![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
170 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
You are the project manager for your organization and you’re working with your supervisor to define the difference between projects and operations. You explain that projects are unique while operations are the core business. Projects are typically initiated for all of the following reasons except for which one?
A. Market demand B. Organizational need C. Ongoing manufacturing of equipment D. Legal requirements
|
Answer: C
Hint: Projects are temporary. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Project Selection Methods
C is correct. It describes operations—an ongoing function of an organization. Projects have a definite ending, while operations will continue longer than the project’s duration. A, B, and D are incorrect because they are legitimate reasons for projects to be initiated. |
|
|
You are the project manager for your organization. Your management team is determining which project should be initiated based on the present value of two projects. Project A will be worth $750,000 in three years. Project B will be worth $478,000 in two years. What is the present value of Project A if the interest rate is 6 percent?
A. $630,000 B. $45,000 C. $710,000 D. Zero |
Answer: A
Hint: Present value needs division. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Project Selection Methods
A is correct. It uses the formula of FV/(1.06)3 to find the present value. B, C, and D are all incorrect calculations for the present value. |
|
|
A group of executives, subject matter experts, stakeholders, and managers that convene to ask questions about a potential project, its value, and likelihood of success to determine which projects should be initiated is called what?
A. A change control board B. A project steering committee C. A murder board D. A technical review board |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s the death of many potential projects. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Project Selection Methods
C is correct. Murder boards are a method that management can use to determine which project is most likely to succeed. A is incorrect because a change control board evaluates proposed changes to an existing project. B is incorrect because a project steering committee may be used to help the project manager make decisions within an existing project. D is incorrect because a technical review board, similar to a change control board, reviews technical changes to an existing project. |
|
|
As a PMP candidate, you should recognize the different methods an organization can use to select projects. Benefits comparison is the most common approach to select projects, but constrained optimization, a more specialized approach to project selection, is also used by organizations. Which one of the following is an example of constrained optimization?
A. Net present value B. Future value C. Benefit/cost ratios D. Linear programming |
Answer: D
Hint: It’s a mathematical model. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Project Selection Methods
D is correct. Linear programming is a mathematical model—an example of constrained optimization. A, B, and C are incorrect. They are examples of benefit comparisons. |
|
|
You are the project manager for the creation of a new warehouse in Knoxville, Tennessee. You and the project team are creating the scope statement and are evaluating the function, purpose, and activities that will take place within the warehouse to help the project customer gather all of the requirements for the scope. This process is an example of which one of the following?
A. Expert judgment B. Product analysis C. Work breakdown structure creation D. Scope change control |
Answer: B
Hint: You’re examining the deliverable. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Define Scope
B is correct. Product analysis consists of product breakdown and functional analysis. A is incorrect because expert judgment relies on experts to develop a portion of the detailed project scope statement. C is incorrect because this is not an example of the WBS creation. D is incorrect because the scope has not been created yet. |
|
|
You are working with your project team to create the project scope for a web-based application to gather information on clients. Henry says the web application can be created with JAVA programming. Marsha agrees, but insists the application can also be created with ASP technology. This is an example of which one of the following?
A. Forcing B. Expert judgment C. Alternative identification D. Team storming |
Answer: C
Hint: There’s no storm here. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Define Scope
C is correct. Henry and Marsha are proposing different approaches to completing the project. A is incorrect because forcing means one person is forcing the decision in their favor. B is incorrect because Marsha and Henry are contributing ideas, not relying on someone else to make the decision. D is incorrect because Marsha and Henry are not in a power struggle for their solution to be selected. |
|
|
During scope definition, Robert, the CEO and stakeholder, demands that the project obtain customer satisfaction to be successful. What is the danger in this request?
A. Customer satisfaction is not quantifiable. B. Customer satisfaction is not known until the project has been paid for. C. Customer satisfaction is only achieved through measurable quality control metrics. D. Customer satisfaction is never achieved through projects, but through operations. |
Answer: A
Hint: Try to measure customer satisfaction first. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Define Scope
A is correct. It’s the best choice because customer satisfaction is not a quantifiable metric. B is incorrect because customer satisfaction is a goal of every project. However, customer satisfaction is not a quantifiable goal for the project. C is incorrect because the metrics in themselves don’t achieve customer satisfaction. D is incorrect as customer satisfaction can be achieved through successful project implementations. Consider organizations that complete projects for others, such as carpenters and architects. |
|
|
Jerry is the project manager of the NHQ Project for his company. He’s working with the project sponsor to define the high-level scope statement of the project. The project scope statement defines many things, including all of the following except for which one?
