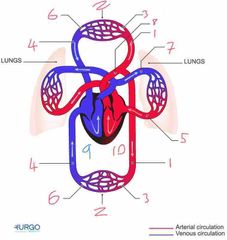
Name number 3 and it’s use |
Arterioles - supply capillaries with oxygenated blood |
|
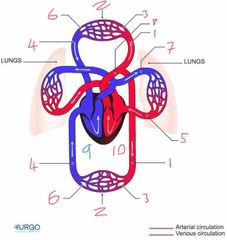
Name number 4 and it’s use |
Veins - carry deoxygenated blood to the heart |
|
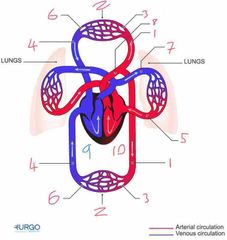
Name number 5 and it’s use |
Pulmonary Vein - carry oxygenated blood from lungs to heart |
|
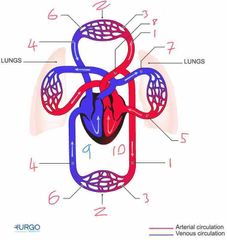
Name number 6 and it’s use |
Venules - supply veins with deoxygenated blood from capillaries |
|
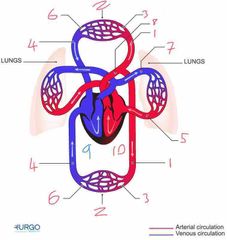
Name number 7 and it’s use |
Pulmonary Artery - carry deoxygenated blood away from heart to lungs |
|
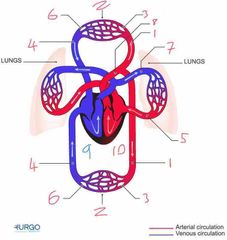
Name number 8 and it’s use |
Aorta - largest artery in the body carrying oxygenated blood away from the left side of the heart |
|
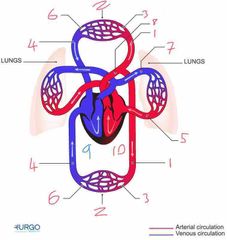
Name number 9 and it’s use |
Right heart - circulation of deoxygenated blood through heart |
|
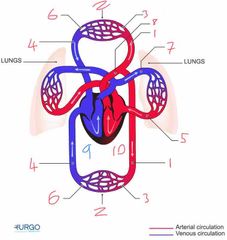
Name number 10 and it’s use |
Left heart - circulation of oxygenated blood through heart |
|
|
mmHg is a unit for what |
Millimeters per mercury |
|
|
What sea level, what is the value of oxygen pressure |
159 mmHg (150 mmHg) |
|
|
At 18,000ft, what is the pressure of the atmosphere |
380 mmHg |
|
|
What is the use of the respiratory system |
Gas exchange (O2 to CO2) allowing us to breathe |
|
|
How is oxygen transported around the body |
Red Blood Cells - haemoglobin in the cells picks up O2 |
|
|
What is the altitude at which partial pressure is 1/2 that at MSL |
10,000ft |
|
|
What is a prevention method for Hypoxia |
Pressurisation of aircraft (8000ft standard with newer aircraft at 6000ft) |
|
|
What factors increase likelihood of Hypoxia |
Cold temperature High activity (faster heart rate) Sickness Fatigue Under the influence Smoking or vaping |
|
|
What is hyperventilation |
Breathing rate is greater than required to expel CO2 causing an imbalance in pH levels in the body due to a lack of CO2 |
|
|
Why is Hypoxia so dangerous |
Slow onset Victim unaware they are being effected |
|
|
What are the causes of hyperventilation |
Anxiety or Fear Mental stress Turbulence |
|
|
What are some symptoms of hyperventilation |
Dizziness Tingling Visual disturbance Hot and cold sensations Loss of muscle coordination Increased heart rate Muscle spasm |
|
|
What is the treatment for hyperventilation |
Calm person/reduce breathing Unconsciousness resets breathing rate to normal Paper bag (build up of CO2 becomes inhaled by person restoring pH levels) |
|
|
Why should you always treat for Hypoxia if unsure between Hypoxia and hyperventilation |
Treatment for hyperventilation can catalyse hypoxia due to an influx in CO2 further reducing oxygen levels |
|
|
What is the value of partial pressure at 10,000ft |
52.5 mmHg (1/2 of MSL) |
|
|
What is the minimum accepted level in aviation at which a breathing mask is required |
10,000ft |
|
|
What is the altitude at which partial pressure is equal to MSL on 100% O2 |
34,000ft |
|
|
42,000ft is equal to what on 100% O2 |
10,000ft MSL (1/2 partial pressure at MSL) |
|
|
Above what altitude is pressure breathing equipment required |
42,000ft |
|
|
What are the four types of Hypoxia |
Hypoxic - environmental (lack of O2 in the air) Anemic/Hypemic - unable to carry enough O2 (lack of red blood cells) Stagnant - lack of circulation (high Gs) Histoxic - Tissue or cell poisoning (Carbon Monoxide) |
