![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Demography |

The study of population statistics E.g. : births, deaths, income, education, disease, etc. |
|
|
Crude Birth Rate |
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in a society |
|
|
Crude Death Rate |
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in a society |
|
|
Overpopulation |
When the number of people in an area exceed the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living |
|
|
Carrying Capacity |
The largest number of people that an environment can support |
|
|
Ecumene |
An area where people can live E.g. : water, food, flat terrain |
|
|
Underpopulation |
When there are too few people in an area to sufficiently develop its resources and improve its peoples quality of life E.g. some places around the world like Africa |
|
|
Arithmetic Density |
The total number of people divided by the total number of land area |
|
|
Physiological Density |
The total number of people per unit of arable (farmable) land. More helpful than arithmetic density |
|
|
Demographic transition model |
Stage 1= low growth stage 2= high growth stage 3= moderate growth stage 4= low growth A country moves from high birth and death rates through time |
|
|
Infant mortality rate |
The number of babies per 1000 births, who die before their first birthday |
|
|
Total fertility rate |
The average number of babies that an average women delivers during her childbearing years |
|
|
Zero population Growth |
When crude birth rates equals crude death rate |
|
|
Population Pyramid |
A model used in population geography to show the age and sex distribution of a particular population |
|
|
Population projection |
An estimate of future population growth based on current data trends |
|
|
Dependency Ratio |
The number of people aged 0-14 and 65+ who cannot work and are dependent on the workforce for support |
|
|
Doubling time |
The number of years that it takes for a country to double it's population |
|
|
J-curve |
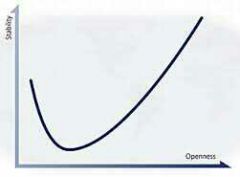
Places countries on a scale based on their openness and stability |
|
|
Agricultural Density
|
number of people living in rural areas per unit of agricultural land
|
|
|
Epidemiological Transition
|
portion of earths surface occupied by permanent human settlement
|
|
|
Epidemiology
|
distribution and control of diseases that are prevalent among population
|
|
|
Malthusian Theory (Thomas Malthus)
|
population was grown rapidly, while food production not.
|
|
|
Medical Revolution
|
medical technology invented in europe and north america that is diffused to poorer countries in latin america, ask and arrived. improved medical practices and technology
|
|
|
Natural Increase Rate (nic)
|
crude death rate subtracted from the crude birth rate
|
|
|
Non Ecumene
|
number of people in an area exceeds the capacity if the environment to support life
|
|
|
Pandemic
|
number of persons per agricultural land
|
|
|
Sex Ratio
|
number of babies born per reproductive age woman
|
|
|
Life Expectancy
|
the average period that a person may expect to live.
|
|
|
Standard of Living |
the degree of wealth and material comfort available to a person or community.
|
|
|
Pro-Natalist (Expansive) Policy |
the policy or practice of encouraging the bearing of children, especially government support of a higher birthrate.
|
|
|
Anti-Natalist (Restrictive) Policy |
position that assigns a negative value to birth or claims that one should not reproduce. It stands in opposition to natalism.
|
|
|
Boserup Theory |
agricultural methods depend on the size of the population.
|
|
|
Contraception |
the deliberate use of artificial methods or other techniques to prevent pregnancy as a consequence of sexual intercourse.
|