A. Project boundaries B. Product acceptance criteria C. Project assumptions D. Lessons learned |
Answer: D
Hint: You work on this document once the project is in motion. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Define Scope
D is correct. Lessons learned are not included in the project scope statement. Lessons learned are created throughout the project to reflect what has, and has not, worked well in the project. A is incorrect because project boundaries are included in the project scope statement. B is incorrect because the product acceptance criteria are included in the project scope statement. C is also incorrect because project assumptions are included in the project scope statement. |
|
|
Beth is a project manager for her organization and she’s just been assigned a new project. This project has a deadline of May 15 and a budget of $250,000. A project with a budget that must not exceed $250,000 is an example of which one of the following?
A. Assumption B. Risk C. Management discretion D. Constraint |
Answer: D
Hint: It restricts. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Document Project Risks, Assumptions, and Constraints
D is correct. A constraint is anything that limits the team’s options. Note that the deadline of May 15 is also an example of a constraint. A is incorrect because an assumption is anything believed to be true, but not proven to be true. B is incorrect because risk is a potential event that has a positive or negative effect on the project’s outcome. C is incorrect because this team is not applicable. |
|
|
Stephen is the project manager of a construction project. He has written into his project plan that the project work be completed during the summer months because the weather is typically better for construction than in winter months. This decision is an example of which one of the following?
A. Management reserve B. Assumption C. Constraint D. Project risk |
Answer: B
Hint: Can you prove it? Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapters 3 and 5 Study Guide Objective: Document Project Risks, Assumptions, and Constraints
B is correct. An assumption is something that you cannot prove to be true, such as the summer weather, but you believe it to be true. A is incorrect because management reserve describes a portion of time allotted for schedule overruns within the project work. C is incorrect because a constraint limits the project team’s options. D is incorrect because a project risk is an uncertain event that may have a negative or positive impact on the project’s outcome. |
|
|
You and the project sponsor are working together to create a project scope statement. The project sponsor has concerns about the demand for safety for the electrical requirements for the project work. The concerns about safety should be documented as which one of the following?
A. Initial risk B. Cost of quality C. Product requirement D. Assumption |
Answer: A
Hint: Shocking. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Document Project Risks, Assumptions, and Constraints
A is correct. The concerns surrounding the electrical work describe a risk. This is an example of a pure risk because this dangerous activity can only have negative outcomes if someone is injured. An investment, such as purchasing faster computer equipment, is a business risk because it can have a positive or negative outcome. B is incorrect because the cost of quality describes the expense to ascertain the expected quality. C is incorrect because a product requirement describes the requirements the project must adhere to. D is incorrect because an assumption is when something is assumed but not proven. Assumptions can become risks, but this is not the best answer in this scenario. |
|
|
As a project manager, you have to document the constraints within your project team. All projects have the Triple Constraints of Project Management, which is made up of which three factors?
A. Time, cost, and scope B. Time, cost, and quality C. Cost, schedule, and stakeholders D. Time, scope, and quality |
Answer: A
Hint: It’s the Iron Triangle of project management. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Document Project Risks, Assumptions, and Constraints
A is correct. Time cost and scope are the Triple Constraints of Project Management. B, C, and D are incorrect because none of these define the Triple Constraints. |
|
|
You are the project manager of a home construction project. You are interviewing the homeowners to determine their wants and needs for the home construction. You are discussing, room by room, what they’d like in their home. This long process is called what?
A. Risk analysis B. Quality determination C. Scope creation D. Stakeholder analysis |
Answer: D
Hint: You cannot do this alone. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Identify and Perform Stakeholder Analysis
D is correct because the question describes stakeholder analysis. Interviewing the project stakeholders is a common stakeholder analysis activity to promote stakeholder engagement. A is incorrect because risk analysis involves determining the impact of the risk events. B is incorrect because this term is not applicable to the question. C is incorrect because stakeholder analysis contributes to scope creation, but it is not scope creation of itself. |
|
|
Benjamin’s project is to build a new bridge over a small creek. The government leaders want the bridge to be completed as soon as possible because of the economic impact the construction will have on the businesses in the community. An environmental group, however, has concerns that the bridge will disrupt the nature and ecological factors surrounding the creek. The environmental group is demanding additional testing, surveys, and analysis before the project can continue. The environmental group is which one of the following in this instance?
A. Stakeholder B. Positive stakeholder C. Negative stakeholder D. Risk owner |
Answer: C
Hint: They are not risky. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Identify and Perform Stakeholder Analysis
C is correct. The environmental group is a negative stakeholder because their concerns may impede the success and progress of Benjamin’s project. A is incorrect because it is too vague. A stakeholder is anyone who has an interest in the project’s outcome and may be affected by the project work. B is incorrect because a positive stakeholder wants the project to move forward as quickly as possible. D is incorrect because a risk owner is a person that owns and is responsible for a project risk. |
|
|
You must identify and perform stakeholder analysis. Key project stakeholders always include all of the following except for which one?
