![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
POM II - Unit 2 - Lec 5 : Noninvasic Cardiac Imaging
|
POM II - Unit 2 - Lec 5 : Noninvasic Cardiac Imaging
|
|
|
1) 5 Non-Invasive Imaging Modalities to detect CAD?
2) 2 Specific types CT? 3) 1 Specific Type ECG? 4) 2 Specific types echo? 5) 1 Specific types MRI? 6) 2 Types SPECT? |
1) CT
ECG Echo MRI SPECT 2) Electron Beam & Multislice 3) Exercise Stress ECG? 4) Exercise Echo & Pharm Stress Echo 5) Cardiac MRI 6) Exercise SPECT perfusion & Pharmacological Stress SPECT Perfusion |
|
|
What is echocardiography?
|
A test that uses ultrasound to examine the heart
|
|

Know this chart on Echocardiography
|
Know this chart on Echocardiography
|
|
|
What is the idea behind cardiac stress testing?
What stress testing prognostic factors make someone high risk? |
Inc Heart Rate -->
Inc Myocardial Work & Oxygen Consumption --> Increase coronary flow --> Monitor electrical changes on EKG & Monitor echo for wall motion and ejection fraction & Monitor Nuclear for old MI or poor echo images Drop in EF, Multiple wall motion abnorms, inc end-systolic volume |
|
|
1) Increasing the heart rate can be done using treadmill, bicycle r what type of drug?
|
1) Dobutamine
|
|
|
Read Through this List of Absolute Contraindications for Cardiac Stress Testing
Acute MI w/in 2 days High Risk Unstable Angina UnCTL'ed, Sx-matic arrhythmia Myocarditis Sx-matic CHF Pericarditis Sx-matic aortic stenosis Aortic Dissection PE Pulmonary Infarction |
Read Through this List of Absolute Contraindications for Cardiac Stress Testing
Acute MI w/in 2 days High Risk Unstable Angina UnCTL'ed, Sx-matic arrhythmia Myocarditis Sx-matic CHF Pericarditis Sx-matic aortic stenosis Aortic Dissection PE Pulmonary Infarction |
|
|
Relative CI to Stress Testing:
LCA Stenosis Moderate stenotic Valvular Dz Electrolyte Abnorms Severe Arterial HTN Tachyarrthythmias Bradyarrhythmias Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy LV Outflow Tract Obstruction Mental / Physical probs --> can't exercise High-Degree AV Block |
Relative CI to Stress Testing:
LCA Stenosis Moderate stenotic Valvular Dz Electrolyte Abnorms Severe Arterial HTN Tachyarrthythmias Bradyarrhythmias Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy LV Outflow Tract Obstruction Mental / Physical probs --> can't exercise High-Degree AV Block |
|
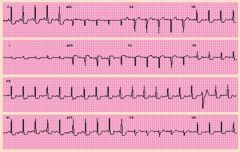
What do you see on this EKG on the bottom left?
|
ST Segment Depression indicating ischemia on exercise
|
|
|
Stress Test ECG Results That Make Someone High Risk:
Can't achieve >6 mets of workload Can't get systolic BP > 120 q/ exercise Can't get diastolic BP to decrease > 10 mmHg w/ exercise ST depression > 3.0 mm @ low workload ST depression > 1.0 lasting > 5 min into recovery period Exercise induced ST elevation in leads WITHOUT Q-waves Limiting Angina V-Tach |
Stress Test ECG Results That Make Someone High Risk:
Can't achieve >6 mets of workload Can't get systolic BP > 120 q/ exercise Can't get diastolic BP to decrease > 10 mmHg w/ exercise ST depression > 3.0 mm @ low workload ST depression > 1.0 lasting > 5 min into recovery period Exercise induced ST elevation in leads WITHOUT Q-waves Limiting Angina V-Tach |
|
|
Treadmill Stress Echo
Ischemia can be detected on TREADMILL Stress Echo as what 3 things? This standard is used when doing TREADMILL stress echocardiography to determine cardiac fnctn using the indicators of: progressive inc in HR Myocardial Work Oxygen Consumption |
Post exercise LV wall motion abnorm
Decreased Ejection Fraction Inc End-Diastolic Volume Bruce Protocol |
|
|
Dobutamine Stress Echo
3 FX of dobutamine that allow it to be used for a stress echo? |
Inc HR
Inc Myocardial Work Inc Oxygen Consumption |
|
|
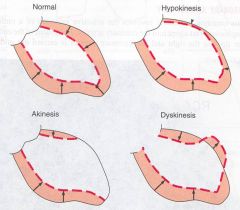
What are 2 types of myocardial wall abnormalities you look for when doing an echo?
