![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the boundaries of the posterior cervical triangle?
|
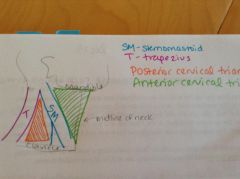
Base - middle of the clavicle
Posterior boundary - trapezius Anterior boundary - sternomastoid Also has a roof and a floor. |
|
|
What makes up the roof of the posterior cervical triangle?
|
The roof is formed by skin, superficial fascia (containing a portion of the platysma) and the investing fascia with spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
|
|
|
What is the investing fascia?
|
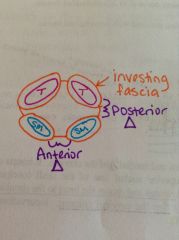
Fascia that surrounds the muscles that make up the boundaries of the anterior and posterior triangles (surrounds the trapezius and sternomastoid). Attached to the mandible, clavicle and manubrium.
|
|
|
What makes up the floor of the posterior cervical triangle?
|
-Splenius capitis
-Levator scapulae -Posterior scalene -Middle scalene -Anterior scalene |
|
|
What is the function of the scalene muscles? Where do they attach?
|

They are accessory respiratory muscles that elevate the upper ribs, increasing the size of the thoracic cage while breathing.
Posterior scalene attaches to rib 2. Middle and anterior scalene attach to rib 1. |
|
|
What are the contents of the interscalene triangle?
|
-subclavian a.
-3 trunks of the brachial plexus -scalene muscles |
|
|
Sternomastoid
|
O: maubrium and medial 1/3 of clavicle
I: mastoid process and laterla 1/2 of the superior nuchal line Inv: spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) A: one contracts-rotates and draws the head to the shoulder, both contract-flex the cervical column |
|
|
What are the contents of the posterior cervical triangle?
|
-Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
-Omohyoid muscle -External jugular v. -Axillary v. -Right and left subclavian a. -Occipital a. -Brachial plexus -Lesser occipital n. -Great auricular n. -Transverse cervical n. -Supraclavicular n. -Lymph nodes |
|
|
Describe the spinal accessory nerve.
|
CN XI, has two roots. The cranial root and spinal root.
Cranial root is accessory to the vagus n. (CN X) b/c it provides part of its motor component. Spinal root is joined by VPR of C2 and supplies sternomastoid, and joined by VPR of C3 and supplies the trapezius. |
|
|
Omohyoid
|
O: medial lip of the suprascapular notch
I: lower border of the body of the hyoid Inv: ansa cervicalis (C2 and C3) which is the motor part of the cervical plexus A: steadies the hyoid, depresses and retracts the hyoid and larynx |
|
|
Describe the external jugular v.
|
Lies superficial to the sternomastoid. Is a tributary to the subclavian v. It has tributaries of its own, the retromandibular, posterior auricular, transverse cervical, suprascapular, and anterior jugular veins.
|
|
|
Describe the axillary v.
|
Continues as the subclavian v where it crosses the lateral border of the first rib. Subclavian passes anterior to 1st rib and anterior scalene muscle to join the internal jugular v., this joined part of the vein is called the brachiocephalic v.
|
|
|
What is the brachiocephalic v.?
|
Comes off the subclavian v. where it meets with the internal jugular v.
|
|
|
Describe the subclavian arteries.
|
Right - branch of the brachiocephalic trunk
Left - direct branch of the aortic arch Both pass posterior to the anterior scalene which defines their 3 parts. |
|
|
What are the 3 parts of the subclavian arteries?
|
1st - lies medial to anterior scalene, branches into the vertebral and internal thoracic arteries, thyrocervical and costocervical trunk
2nd - passes posterior to the anterior scalene 3rd - lies on the upper surface of the 1st rib, producing a groove on the bone, has no named branches |
|
|
Describe the occipital a.
|
Is a branch of the external carotid, runs deep to the sternomastoid, eventually crossing the uppper portion (apex) of the posterior cervical triangle on its way to the scalp in the occipital region.
|
|
|
Describe the brachial plexus.
|
Roots and trunks emerge b/t the anterior and middle scalene muscles and passes laterally into the axilla.
|
|
|
What is the cervical plexus?
|
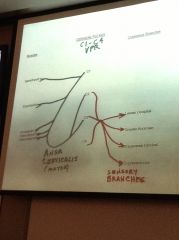
See drawing.
|
|
|
Describe the lesser occipital n.
|
C2 and C3, a cutaneous branch of the cervical plexus, ascends to the scalp posterior to the external ear
|
|
|
Describe the great auricular n.
|
C2 and C3, a cutaneous branch of the cervical plexus, passes anterior to the sternomastoid to supply the external ear, also gives branches to the skin of the mastoid, parotid and masseteric regions.
|
|
|
Describe the transverse cervical n.
|
C2 and C3, a cutaneous branch of the cervical plexus, travels anteriorly to innervate the skin of the anterior cervical triangle.
|
|
|
Describe the 3 suprclavicular nerves.
|
C3 and C4, cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus, descend in the neck to cross the clavicle and be distributed to the skin of the suprclavicular triangle, and the pectoral, deltoid and acromial regions.
|
|
|
What do the lymph nodes in the posterior cervical triangle drain from/to?
|
They drain the occipital scalp and back of the neck, they eventually empty into the jugular lymph trunk.
|