A. Project manager B. Customer/user C. Performing organization D. Vendor |
Answer: D
Hint: You don’t always have one of these. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Identify and Perform Stakeholder Analysis
D is correct because projects don’t always have vendors. This is a good example of a test question that doesn’t seem fair. Vendors can be key stakeholders in the project, but you may not always have a vendor. You will always have a project manager, a customer or user of the project’s outcome, and a performing organization. By process of elimination, the only stakeholder you won’t always have is a vendor. Watch out for these types of questions on your PMP exam. A is incorrect because the project manager is always a key stakeholder. B is incorrect because the customer/user is always a key stakeholder. C is incorrect because the performing organization is always a key stakeholder. |
|
|
Sarah, the CIO, wants to know why you have requested so many meetings with the users of the software your project is creating. While she acknowledges that the users are stakeholders, she doesn’t understand why you believe these stakeholders should be involved so much during the initiation phase of the project. Why should the stakeholders be involved now?
A. Involving the customers and other stakeholders improves project performance. B. Involving the customers and other stakeholders is part of stakeholder engagement. C. Involving the customers and other stakeholders reduces project risk. D. Involving the customers and other stakeholders is needed to obtain project sponsorship. |
Answer: B
Hint: Think customer buy-in. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 13 Study Guide Objective: Identify and Perform Stakeholder Analysis
B is correct. Involving the stakeholders and customers will increase the probability of shared ownership, deliverable acceptance, and satisfaction. This is an ongoing component of stakeholder engagement and it aids in maintaining interest and support of the project. A is incorrect because there is no guarantee that it will improve project performance. C is incorrect because stakeholder participation will not reduce project risk. D is incorrect because stakeholder participation during initiation is not needed for project sponsorship. |
|
|
Eric is the project manager for his organization and he’s been working on drafting the project charter. Beth Ann, a project team member, asks why Eric needs to create the charter at all if everyone already knows this project is going to happen. What is the purpose of the project charter?
A. It allows the project manager to assign the project team to work. B. It assigns authority to the project manager. C. It authorizes the project. D. It identifies the constraints and autonomy of the project manager. |
Answer: C
Hint: You can’t have a project without a charter. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 3 Study Guide Objective: Develop Project Charter
C is correct. The project charter authorizes the project. Even in scenarios where the project is going to happen, a project charter is needed to name the project manager, authorize the project manager to use the project resources, and communicate the backing and support of the project sponsor. A is incorrect. The work authorization system allows the project manager to assign the project team to work. B is not the best choice for the question. While the project manager does receive authority over some of the project resources, the best choice is that the project is authorized to exist in the organization. D is an incorrect statement about the project charter. |
|
|
Eric is the project manager for his organization and he’s been working on drafting the project charter. In this case, Eric needs to define who will issue the project charter since he’s the person writing it. Who issues the project charter?
A. The project manager B. The project sponsor C. The project customer D. The project champion |
Answer: B
Hint: It’s not the champ. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Develop Project Charter
B is correct because the project sponsor issues the charter. The project charter is signed and issued by an entity in the organization that has the power to authorize the project manager to utilize the needed resources for the project to be successful. A is incorrect. The project manager doesn’t issue the project charter. The project manager doesn’t, in most cases, have authority over all of the resources (people, facilities, equipment) the project will need. C is incorrect because the customer may demand the project, but they don’t issue the charter. D is not a valid option. The project champion is a stakeholder that may be “cheering” the project onward, but often this person isn’t the project sponsor. |
|
|
The project charter should always address all of the following except for which one?
A. The project purpose B. The assigned project manager and authority level C. The summary budget D. Project team members |
Answer: D
Hint: It doesn’t exist just yet. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Develop Project Charter
D is correct. Project team members are not identified in the project charter. A is incorrect because the project charter does identify the project purpose. B is incorrect because the project does identify the project manager and the authority level. C is incorrect because the summary budget is identified. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the GHQ Project for your company. As part of project initiation, you need to identify and analyze the project stakeholders. Management recommends that you utilize a salience model as part of this activity. What three components are measured in a salience model?
A. Power, urgency, and legitimacy B. Power, interest, and legitimacy C. Power, impact, and legitimacy D. Power, urgency, and impact |
Answer: A
Hint: There’s power, but not impact. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 13 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Project Charter Approval
A is correct. The salience model typically uses three circles to map out stakeholders’ power, urgency, and legitimacy in the project. B is incorrect because the salience model only uses the characteristics of power, urgency, and legitimacy over the project decisions and objectives. C is incorrect because the salience model only uses the characteristics of power, urgency, and legitimacy over the project decisions and objectives. D is incorrect because the salience model only uses the characteristics of power, urgency, and legitimacy over the project decisions and objectives. |
|
|
Your organization completes projects for others. Which one of the following documents serves as input to project charter creation and approval?
