![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Capital Asset Pricing Model
CAPM |
RFR + b (market - RFR)
CAPM can be also considered a special case of APT where there is only one risk factor and this |
|
|
Standard deviation of investment that
combines risky with risk-free? |

|
|
|
Market Model Predicts
|
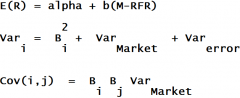
|
|
|
Strategies
|
THINK: BICCCO
Basis Index Curve Correlation Capital Structure Options |
|
|
Law of one price
|
A good should have the same real price in all countries
|
|
|
beta =
|
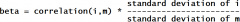
|
|
|
Active Return
|
portfolio - benchmark
|
|
|
Sources of Active Return
|
1. Factor tilts
2. Asset Allocation |
|
|
Active Risk
|
Standard deviation of active return over time
Standard deviation of portfolio - benchmark |
|
|
Information Ratio
|
Active Return........Portfolio - Benchmark...
--------------- = --------------------------- .Active Risk......standard deviation of p - b |
|
|
FCRP
|
Foreign Currency Risk Premium
|
|
|
RFR has what standard deviation/variance?
and covariance with other assets? |
All Zero
|
|
|
Expected Return on 2 asset portfolio
|
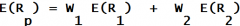
|
|
|
Expected Return Two Assets one being RFR
|
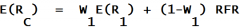
|
|
|
Variance of two assets
|

|
|
|
Variance of equally-weighted portfolios
|

|
|
|
Lower correlation leads to what diversification?
|
Greater
|
|
|
alpha
|
Forecast - CAPM
|
|
|
Foreign Currency Risk Premium
|

|
|
|
2 Ways to calc domestic currency (DC) return to
holding foreign bond |
1. DC return = FC interest + FC appreciation
2. DC return = DC interest + Foreign Currency Risk Premium (FCRP) |
|
|
Money Demand Model
|
Inc real econ activity leads to inc demand domestic currency,
currency appreciates, stock prices up Dec econ activity causes currency depreciation, stock prices down |
|
|
Traditional Model
|
Decrease currency lead to strong economy in
long run |
|
|
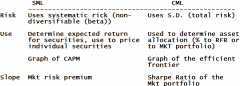
Security Market Line (SML)
|
Expected return vs. Beta
Slope is the market risk premium (Mkt-RFR) Intercept is the RFR Inc expected inflation or RFR moves line up |
|
|
Capital Market Line (CML)
|
Expected return vs. variance
This is a line. Market portfolio (M) is the tagency portfolio of the RFR line to the efficient frontier. At RFR 100% lending (T-bills), at M 100% funds in tagency portfolio, above M on RFR line borrowing since more than 100% invested. Slope = sharpe ratio of market portfolio "Best combination of risk reward" |
|
|
SML vs CML
Security Market Line vs. Capital Market Line |
|
|
|
Capital Market Line (CML) equation
|

|
|
|
Capital Allocation Line (CAL) equation
|
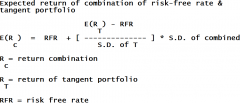
|
|
|
Minimum-Variance Frontier (MVF)
|
Expected Return vs. Variance
Set of portfolios with lowest variance at expected return |
|
|
Capital Allocation Line (CAL)
|
Expected return vs. variance
CAL is the line from the risk-free rate (RFT) to the point of tagency on the efficient frontier "Best risk portfolio" |
|
|
Capital Allocation Line (CAL) equation
|

|
|
|
Differences between CAL and CML
|
1. Only one CML - the tagency is the market portfolio
2. Unlimited CALs, each developed unique per investor 3. Tangency for CAL can differ accros investors depending on expectations. 4. CML is a special case of CAL. CML is the "Market Portfolio" |
|
|
Market Model
|
the regression mode used to estimate beta
Return = alpha + (beta)(return on market) + error |
|
|
Multifactor Models. Give 3 types:
|
Market Model is 1 factor model. Assests explained by return of
market porfolio 1. Macroeconomic 2. Fundamental 3. Statistical |
|
|
International CAPM
ICAPM |

|
|
|
In ICAPM R sub f
is |
domestic currency risk free rate
|
|
|
Market Price of Risk
|
= Sharpe ratio of market portfolio
= Slope of CML (Capital Market Line) = Market risk premium per unit of market risk |
|
|
If CAPM assumptions don't hold
|
1. Market Porfolio not on efficient frontier
2. non-linear relation expected return and beta 3. Not allowing shorts 4. Risk adverse investor may hold diff then more risk-adverse investor |
|
|
Portfolio Management Planning Process
|
Analyse
1. Risk/Return 2. Constraints: Liquidity, time horizion, legal/regulation, taxes, unique circum 3. Develop IPS: purpose, duties, objectives, modify policy, rebalancing guidlines 4. Determine Strategy: Passive/Active 5. Select Asset Allocations: Weight based on capital market expectations |