|
Hypokinetic: Dec Mvt
Akinetic: No Mvt |
|
|
Nuclear Cardiology
What is the first type of Nuclear Cardiology? What 2 things does SPECT assess? "Gating" allows SPECT to assess what2 things? |
Gated SPECT
(Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) EF & Post-Stress Regional Wall Motion Ventricular wall motion End-Systolic & End-Diastolic Ventric Vols LV Ejection Fraction |
|
|
Nuclear Medicine
What are MC type of nuclear mediicne used to assess cardiac fnctn? MPS (TST) allows for assessment of what 6 aspects of Cardiac fnctn? An area of ischemia will initially have inc or dec uptake of the tracer? Infarction? When for both? Resting studies can provide info about what? |
Myocardial perfusion study (Thallium Stress Test)
Coronary Blood Flow Perfusion of LV Myocardium EF 3D-Reconstruction of Heart Differentiate Ischemia from MI Demonstrate Myocardial Cariability (If their's a "Hibernating Heart") Ischemia is Decreased reuptake of tracer WITH STRESS ONLY! Infarction is NO reuptake of tracer on REST & STRESS! Acute MIs |
|
|
CT
These are the uses of CT Listed: CORONARY CALCIFICATION SCORE!!!! Congenital Heart Dz Intracardiac Mass Pericardial Dz 64 slice CT for: Coronary Art Imaging |
CT
These are the uses of CT Listed: CORONARY CALCIFICATION SCORE!!!! Congenital Heart Dz Intracardiac Mass Pericardial Dz 64 slice CT for: Coronary Art Imaging |
|
|
Indications to use CT Listed
Chronic Chest Pain Syndrome Acute Chest Pain evluzation of Suspected Coronary Abnorms Assesment of complex congenital heart Dz New onset CHF to assess coronary etiology Assessment of cardiac mass Assessment of pericardial disease Assessment of pulmonary veins pre-ablation Assessment of coronary veins for biventricular pacemaker Assessment of coronary anatomy prior to repeat CABG Evaluation of aortic disease (dissection, aneurysm) Evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism |
Indications to use CT Listed
Chronic Chest Pain Syndrome Acute Chest Pain evluzation of Suspected Coronary Abnorms Assesment of complex congenital heart Dz New onset CHF to assess coronary etiology Assessment of cardiac mass Assessment of pericardial disease Assessment of pulmonary veins pre-ablation Assessment of coronary veins for biventricular pacemaker Assessment of coronary anatomy prior to repeat CABG Evaluation of aortic disease (dissection, aneurysm) Evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism |
|
|
The Framingham Risk Score is not always reliable. A better risk assesment would be what?
|
Coronary Artery Calcium Score using CT
|
|
|
MRI
Uses of MRI Listed: Congenital Heart Dz Infracardiac Masses Pericardial Dz Arrhmogenic RV Dysplasia Aortic Dz |
MRI
Uses of MRI Listed: Congenital Heart Dz Infracardiac Masses Pericardial Dz Arrhmogenic RV Dysplasia Aortic Dz |
|
|
Ustable hemodynamics post-MI would be assessed using what?
|
Echocardiography
|
|
|
Nuclear cardiology usually uses what 2 types of tracers?