|
|
What are the causes of Hypoxia |
Reduced pressure at altitude Inhalation of carbon monoxide Sustained high Gs |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Hypoxia |
Increased breathing rate Dizziness Tingling Sweating Reduced visibility (tunnel vis) Sleepiness Blue colour Euphoric/over confident Failing concentration Impaired reasoning Attention and memory failure |
|
|
What is the treatment for Hypoxia |
Provide oxygen Descend to lower altitude |
|
|
What is the altitude at which partial pressure is 1/2 that at MSL |
10,000ft |
|
|
What is a prevention method for Hypoxia |
Pressurisation of aircraft (8000ft standard with newer aircraft at 6000ft) |
|
|
What factors increase likelihood of Hypoxia |
Cold temperature High activity (faster heart rate) Sickness Fatigue Under the influence Smoking or vaping |
|
|
What is hyperventilation |
Breathing rate is greater than required to expel CO2 causing an imbalance in pH levels in the body due to a lack of CO2 |
|
|
Why is Hypoxia so dangerous |
Slow onset Victim unaware they are being effected |
|
|
Define hyper |
Fast/over |
|
|
What are the causes of hyperventilation |
Anxiety or Fear Mental stress Turbulence |
|
|
What are some symptoms of hyperventilation |
Dizziness Tingling Visual disturbance Hot and cold sensations Loss of muscle coordination Increased heart rate Muscle spasm |
|
|
What is the treatment for hyperventilation |
Calm person/reduce breathing Unconsciousness resets breathing rate to normal Paper bag (build up of CO2 becomes inhaled by person restoring pH levels) |
|
|
Why should you always treat for Hypoxia if unsure between Hypoxia and hyperventilation |
Treatment for hyperventilation can catalyse hypoxia due to an influx in CO2 further reducing oxygen levels |
|
|
What is barotrauma |
Also known as entrapped gases, barotrauma is pain from excessive pressure differential caused by barometric changes |
|
|
What is the value of partial pressure at 10,000ft |
52.5 mmHg (1/2 of MSL) |
|
|
When is barotrauma most common |
Eustachian tube becomes blocked on descent causing ear to be unable to equalise inside pushing eardrum in |
|
|
At 18,000ft, pressure has expanded to what degree |
2.2x |
|
|
At what altitude has pressure expanded 3x |
25,000ft |
|
|
At 34,000ft, pressure has expanded at what rate |
5x |
|
|
In what five places is barotrauma likely |
Ears Sinuses Gastrointestinal Tract Teeth Lungs |
|
|
What types of barotrauma are most likely during ascent |
Gastrointestinal - expands with increase in altitude that can cause pain if not vented (fart) or blocked in small bowel by food Teeth - gases trapped in fillings expand with altitude |
|
|
What type of barotrauma is most likely on descent |
Ears - Eustachian tube closes under increasing pressure Sinuses - trapped gases blocked by cold or flu inflammation |
|
|
Explain barotrauma in the lungs and when it’s most likely |
Failure or breath out during sudden decompression can cause damage |
|
|
What is the minimum accepted level in aviation at which a breathing mask is required |
10,000ft |
|
|
What is the altitude at which partial pressure is equal to MSL on 100% O2 |
34,000ft |
|
|
42,000ft is equal to what on 100% O2 |
10,000ft MSL (1/2 partial pressure at MSL) |
|
|
Above what altitude is pressure breathing equipment required |
42,000ft |
|
|