A. Project calendar B. Project constraints C. Contract D. Risk matrix |
Answer: C
Hint: You’re a vendor. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Project Charter Approval
C is the best answer because contracts are needed when you’re completing projects for other organizations. Contracts, also called agreements for internal projects, should define all of the expectations for all parties involved in the contracted project work. There are five inputs to consider for a project charter: project statement of work, business case, agreements, enterprise environmental factors, and organizational process assets. A is incorrect because calendars are not an input to the project charter. B is incorrect because constraints are not an input to the project charter. D is incorrect as the risk matrix has likely not been created yet. |
|
|
The project management team is creating the project charter and they are relying on several tools to help them. They want the project charter to be accurate to ensure its approval. Which one of the following is not a tool or technique that should be used when creating the project charter?
A. Project product analysis B. Project selection methods C. Project management methodology D. Expert judgment |
Answer: A
Hint: Not the thing. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Project Charter Approval
A is correct because product analysis is not a tool or technique for the project charter development. B is incorrect because project selection methods are acceptable tools. C is incorrect because project management methodology is an acceptable tool. D is incorrect because expert judgment is an acceptable tool. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the BDS Project. Your project must be completed by October 13 and cannot exceed $250,000. October 13 is an example of which one of the following?
A. A constraint B. An early finish for the project C. A scheduled completion date D. An assumption |
Answer: A
Hint: You must. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 3 Study Guide Objective: Define and Record Requirements, Constraints, and Assumptions
A is correct. The project must be completed by October 13th, so this date reflects a constraint on the project. B is incorrect because the project may be able to finish earlier than October 13. We do not have enough information to determine if this is the earliest the project can be completed. C is incorrect because the project could be scheduled to finish earlier than October 13. The constraint is that the project be finished by October 13. D is incorrect because an assumption is something believed to be true, but not proven to be true. |
|
|
Mari, the project manager, has allotted two weeks for travel delays within her project. She has no proof that travel days will happen. This is an example of what?
A. Change control B. Constraint C. Ineffective project management D. Assumption |
Answer: D
Hint: You can’t prove it. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Define and Record Requirements, Constraints, and Assumptions
D is correct. Mari has made an assumption that there will be travel delays within her project. Assumptions must be tested for their correctness. An assumption that proves false can become a risk for the project success. A is incorrect because this is not an example of change control. B is incorrect because constraints are things that limit the project team’s options. C is incorrect because this is an example of effective project management. |
|
|
You have scheduled your project team to work full-time on the project work of building a brick wall during the week of August 16. You have allotted six hours of labor per worker for each day of the week. The six hours of labor is considered what?
A. An assumption because you believe the project team will only contribute six hours of labor each day to the construction. B. An assumption because the labor union will allow the project team members to work only six hours each day. C. An assumption because you have historical information to base your estimate on. D. An assumption because you know the building inspector will be onsite for two hours each work day. |
Answer: A
Hint: It’s your belief. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 Study Guide Objective: Define and Record Requirements, Constraints, and Assumptions
A is correct because you believe the project team will only contribute six hours, but you haven’t proven this to be true. The project team could work more, or less, than six hours per day. B is not a valid choice because if it’s true that the labor union will only allow six hours of work, then it would be a constraint. C is incorrect because if you have historical information to base your time estimate on, then it’s factual rather than an assumption. D is incorrect because if you know the building inspector will be onsite for two hours each day, this is a constraint. |
|
|
Assumptions must be identified and documented as part of project planning. Which one of the following is an assumption?
A. The project must be completed by November 1. B. The project must cost less than $250,000. C. The project must be completed in the summer because the weather is better. D. The project must be completed by the end of the year because of a new regulation. |
Answer: C
Hint: Wait for the sunshine. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 Study Guide Objective: Define and Record Requirements, Constraints, and Assumptions
C is the best choice because weather is a typical example of an assumption. A is incorrect because this is an example of a time constraint. B is incorrect because this is an example of a cost constraint. D is incorrect because this is an external constraint. |
|
|
The project team is obviously struggling over who will be leading the project. This happens in which phase of team development?
A. Forming B. Storming C. Norming D. Performing |
Answer: B
Hint: Boomers. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Improve Team Performance
B is correct because storming is when the project team moves through power struggles about who’s in charge of the project. A is incorrect because forming happens when the team first meets. C is incorrect because this happens once the project team settles into their roles. D is incorrect because this happens once the project team focuses on getting the project work completed. |
|
|
You are the project manager for a new construction project. There are several building codes that your project team must adhere to during the design and construction phases of your project. The building codes are examples of which one of the following?
