![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the speed of the recovery depend on? |
-Breed -Existing illness - renal, hepatic, respiratory,cardiac -Temperature -Duration & type of anaesthesia -Route of drug administration |
|
|
What might be needed in the recovery area? |
-Heat sources -Laryngoscope / ET tubes -Suction -O2 therapy -Temperature probe -Stethoscope |
|
|
What are the considerations for early extubation? |
-Risks inhalation of FBs -Best for cats -Not for brachycephalic dogs -Allow pollution of atmosphere |
|
|
What are the considerations for late extubation? |
-Airway protected until gag response returns -Best for potential airway obstruction -Risk of laryngeal spasm in cats -Less pollution of atmosphere -Prolonged O2 breathing |
|
|
What does pale mm's indicate? |
-Sympathetic vasoconstriction -Inadequate circulating volume -Haemorrhage |
|
|
What do cyanosis (blue) mm's indicate? |
-Poor oxygenation -Poor circulation -Peripheral vasoconstriction |
|
|
What do red mm's indicate? |
-Toxaemia -Hypercapnia |
|
|
What are special procedures that need to be monitored carefully on recovery? |
-Ophthalmic procedures -Abdominal surgery -Thoracic surgery -Tracheostomy -Orthopaedic procedures -Myelography |
|
|
How can oxygen be supplemented? |
-flow - past
-Oxygen tent -Mask -Intranasal catheter |
|
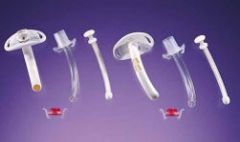
What is this piece of equipment? |
-Tacheotomy tubes |
|
|
What are some possible anaesthetic complications? |
-Cardiopulmonary arrest -Airway obstruction -Respiratory depression / arrest -Circulatory insufficiency -Hypothermia -(hyperthermia) |
|
|
What is cardiopulmonary arrest? |
-Most common cause is overdose of inhalation agent -If monitoring is adequate will spot the increasing anaesthetic depth -Respiratory changes occur before cardiac arrest -Electrical abnormalities will also will be evident |
|
|
What are the signs of impending arrest? |
-Changes of respiratory rate, depth & pattern -Changes in pulse quality & rhythm -Unexplained changes in GA depth -Abnormal ECG rhythms |
|
|
What are the signs of arrest? |
-No heart sounds or pulse palpable -No respiratory movements or " agonal" gasping - Cheyne Stokes breathing -Fixed & dilated pupils -Grey or cyanotic mms -Dry cornea with loss of reflexes -Arrhythmia on ECG |
|
|
What are the causes of cardiopulmonary arrest? |
-Anaesthetic overdose -Hypoxia & hypercapnia -Hyptotension - Dysrhythmias -Pre - existing heart disease -Vagal stimulation -Electrolyte imbalances -Hypothermia -Toxaemia |
|
|
What are the protocols for cardiopulmonary resuscitation? |
-Airway -Breathing -Circulation -Drugs -Electrical defibrillation -Follow up |
|
|
What drugs should be kept in the anaesthetic emergency box? |
-Adrenaline -Atropine -Lidocaine -Furosemide |
|
|
What are the signs of airway obstruction during or after anaesthesia? |
-Increased respiratory effort / noise -Paradoxical chest wall movement -No movement of reservoir bag -Cyanosis |
|
|
What actions need to be taken when airways are obstructed during or after anaesthesia? |
- Check ET tube -If not intubated, extend head & neck, use a mouth gag & check for obstructions. Intubate if necessary -If regurgitating / vomiting, lower head -Consider tracheostomy |
|
|
What should be done if there is no movement from the reservoir bag during respiratory depression / arrest? |
- Check the expiratory valve of the circuit is open |
|
|
What are the other causes for respiratory depression / arrest? |
-Anaethetic or opioid overdose -Chest wall movement inadequate -Respiratory movements unable to inflate lungs -Tachypnoea |
|
|
What are the signs of respiratory depression / arrest? |
-Reduced minute volume -Increased respiratory rate -Cyanosis -(Inflated chest, full reservoir bag, odd whistling) |
|
|
What actions are needed when patient in respiratory depression / arrest? |
-Remove underlying cause -Assess anaesthetic depth & pain levels -Supply 100% O2 -Use IPPV |
|
|
What are the signs of circulatory insufficiency? |
-Weak peripheral pulses - Pale mms -Increased CRT -Low measured BP -Increased HR -Poor urinary output -Diminished bleeding |
|
|
What action need to be taken for circulatory insufficiency? |
-Assess depth of anaesthesia -Rapid iv fluid infusion -Reposition patient if possible -Control haemorrhage -Inotropic drugs
|
|
|
What are the causes of hypothermia under GA? |
-Shivering is prevented under GA -Anaesthetic agents may cause peripheral vasodilation -Heat generated by skeletal activity has stopped -Visceral surfaces are exposed in abdominal surgery -Inspired anaesthetic gases are cold & dry |
|
|
How can hypothermia be prevented under GA? |
-Choice of anaesthetic agents -Thermovent -Warming aids -Monitoring iv fluids -Monitoring -Keep operating theatre warm |