What are the four types of Hypoxia |
Hypoxic - environmental (lack of O2 in the air) Anemic/Hypemic - unable to carry enough O2 (lack of red blood cells) Stagnant - lack of circulation (high Gs) Histoxic - Tissue or cell poisoning (Carbon Monoxide) |
|
|
What are the causes of Hypoxia |
Reduced pressure at altitude Inhalation of carbon monoxide Sustained high Gs |
|
|
What is the treatment for Hypoxia |
Provide oxygen Descend to lower altitude |
|
|
How is DCS formed |
Nitrogen coming out of solution and forming bubbles in various parts of the body |
|
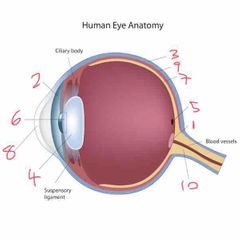
Name number 1 and it’s use |
Optic lens - blind spot |
|
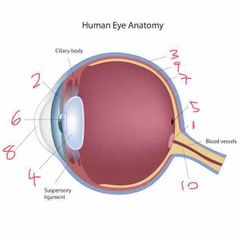
Name number 2 and it’s use |
Iris - coloured bit of the eye |
|
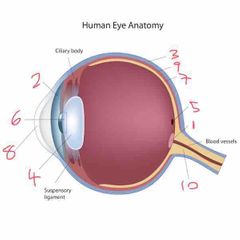
Name number 3 and it’s use |
Sclera - outer layer of the eye |
|
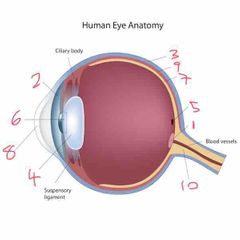
Name number 4 and it’s use |
Lens - further refracts light onto retina |
|
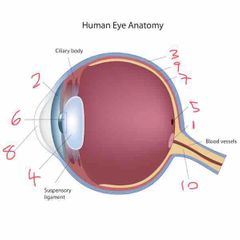
Name number 5 and it’s use |
Fovea - gap in retina/photo sensitive cells (cones) |
|
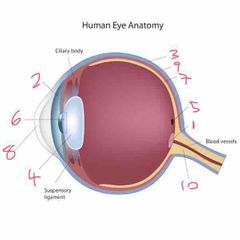
Name number 6 and it’s use |
Pupil - dictates the amount of light allowed into the eye |
|
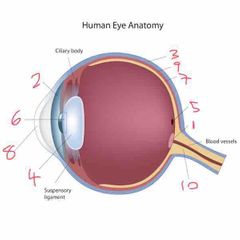
Name number 7 and it’s use |
Retina - absorbs light that enters the eye |
|
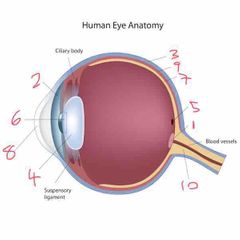
Name number 8 and it’s use |
Cornea - refracts majority of light |
|
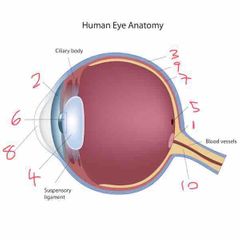
Name number 9 and it’s use |
Choroid - middle layer of the eye |
|
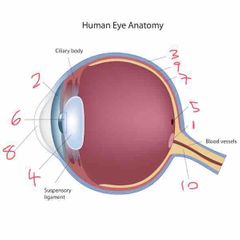
Name number 10 and it’s use |
Optic nerve - transports info to brain |
|
|
What cell is colour sensitive |
Cones |
|
|
What use are rods greatest for |
Peripheral vision |
|
|
“The creeps” is a form of DCS in what part of the body and what is the symptom |
Skin, tingling skin |
|
|
DCS in the nervous system is called ____ and what is the symptom |
“The creeps”, partial paralysis |
|
|
“The chokes” occurs in what part of the body and what are the symptom |
Lungs, possibly fatal/difficulty breathing |
|
|
How long must you wait after diving to 10m |
12 hours |
|
|
How long must you wait after diving further than 10m |
24 hours |
|
|
What can help reduce the effects of DCS while diving |
Making required recompression stops |
|
|
What is the inflight treatment for DCS |
Put patient on O2 and stop body movement Descend aircraft |
|
|
Why is it dangerous to fly after diving |
Increases pressure differential, increasing the risk of DCS due to increased levels of nitrogen during diving |
|
|
When does a night blind spot occur and why |
At night in poor lighting - light is below the threshold and cones are not stimulated |
|
|
How long does the first stage of dark adaption occur and what occurs |
Less than one second Pupil expands to allow more light |
|
|
How long does stage 2 of dark adaption last and what occurs |
7 minutes Cones shut down |
|
|
How long does the third stage of dark adaption last and what occurs |
30 minutes Rods build to greatest sensitivity over this period (cones have shut down) |
|
|
What is the total time of dark adaption |
30 minutes |
|
|
What UV percentage should sunglasses contain when used in aviation |
100% |
|
|
Why should you avoid tinted glasses |
Tints cause colour distortion |
|
|
Why should you avoid polarised sunglasses |
