![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PCR is a technique for making millions of copies of specific target sequence of nucleotides (genom).
used as a diagnostic aim for certain diseases. |
?? What is P.C.R. ??
by YMH |
|
|
1- Template (sample dsDNA)
2- Primers (small pieces of ssDNA) 3- DNA polymerase 4- dNTPs (deoxyribo nucleoside triphosphate)- all the four types: ATP, TTP, GTP, CTP 5- Buffer & MgCl |
?? Requirements for P.C.R. ??
by YMH |
|
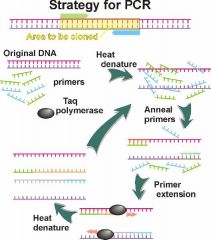
1st) Denaturation step: initial heating to about 94°C denatures the dsDNA (Template) into 2 single strands.
2nd) Annealing step: Transient cooling to 45-60°C allow the primers to bind (anneal) to their complementary sites on the sample DNA 3rd) Extension step: a change to 72°C permits the DNA polymerase enzyme to start DNA amplification from the 3 end of each primer. 4th) Temperature cycle is repeated, here the newly synthesized strands act as templates & so on.. |
?? What are the steps of PCR ??
by YMH |
|
|
1- Diagnosis of microbial diseases especially those that cannot be cultured or that grows very slowly
2- Detection of genes coding for virulence 3- Determination of antibiotic resistance 4- PCR products maybe used as DNA probe to identify unknown sequences |
?? Uses of P.C.R. ??
byYMH |

