![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Political Ideology |
ideology decribe the present offer a future-oriented vision and an action plan. - internally, externally contested -reflect historical conditions - ideologies and the enlightenment |
|
|
Classical Liberalism |
rooted individualist philosophies - protection of individual - property rights, rule of law - limited govt intervention -liberty -tolerance |
|
|
Negative Liberalism |
defined as an absence of interference -valorization of free markets |
|
|
Modern Liberalism |
5 PONT CRITIQUE OF MARKET FUNDAMENTALISM - equality of opportunity individual freedom and rights
|
|
|
Positive Liberty And Entitlements |
Freedom involves capacity to determine and achieve own goals - exercise conflict of freedom -entitlements and the safety network. |
|
|
Conservatism |
emerged as a response to liberalism and enlightenment - critique of abstract principles - tradition, modernism, duty, honor skepticism towards change |
|
|
EDMUND BURKE |
Natural Aristocracy and its consequences |
|
|
Modern Conservatism's |
Social and Cultural conservatism - signifigant moral component religion, tradition, family values "one nation" |
|
|
Neoconservatism |
mix classical liberalism with social/cultural conservatism - patriotism - state sovereignty against international institutions knowing friends for enemies. |
|
|
Bourgeoisie |
owners of means of population |
|
|
Proletariat |
workers who sell their labor power |
|
|
Petty Bourgeoise |
shop owners, artisans, tradesman |
|
|
Lumpenproletariat |
the unemployed, the unemployable, criminal element |
|
|
Class Interests |
objective position within economy and class system |
|
|
Capitalism and Alienation 4 Instances |
Alienation and the products of production Alienation and the labor process Alienation and or species being Alienation and each other |
|
|
State Origins |
from feudalism to capitalism URBANIZATION |
|
|
Critique of Marxism |
the state does oppose certainly businesses interest |
|
|
HEGEMONY |
dominant ideas and practices are turned into common sense. |
|
|
Law, Constitutions, and Federalism |
what legitimizes laws in democratic society? the state's monopoly on authority a mandate from the public the practice of checks and balances |
|
|
Rule of Law |
1- govt must follow the law that it makes. 2- No one is exempt from the operation of the law- it applies equally to all 3- general rights emerge out of particular |
|
|
CONSTITUTION |
a set of rules that authority establishes both structure and fundamental principles of the political regime |
|
|
law and the constitution |
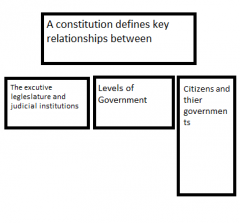
a constitution defines the key relationship between: |
|
|
The living tree doctrine |
allows for a constitution to change to change and evolve over time while still acknowledging its original intentions. |
|
|
originalism |
doctrine: views a constitutions meanings as fixed as of the time of enhancement. |
|
|
Federalism |
a political organization in which the activities of government are divided between regions and a central govt so that each level has areas of authority wherein it is supreme |
|
|
Unitary States |
maintain power in the centre and exercise it through a national govt, |
|
|
Federations |
dispute powers among 2 or more levels of govt. |
|
|
Consociationalism |
the brokering of power be entities in a state that have major diversions along ethnic, religious or linguistic lines. |
|
|
Asymmetrical Decentralization |
a hybrid version of federalism and consociationalism where some substrate units have greater power than others. |
|
|
branches of govt, |
Executive Judiciary Legislative |
|
|
Legislature |
the law making of a political unit (province) where in legislation (laws) presented debated and voted on. |
|
|
FUNCTIONS OF A LEGISLATURE- Representational |
geographic representation (constituencies) group representation (personal characteristics) party representation |
|
|
FUNCTIONS OF A LEGISLATURE Governmental |
legislators are responsible for - writing, debating and passive laws committee work |
|
|
Functions of a Legislature Procedural |
vote on new policies and adjust old ones. Every action is subject to procedure which ritualizes conflict and ensures transparency, |
|
|
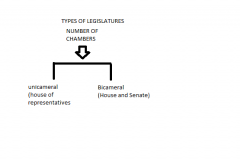
TYPES OF LEGISLATURES |
|
|
|
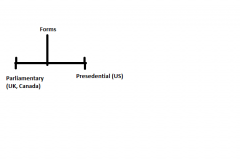
Forms of Legislatures |
|
|
|
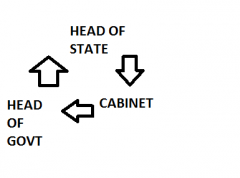
WHO MAKES UP THE EXECUTIVE |
|
|
|
The Judiciary |
allocates power between govt - guards the constitution - regulation of societal exchanges (mutual rights and responsibility) - a third part adjudicator to settle legal disputes |
|
|
Three Features of the Judiciary Judicial Impartiality |
Judges must be free from prejudice for or against any party appearing before them. |
|
|
Judicial Interdependence |
the autonomy of judges- collectively from other individuals and institutions |
|
|
Equality before the law |
judges must be able to recognize the difference normal equality and sustantive equality |
|
|
electoral system |
the means by which votes cast for candidates or parties are translated into leg leisure seats |
|
|
District Magnitude |
the number of elected candidates per district/riding |
|
|
ballot type |
does the ballot allow the voter to choose 1 or more candidate? can the voter rank candidates. |
|
|
plurality |
one rep from each constituency not gain majority votes just more than any other candidate Canada, US, UK |
|
|
majoritarian |
one member per riding - france austria finland russia |
|
|
proportional representation |
choose match between % of votes and % of seats Germany , ireland, Denmark |
|
|
mixed representation |
uses elements of plurality/majority and PR (Jaden, new zealand) |
|
|
mass parties |
a party that attempts to base itself on an appeal to the masses usually rejects elite politics (reform party) Canada |