Interferes with glass displays |
|
|
Why should you avoid photo-chromatic sunglasses |
Increased time taken to clear in low light |
|
|
Why should you avoid thicc framed sunglasses |
Obstruct field of view |
|
|
What are the fife requirement for sunglasses in aviation |
100% UV Avoid tints Avoid polarisation Avoid photo-chromatic Avoid thicc frames |
|
|
What is photopic lighting and why does it result in greater visibility |
Day vision, greater object size, illumination, contrast, clarity, both eyes working to provide depth perception, etc |
|
|
What is scotopic vision and why is it a limitation to the eye |
Night vision, Light intensities are low causing rods to take over reducing colour discrimination and acuity Identification range reduced |
|
|
What is the limitation of excessive light during the day |
Glare - causes squinting, watery eyes, temporary blindness (all reduce vision) |
|
|
What is the limitation of the eye results in the inability to distinguish or accurately identify objects |
Lack of contrast |
|
|
What limitation of the eye can poor cockpit design lead to |
Blind spots |
|
|
How many types of pigment do rods contain |
1 |
|
|
How many types of pigment do cones contain |
3 |
|
|
Why is the use of a red light preferable over a white light at night |
Does not affect dark adaption |
|
|
What is a limitation of the use of red light at night |
Can distort vision |
|
|
What is empty field myopia and why is it caused |
Low visual stimulus causes relaxed resting state focal length resulting in lack of vision past 3-4 meters |
|
|
How is empty field myopia overcome |
Refocus eye (look out to object in the distance or out to the wingtip) Keep busy |
|
|
What sector scan technique is recommended |
20 degrees for 2 seconds |
|
|
What is the total time a pilot has to identify and avoid an aircraft |
5 - 7.5 seconds |
|
|
Explain the process of hypothermia |
- Occurs when body temperature is below what is required for survival - Symptoms include: Blue colour, shivering then stop shivering, can't focus, sleepy |
|
|
List the priorities of survival in order of importance |
1. Protection 2. Location 3. water 4. Food |
|
|
Explain the basic steps in post-crash survivor management. |
STOP Sit - Think - Observe - Plan |
|
|
State the components of a pre-flight passenger briefing by a pilot withrespect to aircraft safety features and equipment. |
Must Include: Smoking regulation, stowage of tray tables, requirements of seatbelts, location of doors and emergency exits, evacuation procedures, restrictions of electronic devices When Required: Location of survival and emergency equipment, use of floatation devices, use of passenger oxygen |
|
|
Describe the basic principles of cardiopulmonary Resuscitation |
- Is for person who isn't breathing or heart has stopped - Performed by chest compressions and rescue breaths - CPR can maintain circulation and breathing until emergency medic arrives |
|
|
Describe the basic principles of first aid |
D angers R esponse S end for help A irways B reathing C irculation D efibrillation |
|
|
Identify the phases of flight where a checklist plays an important role. |
Take-off Approach Landing |
|
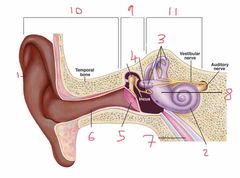
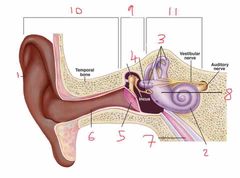
Name number 1 and it’s use |
Pinna - direct noise down the auditory canal |
|
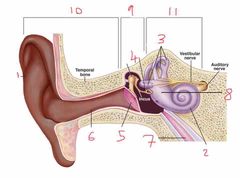
Name number 2 and it’s use |