A. Standards B. Government-imposed requirement C. Quality management concern D. Scope |
Answer: B
Hint: You must adhere to the codes. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapters 1 and 5 Study Guide Objective: Define and Record Requirements, Constraints, and Assumptions
B is the best choice because building codes are an example of a government-imposed requirement. A is incorrect. Standards are optional, regulations are not. C is incorrect. While quality may be affected by adherence to the building code, B answers the question more accurately. D is incorrect because scope does not answer the question |
|
|
The project scope statement includes constraints, assumptions, and requirements. All of the following are examples of constraints except for which one?
A. A preset project budget B. A project that has been completed before C. A project due date as defined by management D. A project that requires a mechanical engineer for the month of January |
Answer: B
Hint: It’s not a requirement. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7 Study Guide Objective: Define and Record Requirements, Constraints, and Assumptions
B is the best choice because this describes historical information rather than a constraint. A is incorrect because a preset project budget describes a project constraint. C is incorrect because a due date is an example of a project constraint. D is incorrect because it describes a resource constraint for the mechanical engineer. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the XHG Project. Your manager has determined that the project must be completed by January 31. In order to meet this constraint, what will you and the project team likely need to do?
A. Work overtime B. Add more project team members C. Schedule backward from the completion date D. Require additional funds |
Answer: C
Hint: Start at the end. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 3 Study Guide Objective: Define and Record Requirements, Constraints, and Assumptions
C is the best answer. An imposed completion date will likely require you and the project team to schedule from the completion date. A is incorrect. There’s no evidence you must work overtime to complete the project. B is incorrect because there’s no evidence you will need additional labor to complete the project by the schedule date. In addition, the work may not be affected by the added labor (considered activities of fixed duration). D is incorrect. The scheduled completion date doesn’t necessarily correlate to more funds to complete the project. |
|
|
It is important for the project manager to identify the organizational structure she is operating within to better plan the project. Which organizational structure provides the least amount of power for the project manager?
A. Functional B. Weak Matrix C. Strong Matrix D. Projectized |
Answer: A
Hint: It’s no “fun” for the project manager. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Identify Project Team and Define Roles and Responsibilities
A is correct because the Functional structure provides the least amount of authority for the project manager. B is incorrect because the Weak Matrix provides more power than the Functional Structure, but still limits the project manager’s authority. C is incorrect because the Strong Matrix provides the project manager more power than the functional manager. D is incorrect because the Projectized structure provides the most power for the project manager. |
|
|
Project managers may need to work with union labor as part of the project execution. This requires planning and consideration of all the union agreements, rules, and restrictions. A contract between the performing organization and a union is an example of which one of the following?
A. Stakeholder B. Collective bargaining agreement C. Assumption D. Management |
Answer: B
Hint: More than just a stakeholder. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Identify Project Team and Define Roles and Responsibilities
B is correct because the contract between the performing organization and the union is called a collective bargaining agreement. A is incorrect because the union is a stakeholder if they’re involved with the project but their contract is not. C is incorrect because the contract may list constraints, but not assumptions. D is incorrect because management is not a valid answer. |
|
|
You are managing a project in a matrix-structured organization. You would like to create a chart that depicts each department’s contributions to the project. Which one of the following can best accomplish this goal?
A. Work breakdown structure B. Project network diagram C. Text-oriented organization chart D. Organizational breakdown structure |
Answer: D
Hint: It organizes the work. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Identify Project Team and Define Roles and Responsibilities
D is correct because the organizational breakdown structure shows the hierarchy of the organization and lists each department’s contributions to the project. A is incorrect because the WBS lists the deliverables of the project, not which department will contribute to the creation of the WBS deliverables. B is incorrect because the project network diagram shows the workflow of activities within the project. C is incorrect because a text-oriented organization chart does not show department-by-department contributions to the project work. |
|
|
You would like to create a matrix chart that shows each team member’s involvement with each activity. What is this chart known as?
A. The RACI chart B. The Pareto chart C. The Roles and Responsibility Matrix D. The HR Interaction chart |
Answer: A
Hint: Race to the finish. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Identify Project Team and Define Roles and Responsibilities
A is correct because a RACI chart depicts the roles of each team member as Responsible, Accountable, Consult, and Inform. B is incorrect because a Pareto chart shows categories of failure and is used with quality control measures. C and D are incorrect because both of these terms are not applicable. |
|
|
A major component of project planning and management is the project’s work breakdown structure. The smallest item in the WBS is called what?
