![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Ligmentum teres?
Iliofemoral? Pubofemoral? Ischiofemoral? Transverse acetabular lig |
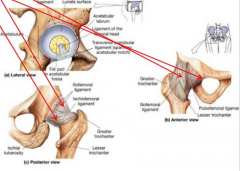
Ligmentum teres - limits F, ER, Add
Iliofemoral - limits E, ER, Add Pubofemoral - limits E, ER, Abd Ischiofemoral - limits E, IR, Abd |
|
|
|
Bursea in the Hip
|
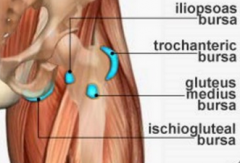
1. greater trochanteric bursa
2. deep trochanteric bursa 3. iliopsoas bursa 4. gluteus medius bursa 5. ischiogluteal bursa 6. ischial tuberosity bursa |
|
|
|
muscles change action due to the joint position and angle of fibres:
-piriformis -gluteal medius |
-ER in <60 hip F and IR in >60 hip F
-hip Abd, ER in 30 hip F and IR in >30 hip F |
|
|
|
Femoral Triangle
|
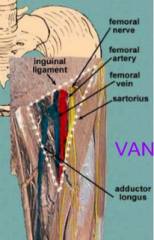
base - inguinal lig
lat border - sartorius med border - add longus inside - femoral VAN |
|
|
|
hip OA
risk factors indications Mx |
-obesity, dysplasia, age
-pain, stiffness, limited ROM in 3 planes, >50 y/o indicate high chance of hip OA :- 1. multidisciplinary team approach 2. patient edu and self-Mx (age, sex, activity modification, exercise, weight reduction and methods of unloading arthritic joint) 3. medical Mx (meds, joint injections - hyaluronic acid, surgery) 4. physiotherapy (manual therapy, exercise therapy) |
|
|
|
hip dysplasia or instability in infants
|
limited hip Abd in infants can be useful in identifying hip dysplasia or instability
|
|
|
|
Muscle Length tests
|
1. thomas test - iliopsoas, rec fem, TFL, Abd
2. prone knee bend - rec fem 3. obers - TFL 4. straight leg raise - hamstrings 5. adductors |
|
|
|
Hip Pathology
|
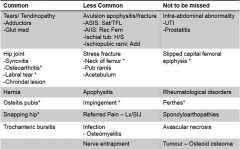
|
|
|
|
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
-common age and sex -Salter-Harris type -symptoms -can be influenced by? -key predisposing factors -Rx |
-children 12-15y/o and > in overweight boys
-type 1 fracture -wadding gait, loss of hip range, ER foot and pain in knee/groin/hip -influenced by endocrine disorders, obesity, femoral or acetabular retroversion and coxa profundus -adolescent growth spurt and obesity -orthopaetic surgery and failure to treatment may lead to avascular necrosis AVN |
|
|
|
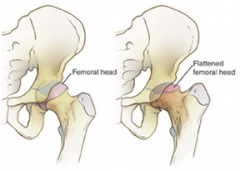
Perths' Disease
-common age and sex -description -possible factors -S+S -Mx |
-kids 4-10 and > males
-idiopathic osteochrondrosis affecting femoral head - vascular interruption -heredity, trauma, endocrine, inflammatory and nutritional -antalgic gait, low grade pain in thigh/groin/knee and limited Abd, IR -rest, maintenance of range, brace, possibly surgery -OA may proceed due to irregularity of joint |
|
|
|
Stress #
-location most common -sex, age, population -symptoms -imaging -conservative Mx |
-femoral neck, femoral shaft less common
-females, endurance, adolescents, army recuits -pain with WB activities, repetitive loading -bone scan, XR, MRI -cease WB activity, proprioceptive and motor control training, slow progression back into sport with monitoring of site, stabilisation surgery |
|
|
|
Labral Tear
-most common -Hx of injury -S+S -further problems -which test test to use -Imaging -conservation Mx |
-intra-articular hip injury in athletic populations
-single or repetitive trauma - rot and flexion, FAI can increase chance of labral tear -clicking, locking, catching, giving way and pain located ant/posteriorly or groin -vascularisation can hinder healing and lead to OA -FABER -MRI most sensitive and arthroscope is gold standard -deloading, avoidance of repetitive mvts, lumbopelvic proprioceptive training and motor pattern correction of deep stabilising muscles -possibly surgery |
|
|
|
Femoroacetabular Impingment (FAI)
-3 types -common position for impingment |
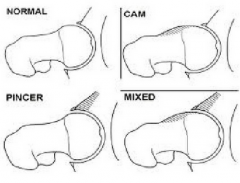
-cam: increased bone formation at the anterior surface of femur - decreased femoral head-neck offset
pincer: bony growth at acetabulum generally anterior mixed: both cam and pincer bony changes are presented -F + IR + Add |
|
|
|
Osteitis pubis
-commonly known as: -causes -multiple pathologies -Ax -imaging -Mx |
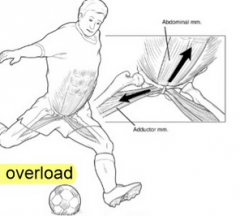
-sportsman's groin
-repetitive mircotrauma, training overload -add tendonitis, pubic bone edema/stress reaction/periostitis pubis -+ve squeeze test -XR, bone scan, MRI -1. lumbopelvic and hip stabiliser motor control - decrease hip F/IR 2. optimal length and strength - Add weakness 3. pain free exercises surgery, botox |
|
|
|
Snapping Hip
-caused from -common age, sex -associated with activity -symptom -Mx |
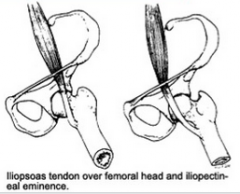
-iliopsoas "snaps" over the iliopectineal eminence
-young females -repetitive hip F -deep clunk when bringing hip from F to E - noise can be modified if put pressure over the tendon -improving hip extension, length of iliopsoas, hip rot strength |
|
|
|
Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome (GTPS)
-also referred to as: -pain where -risk factor -GTPS vs OA |
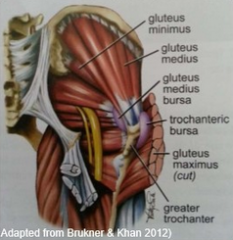
-tendinopathies of the gluteal tendons and bursa
-lateral hip area: glut med/min tendinophy glut med/min tears trochanteric bursitis -lower neck shaft angle -lateral pain on palpation, no difficulty in putting on shoes, reproduction of pain with FABER |
|