Cochlea - transmits sound via neurological signals to the brain |
|
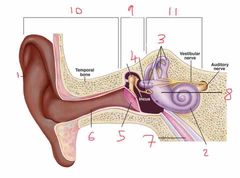
Name number 3 and it’s use |
Semicircular canals - measure pitch, roll and yaw (angular velocity) |
|
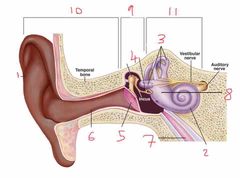
Name number 4 and it’s use |
Auditory Ossicles - aid in sound wave transmission |
|
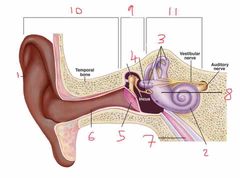
Name number 5 and it’s use |
Tympanic membrane - ear drum |
|
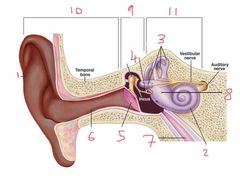
Name number 6 and it’s use |
Auditory canal |
|
Name number 7 and it’s use |
Eustachian tube - connects middle ear to nasal passage |
|
Name number 8 and it’s use |
Otolith organs - measure linear acceleration (longitudinal and latitudinal) |
|
Name number 9 and what the content can be found in it |
Middle ear - filled with air |
|
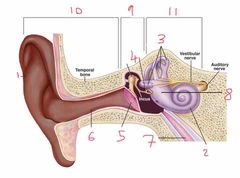
Name number 10 |
Outer ear |
|
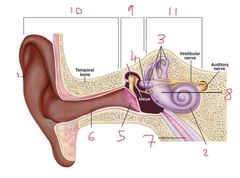
Name number 11 and the content that is found within |
Inner ear - filled with fluid |
|
|
What percentage of spatial orientation does the visual system account for |
70% |
|
|
Other than the vestibular system and visual system, what other parts in the body generate positional information |
Nerve endings known as proprioceptors |
|
|
How is “the leans” caused |
Slow roll not picked up by fluid in the ear. There becomes a strong feeling of being at one attitude while instruments display another |
|
|
Describe sub threshold stimulation |
Slow lean not picked up by semicircular canals that is eventually noticed on the instruments and corrected. By doing so there becomes a strong sensation of a roll in the same direction leading to “the leans” |
|
|
What are the four methods for protection of hearing |
Earmuffs Earplugs Communications headset Earmuff/helmet combinations (airforce helmets) |
|
|
Name number 7 and it’s use |
Eustachian tube - connects middle ear to nasal passage |
|
|
What is the name given to age induced hearing loss |
Presbycusis |
|
|
What are the symptoms of presbycusis |
Difficulty hearing people around you Frequently asking people to repeat themselves Frustration Certain sounds seem loud Problems hearing in noisy areas Problems with certain sounds such as “s” and “th” Difficulty hearing higher pitch Tinnitus (ringing in ears) |
|
|
When does the Eustachian tube open and why |
When we yawn, swallow or chew - allows air to flow into the middle ear and mucus to flow out keeping air pressure equal |
|
|
If the Eustachian tube becomes blocked on descent describe what happens |
Air pressure on the outer ear become greater than that in the middle ear thus pushing the ear drum inward creating pain (barotrauma) |
|
|
What are the effects of colds on the Eustachian tube and sinuses |
Inflammation or excessive mucus build up with cause blockage resulting in unequal air pressure and therefore pain |
|
|
Define spacial orientation |
Ability to correctly interpret aircraft attitude, altitude and airspeed in relation to the earth or a point of reference |
|
|
What causes somatogravic illusion |
The otolith not being able to distinguish between and acceleration/deceleration and a head or body tilt backwards/forwards |
|
|
What is the sensation felt during a somatogravic illusion |
A fast acceleration, by the likes of a go around, will result in a feeling of a steep climb possibly causing the pilot to pitch down rapidly into the ground |