|
Technitium & Thallium
|
|
|
Which non-invasive imaging modality is best for assesing myocardial perfusion?
|
Nuclear Medicine
|
|
|
Which nuclear medicine tracer detects resting ischemia (hibernating myocardium)?
|
Thallium
|
|
|
Which nuclear med modality shows acute imaging of MI?
|
Sestamibi
|
|
|
Stress Testing w/ Imaging (Echo vs. Nuclear Med)
1) Stress test w/ iaging is used for what 6 groups of ppl? 2) Stress testing with echo shows? 3) Stress testing w/ nuclear med is preferred when? |
1) women
ST-T Abnorms LVH LBBB Pacing Pre-Excitation 2) Structural Info 3) when echo images are poor AND when an old infarct is present |
|
|
4 Instances in whihc CT is used?
|
Congenital Heart Dz
Intracardiac Mass Pericardial z To get a coronary calcification score |
|
|
5 Instances in which MRI or MRA are used?
|
Congenital Heart Dz
Intracardiac Mass Pericardial Dz Arrhythmogenic RV Dysplasia MRA of Aorta |
|
|
PET will assess what 2 things?
|
Myocardial blood flow & Metabolism
|
|
|
POM II - Unit 2 - Lec 6 Invasive Diagnostic Cardiac Catherization
|
POM II - Unit 2 - Lec 6 Invasive Diagnostic Cardiac Catherization
|
|
|
Arterial Catherization is used to assess what side of what?
Venous Catherization is used to assess what? |
L Side of Heart, Aorta, Coronary Arts
R. side of Heart, Pulmonary Art |
|
|
Cardiac catherization allows for what 2 types of dx-ic modalities?
|
Pressure measurements & Contrast Imaging
|
|
|
The Following Statement Describes When You Should Use This Cardiac Diagnostic Modality?
“Only when there is a need to confirm the presence of a clinically suspected condition, define its anatomic and physiologic severity, and determine whether important associated conditions are present.” The MC indication for a cardiac caterization? See PPT for more Indications |
Cardiac Catherization
Coronary Artery Dz |
|
|
What are the absolute Contradindications for Cardiac Catherizations?
See PPT if you want the relative contraindications for Cardiac Catherization |
NONE
|
|
|
R. Heart Cardiac Catherization Shows:
LV dysfunction, valve dis, myopericardial dis, intracardiac shunts Balloon or multipurpose catheter SAO2 and pressure measurements in VC, RA, RV, PA and PCWP Cardiac Output by Fick (Q L/min=O2 consumption mL/Min/A-V O2 difference mL/L) or thermodilution Contrast imaging Pulmonary Vascular Resistance |
R. Heart Cardiac Catherization Shows:
LV dysfunction, valve dis, myopericardial dis, intracardiac shunts Balloon or multipurpose catheter SAO2 and pressure measurements in VC, RA, RV, PA and PCWP Cardiac Output by Fick (Q L/min=O2 consumption mL/Min/A-V O2 difference mL/L) or thermodilution Contrast imaging Pulmonary Vascular Resistance |
|
|
L. Heart Cardiac Catherization Shows:
LV dysfunction, CAD LV and aorta pressure measurements SAO2 in aorta Systemic vascular resistance Lt ventriculogram Coronary arteriography Aortography |
LV dysfunction, CAD
LV and aorta pressure measurements SAO2 in aorta Systemic vascular resistance Lt ventriculogram Coronary arteriography Aortography |
|
|
3 Rx steps must be taken BEFORE performing a cardiac cath?
INR should be what before doing a cardiac catherization? |
Aspirin, Versed IV, NO WARFARIN
<1.5 |
|
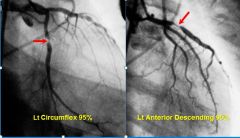
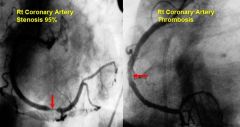
Some Images to Look At
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Last pic
|

