![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Types of pinch
|
1. pulp pinch: thumb + index/middle finger - pin
2. lateral pinch: thumb and lateral side of index finger - key 3. tripod pinch: thumb + middle and index finger - pen 4. 5 finger pinch: thumb + forefingers, no contact w/ palm - probe 5. diagonal volar: thumb + across fingers on diagonal - screw driver 6. transverse volar: thumb and fingers wrapped around - hammer 7. spherical: object surrounded by thumb and 4 fingers - ball 8. extensor grip: held on palm w/ fingers and thumb spread – tray |

|
|
|
Grasping – a 3 phase process
|
1. Transport: moving the hand into the optimal position to grasp
2. Grasp: object is held in the hand 3. Object manipulation: object is used as intended, e.g. moving it to another locaiton |
|
|
|
Development of hand function:
sensory information is used to refine grasp stability |
1. tactile information: size, shape, surface texture, firmness of object
2. visual information: to guide the hand to the object |
|
|
|
Development of writing
|
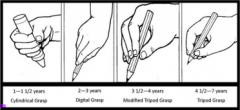
↑ vision, ↑ time to reach, ↑ tactile information before grasping
TO ↓ vision, ↓ time to reach, ↓ tactile information before grasping |
|
|
|
Assessment
1. outcome measure 2. physical exam |
- Assess the impact of the disorder. Note that compensatory strategies may “hide” issues
- Consider personal goals of treatment - Assess grips and relate to aggravating factors - Assess upper limb joints and structures, and the cervical spine - Assess sensation |
|
|
|
Assessment - Physical examination
|
1. Observation
2. Palpation 3. ROM 4. intrinsic M anatomy - dorsal interossei, palmar interossei, lumbricals 5. Strength - MMT, specific nerve 6. Sensation - detection, discrimination |
|
|
|
Assessment
1. Observation press H |
1. Observation: wounds, scars, laceration
skin condition oedema deformity and wasting |
|
|
|
Assessment
2. Palpation |
2. Palpation: temp, sweating
scar tethering hypersensitivity M spasm tenderness |
|
|
|
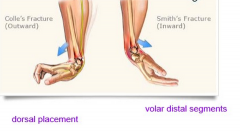
Distal Radial #
1. Population 2. contributing factor for # 3. MOI: 4. Classification (press H) |
1. Population:
-young patients high energy injuries -older patients low energy, falls 2. contributing factor for #: osteoporosis, ↑ incidence in falls in women 3. MOI: FOOSH, axial compression, wrist E or F 4. Classification: -colles, smith, bartons # |
|
|
|
Indications for non-operative Mx for DR#
|

|
|
|
|
Indications for Surgical Mx for DR#
|

|
|
|
|
Physiotherapy Mx for DR#
|
1. Management of oedema and pain
2. Maintain active motion of unaffected proximal joints 3. Maintain motion of fingers and thumb 4. Increase motion of wrist and forearm 5. Increase strength of wrist and hand musculature |
|
|
|
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS)
1. Definition 2. Risk factors press H for picture |
1. Definition
A systemic disorder, involving PNS & CNS Type 1: without peripheral nerve injury Type 2: with peripheral nerve injury 2. Risk factors » Tight cast » Median Nerve compression » Injury to Median and Ulna nerves » Over distraction to reduce fracture |
|
|
|
CRPS
3. Rx for adults and kids |
3. Rx:
Role of physiotherapy - Early diagnosis Treatment in adults - Graded motor imagery (mirror imagery) + medical management ↓ pain for 6/12 - Pain management (connective tissue massage, coping skills, relaxation, compensatory skills) + medical management Treatment in children - May consist of hydrotherapy, strengthening, stretching, proprioceptive exercise, aerobic exercise, weightbearing, desensitisation |
|
|
|
Flexor Tendon injuries
1. definition 2. tendon healing 3. post op dependent on 4. Mx |
1. definition
-Laceration to flexor tendon -nerve injury 2. tendon healing 1-10 days post op: Inflammatory phase, Decrease in strength of repair 3-6 weeks post op Strength increases with the formation of granulation tissue 7-12 weeks post op Remodelling phase, Gains full strength at 12 weeks post op 3. post op dependent on -Mechanism of injury: clean, jagged -Surgeon’s preference -Type and position of repair (zone) -Condition of the tendon: amount of repair -Involvement of other issues, e.g. digital nerve, artery -Patient 4. Mx -Surgery –6/52: protection in splint, no use of the hand -6-8/52: light functional use of the hand, use splint in risky situations -8-12/52: no protection required, gradually progress to full use |
|
|
|
Extensor tendon injuries
press H for picture |
» Zone 1 & 2: Mallet finger
» Zone 3 & 4 central slip – Boutonneire deformity » Zone 5: level of MCP jts |
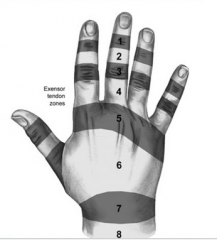
|
|
|
Mallet finger
1. definition 2. Mx |
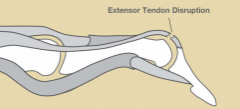
1. definition
- Injured through passive DIP flexion with resisted extension - May involve a fracture 2. Mx - Immobilise DIP in 5-15° hyperextension with PIP jt free for 6-8/52 - ROM of unaffected joints - At 8/52 commence gentle DIP F |
|
|
|
Radial wrist pain
|
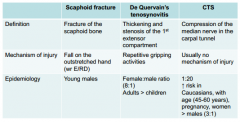
-scaphoid #
-de quervains disease -CTS |
|
|
|
de quervains DDx
scaphoid # DDx |
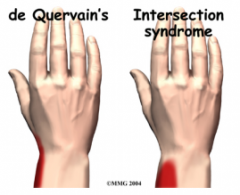
1. 1 CMC jt OA
2. Intersection syndrome 3. Wartenburg’s Syndrome 1. distal radius # 2. FCR/ECR strain 3. scapholunate dissociation |
|
|
|
test scaphoid # with which tests
|
- Tenderness in the anatomical snuff box
(90% sensitivity, 40% specificity) - Pain with scaphoid compression test (70% sensitivity, 22% specificity) |
|
|
|
scaphoid #
Rx *2 Mx |
1. Closed treatment
» Stable, non-displaced # of waist or distal pole » Immobilised in POP until radiological evidence of union (usually 12/52) 2. Surgical treatment » Proximal pole fractures, unstable fractures, fracture dislocations » ORIF +/- bone graft » While in POP: control oedema, maintain motion of uninvolved joints » Post POP removal: wrist & thumb active motion, progress to resistance exercises » Use wrist splint for protection |
|
|
|
de quervains disease
Mx |
Rest – immobilise in a rigid splint day & night
- ADL / work modification - When pain free » Gentle wrist / thumb ROM exercises |
|
|
|
CTS
Mx |
- Work / ADL modification: avoid
prolonged / repeated gripping - Manage inflammatory conditions and obesity if present » Night splints » Oral corticosteriods » Surgery |
|