|
|
What is the requirement for a somatogyral illusion |
Pilot affected by unaware that they have the leans |
|
|
Describe somatogyral illusion |
Pilot experiencing the leans resulting in a spiral dive. Increased speed causes pilot to pull back on column as he believes he is in a wings level dive thus increasing the intensity of the spiral dive |
|
|
Name number 8 and it’s use |
Otolith organs - measure linear acceleration (longitudinal and latitudinal) |
|
|
The graveyard spiral is a name given to what illusion |
Somatogyral illusion |
|
|
Describe the cross coupled turning illusion |
Head movement during prolonged bank (bank no longer felt by semicircular canals) causing immediate vertigo. The pilot would attempt to counter this resulting in a spin or stall leading to a crash |
|
|
Name number 9 and what the content can be found in it |
Middle ear - filled with air |
|
|
Name number 10 |
Outer ear |
|
|
Name number 11 and the content that is found within |
Inner ear - filled with fluid |
|
|
Hearing occurs between what parts of the ear |
Eardrum to cochlea |
|
|
What parts of the ear are responsible for balance/acceleration |
semi-circirular canals and otolith organs (vestibular sac/tube) |
|
|
At what point does sound become uncomfortable |
120 dB |
|
|
At what point does sound become painful |
130 dB |
|
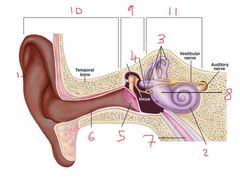
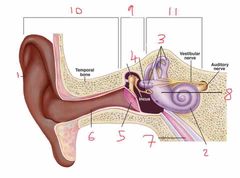
Name number 6 and it’s use |
Auditory canal |
|
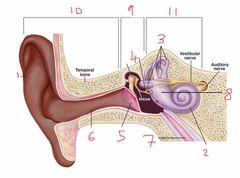
Name number 7 and it’s use |
Eustachian tube - connects middle ear to nasal passage |
|
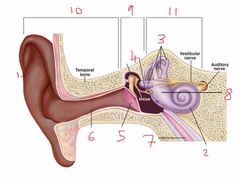
Name number 8 and it’s use |
Otolith organs - measure linear acceleration (longitudinal and latitudinal) |
|
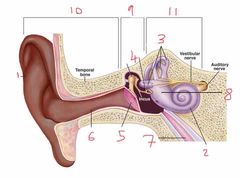
Name number 9 and what the content can be found in it |
Middle ear - filled with air |
|
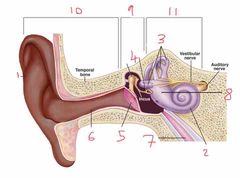
Name number 10 |
Outer ear |
|
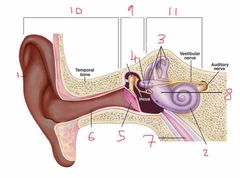
Name number 11 and the content that is found within |
Inner ear - filled with fluid |
|
|
What percentage of spatial orientation does the visual system account for |
70% |
|
|
Other than the vestibular system and visual system, what other parts in the body generate positional information |
Nerve endings known as proprioceptors |
|
|
How is “the leans” caused |
Slow roll not picked up by fluid in the ear. There becomes a strong feeling of being at one attitude while instruments display another |
|
|
Describe sub threshold stimulation |
Slow lean not picked up by semicircular canals that is eventually noticed on the instruments and corrected. By doing so there becomes a strong sensation of a roll in the same direction leading to “the leans” |
|
|
What are the four methods for protection of hearing |
Earmuffs Earplugs Communications headset Earmuff/helmet combinations (airforce helmets) |
|
|
Name number 7 and it’s use |
Eustachian tube - connects middle ear to nasal passage |
|
|
What is the name given to age induced hearing loss |
Presbycusis |
|
|
What are the symptoms of presbycusis |
Difficulty hearing people around you Frequently asking people to repeat themselves Frustration Certain sounds seem loud Problems hearing in noisy areas Problems with certain sounds such as “s” and “th” Difficulty hearing higher pitch Tinnitus (ringing in ears) |
|
|
When does the Eustachian tube open and why |