A. A leaf object B. A task C. A work package D. A deliverable |
Answer: C
Hint: No rakes needed. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Create the WBS
C is correct. The smallest item in the WBS is called the work package. A is incorrect because this is not a valid term. B is incorrect because a task is the actual work, not the smallest item in the WBS. D is incorrect because a deliverable does not accurately define what the smallest item in the WBS is. |
|
|
What should be implemented when determining how detailed the decomposition of the deliverables in the WBS should be?
A. The 8/80 rule B. The law of diminishing returns C. The priority of the project D. The timetable to create the WBS |
Answer: A
Hint: It is a heuristic. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Create the WBS
A is correct because the 8/80 rule states that the work package should not equate to less than eight hours of labor to create and no more than 80 hours of labor to create. B is incorrect because the law of diminishing returns describes the effect of added labor and the return for that labor. C is incorrect because the priority of the project doesn’t affect the decomposition of the project. D is incorrect because the timetable to create the WBS does not dictate the level of detail required for decomposition |
|
|
Management would like for you to identify each deliverable within the WBS with a number. The numbering system you should use with your WBS is called what?
A. Chart of accounts B. Bill of materials C. Code of accounts D. WBS dictionary |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s not a secret. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Create the WBS
C is correct. The code of accounts is used to provide a hierarchical structure for the deliverables identified in the WBS. A is incorrect because the chart of accounts is an accounting tool for assigning predefined costs for deliverables such as cost per square foot, cost per hour, or cost per unit. B is incorrect because a bill of materials identifies all of the materials needed to create the things identified in the WBS. D is incorrect because the WBS dictionary defines what each work package in the WBS is and its associated time and cost estimate. |
|
|
The difference between what was planned and what was experienced in the project is called a project variance. Project variances are often compared against the project baselines, such as time, cost, and scope. What document serves as the scope baseline? (Choose the best answer.)
A. The summation of the cost and time baselines B. The WBS C. The project charter D. The project scope |
Answer: B
Hint: Equates to the scope. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Create the WBS
B is correct. The WBS is the scope baseline. Technically, the WBS, the WBS dictionary, and the detailed project scope are the scope baseline. A is incorrect because the time and cost baselines do not reflect the scope. C is incorrect because the project charter does not capture all the deliverables the project will create. D is incorrect because the project scope is decomposed into the WBS. The WBS, in effect, reflects the entire project scope. |
|
|
Mary is the project manager of the GHQ Project. Her project is part of a program in her organization. Thomas is the program manager, while Joan is the project sponsor. Who creates the WBS?
A. The project manager B. The project sponsor C. The project team D. The program manager |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s not a solo activity. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Create the WBS
C is correct. The project team creates the WBS. A is incorrect because the project manager doesn’t complete the WBS alone. B is incorrect because the project sponsor doesn’t complete the WBS. D is incorrect because the program manager doesn’t create the WBS for the individual projects within the program. The WBS creation is the responsibility of the project manager and the project team. |
|
|
The process of breaking down the project scope into the WBS is called what?
A. Progressive elaboration B. Rolling wave planning C. WBS composition D. Work structure |
Answer: A
Hint: No surfing. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Create the WBS
A is correct because progressive elaboration means developing in steps and continuing in increments, as in the WBS creation. B is incorrect because rolling wave planning allows for ebb and flow in planning. C and D are incorrect because both of these terms are not valid. |
|
|
Holly Ann is the project manager of the GVF Project, which is similar to the HGF Project she just completed. She and the project team are about to begin creating the WBS for the GVF Project and she would like to use the WBS from the HGF Project to create the current WBS. This is an example of which one of the following?
A. Top-down estimating B. Historical information C. Poor project management D. WBS template |
Answer: D
Hint: It’s like a cookie cutter. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Create the WBS
D is correct because when Holly uses a previous project’s WBS to create the current project’s WBS, she is using a template. A is incorrect because she is not estimating at this point in the project. B is incorrect because while this may be a loose example of historical information, WBS template answers the question more accurately. C is incorrect because this is not an example of poor project management. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the NHH Project and are working with your project team to create the WBS. One portion of the WBS cannot be decomposed until later in the project. You have decided to wait until more details become available about the element and to decompose the deliverable at that point. This is sometimes called what?
A. The WBS template B. Rolling wave planning C. Iterative WBS creation D. Scope creep |
Answer: B
Hint: Surf’s up! Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Create the WBS
B is correct. This approach is sometimes called rolling wave planning. A is incorrect because this is not an example of a WBS template. C is incorrect because this term is not valid. D is incorrect because this is not an example of scope creep. |
|
|
In most projects, change is inevitable. Change for time, cost, scope, and even contracts must be captured, analyzed, and incorporated into the project plan. What system controls changes within a project?