When we yawn, swallow or chew - allows air to flow into the middle ear and mucus to flow out keeping air pressure equal |
|
|
If the Eustachian tube becomes blocked on descent describe what happens |
Air pressure on the outer ear become greater than that in the middle ear thus pushing the ear drum inward creating pain (barotrauma) |
|
|
What are the effects of colds on the Eustachian tube and sinuses |
Inflammation or excessive mucus build up with cause blockage resulting in unequal air pressure and therefore pain |
|
|
Define spacial orientation |
Ability to correctly interpret aircraft attitude, altitude and airspeed in relation to the earth or a point of reference |
|
|
What causes somatogravic illusion |
The otolith not being able to distinguish between and acceleration/deceleration and a head or body tilt backwards/forwards |
|
|
What is the sensation felt during a somatogravic illusion |
A fast acceleration, by the likes of a go around, will result in a feeling of a steep climb possibly causing the pilot to pitch down rapidly into the ground |
|
|
What is the requirement for a somatogyral illusion |
Pilot affected by unaware that they have the leans |
|
|
Describe somatogyral illusion |
Pilot experiencing the leans resulting in a spiral dive. Increased speed causes pilot to pull back on column as he believes he is in a wings level dive thus increasing the intensity of the spiral dive |
|
|
Name number 8 and it’s use |
Otolith organs - measure linear acceleration (longitudinal and latitudinal) |
|
|
The graveyard spiral is a name given to what illusion |
Somatogyral illusion |
|
|
Describe the cross coupled turning illusion |
Head movement during prolonged bank (bank no longer felt by semicircular canals) causing immediate vertigo. The pilot would attempt to counter this resulting in a spin or stall leading to a crash |
|
|
The cross coupled turning effect is also known as what |
The coriolis effect |
|
|
Explain pressure vertigo |
Blocked Eustachian tube on descent results in higher pressure outside the ear that may cause perforation of the ear drum if great enough. This will result in nausea and vertigo |
|
|
What are the four methods to prevent disorientation |
Do not fly by the “seat of your pants” Transition to instruments early at night or reduced visibility Maintain instrument and night proficiency Trust your instruments |
|
|
State the five stages and times within the see and avoid method |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
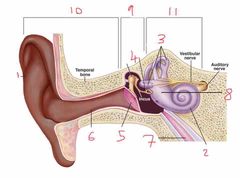
Name number 9 and what the content can be found in it |
Middle ear - filled with air |
|
|
Name number 10 |
Outer ear |
|
|
Name number 11 and the content that is found within |
Inner ear - filled with fluid |
|
|
Hearing occurs between what parts of the ear |
Eardrum to cochlea |
|
|
What parts of the ear are responsible for balance/acceleration |
semi-circirular canals and otolith organs (vestibular sac/tube) |
|
|
At what point does sound become uncomfortable |
120 dB |
|
|
State the five stages and times within the see and avoid method |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
How long can eyes be exposed to a bright light source before night vision becomes impaired |
1 second or less |
|
|
What are the four methods for maintaining dark adaption |
Dim instruments Avoid inhaling CO Get enough vitamin A Avoid exposure to bright lights |