A. Change control system B. Change control board C. Cost change control system D. Change approval system |
Answer: A
Hint: Read the question. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Develop Change Management Plan
A is correct. The change control system controls changes to the project. B is incorrect because the change control board may be used as part of the change control system. C is incorrect because costs may be affected by the changes, but there is no cost change control system. D is incorrect because this term is not valid. |
|
|
Which system is responsible for identifying and documenting the functional and physical characteristics of a product or component that a project is creating?
A. The requirements gathering process B. Stakeholder analysis C. The planning process group D. The configuration management system |
Answer: D
Hint: It is a system. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Develop Change Management Plan
D is correct. The configuration management system is responsible for identifying and documenting the functional and physical characteristics of a product or component that a project is creating. A is incorrect because the requirements gathering process does not fully answer the question. B is incorrect because stakeholder analysis does not complete this function. C is incorrect because the planning process group is too broad to fully answer the question. |
|
|
Because change can have a significant impact on a project’s success, there must be a documented approach to change management for the project scope. Which plan documents the project scope change control system?
A. The project management plan B. The project scope management plan C. The change control system D. The risk response plan |
Answer: B
Hint: Not risk. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Develop Change Management Plan
B is correct. The Project scope management plan documents the project scope change control system. A is incorrect because it is too broad and does not answer the question as completely as B. C is incorrect because this is the system for managing changes. D is incorrect because this documents risk responses. |
|
|
You have hired another company to complete a project for you. You would like to change some details in the project scope which will affect the contract between you and the vendor. Which system would manage these changes?
A. The schedule change control system B. The cost change control system C. The procurement management system D. The scope change control system |
Answer: D
Hint: Control the project scope first. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Develop Change Management Plan
D is correct. Even changes to the contracted work must flow through the scope change control system. A is incorrect because the schedule change control system is invoked if there are changes to the schedule. The question does not define if the changes will affect the schedule or not. B is incorrect because the cost change control system is invoked if there are changes to the cost. The question does not define if the changes will affect the costs or not. C is incorrect because it does not fully answer the question. |
|
|
A change has been proposed to the project scope. You have routed the change through the change control system as planned. You need to examine cost, time, quality, human resources, communications, risks, and procurement when examining the proposed change. Your manager wants to know why all of these areas must be examined. In regard to the proposed change, what are you doing by examining each project area?
A. Configuration management B. Integrated change control C. Scope change control D. Effective project management |
Answer: B
Hint: It all works together. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Develop Change Management Plan
B is correct. This is part of integrated change control. A is incorrect because configuration management doesn’t fully answer the question. C is incorrect because scope change control is part of integrated change control. In this question, you are examining the impact of a change on all knowledge areas. D is incorrect because while this may qualify as effective project management procedures, integrated change control more fully answers the question. |
|
|
The configuration management system accomplishes all of the following except for which one?
A. Provides opportunities to validate and improve the project by considering the impact of each change B. Provides opportunities for the project management team to communicate all changes to the stakeholders C. Provides a method to identify and request changes to established baselines D. Provides a method for project management processes to be removed or added to the project |
Answer: D
Hint: All of these already exist. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Develop Change Management Plan
D is correct because the configuration management system does not provide a method for project management processes to be removed or added to the project. A, B, and C are incorrect because all of these statements are true. |
|
|
You are the project manager of a new home construction project. You are inspecting the home as part of quality control. You’ve noticed faulty work during one of your quality control inspections. What is needed?
A. Project scope change control for the new work B. Recommended defect repair for the incorrect work C. Change request for the additional work D. Recommended corrective actions |
Answer: B
Hint: Fix it. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Develop Change Management Plan
B is correct. You typically find faulty work during quality control inspections and then you make recommendations to fix the problems. A is incorrect because you are not changing the project scope. C is incorrect because you are not requesting for the project scope to change with additional work. D is incorrect because you are not making actions to bring future results back into alignment with the project plan. You are fixing errors—thus, this is defect repair. |
|
|
A project manager is completing a project to build a new condo. He needs to confirm that any field drawings by the architect match the office drawings that will go into the project archives. Which project management system ensures that changes to the project scope and the product scope are thoroughly considered and documented?
A. The change control system B. The integrated change control process C. The configuration management system D. The communication management system |
Answer: C
Hint: Go configure. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Develop Change Management Plan
C is correct. The configuration management system ensures that requested changes to the project scope and the product scope are thoroughly considered and documented. A is incorrect because it does not fully answer the question. B is incorrect because the configuration management system processes happen before integrated change control. D is incorrect because this term is not applicable to this scenario. |
|
|
Not all risks are negative, and some negative risks are worth accepting into the project based on the impact, the possible outcomes, and the perceived benefits that the risk may bring. What terms describes a person’s or organization’s willingness to accept risk?
A. Utility function B. Risk exposure C. Mitigation D. Risk probability |
Answer: A
Hint: It’s based on Bernoulli’s curves. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Identify Risks and Define Risk Strategies
A is correct. Utility function is a term used to describe a person’s or organization’s willingness to accept risk. The lower the utility function, the more risk response planning is needed. B is incorrect because risk exposure is based on each project. C is incorrect because mitigation is one response to a risk event. D is incorrect because risk probability describes the likelihood of a risk event actually happening. |
|
|
Risk analysis is an iterative process within any project. It sometimes helps to classify and break down the risk events to provide a deeper understanding of them. Which structure lists the categories and subcategories for risks within a project?
A. The work breakdown structure B. The organizational breakdown structure C. The risk breakdown structure D. The bill of materials structure |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s about risk. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Identify Risks and Define Risk Strategies
C is correct. A risk breakdown structure illustrates the risk categories within a project. A is incorrect because the WBS shows the decomposition of the project scope. B is incorrect because the OBS shows the structure of an organization, not the risks within the organization. D is also incorrect because the BOM describes the materials needed in order to build the project scope. |
|
|
One of the most important processes of risk management is risk identification. When does the risk identification conclude?
A. With the planning process group B. With the execution process group C. With the closing process group D. When the project customer deems all the risks have been identified. |
Answer: C
Hint: It ain’t over until it’s over. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Identify Risks and Define Risk Strategies
C is correct because risk identification happens throughout the project life cycle. A is incorrect because risk identification happens throughout the project. B is incorrect because risk identification is iterative and happens throughout the project. D is also incorrect. The project customer may not know enough about the project’s discipline to understand when all of the risks have been identified. Risk identification is iterative and happens throughout the project. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the Highway Automation Project and are facilitating the risk identification process with your project team and other key stakeholders. You have encouraged the participants to identify as many project risks as possible. All of the following are acceptable risk identification techniques except which one?
A. The Delphi Technique B. SWOT analysis C. Qualitative analysis D. Root cause analysis |
Answer: C
Hint: This happens later. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Identify Risks and Define Risk Strategies
C is correct. Qualitative analysis happens after risk identification. A, B, and D are incorrect because all of these are risk identification methods. |
|
|
Risk identification and analysis includes careful consideration of project requirements, scope objectives, the nature of the project work, and the project documentation. Based on this information, which one of the following statements must be examined for risk?
A. The product requires a foil stamp of .32 millimeters. B. The product requires oak beams. C. The product must be constructed during the summer months due to the expected good weather. D. The product must be approved by a building inspector before August |
Answer: C
Hint: Assumptions. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Identify Risks and Define Risk Strategies
C is correct because all assumptions must be tested. A is incorrect because this is not an assumption, but a requirement. Both B and D are incorrect because these are project requirements. |
|
|
It’s difficult to capture and analyze all risks that may affect the project objectives. One approach is using the risk register. What exactly is the risk register?
A. It’s a central database for all risks within an organization. B. It’s a listing of all risks that have been identified within a project. C. It’s a listing of all risks that have been identified and responded to within an organization. D. It’s a listing of all risks that must be mitigated within a project. |
Answer: B
Hint: Keep it simple. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Identify Risks and Define Risk Strategies
B is correct because the risk register is simply a list of identified risks within a project. A, C, and D are incorrect because these statements are not true. |
|
|
You have identified a risk within your project dealing with the installation of the electrical system in a building expansion. You have hired a licensed electrician to complete this portion of the project. This is what type of risk response?
A. Transference B. Mitigation C. Procurement D. Avoidance |
Answer: A
Hint: Choose the best answer, or get someone else to do it. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Identify Risks and Define Risk Strategies
A is correct because whenever you hire someone else to own a risk, you are participating in risk transference. B is incorrect. Mitigation is an effort to reduce the probability or impact of a risk event. C is incorrect because this term is not valid for this scenario. D is incorrect because you are not avoiding the risk, you’re transferring it. |
|
|
There’s a risk that a new law will cause your project to fail. What risk response can you use for this possible law?
A. Mitigation B. Transference C. Exploit D. Acceptance |
Answer: D
Hint: There’s nothing you can do about it. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Identify Risks and Define Risk Strategies
D is correct because the only response you can do is to accept the risk. A is incorrect because you cannot mitigate the risk. B is incorrect because you cannot transfer the risk. C is incorrect because you cannot accept the risk. |
|
|
You are working with management on the project planning processes. They want to know why you’re spending time on risk management planning so early in the project planning. Which one of the following is the best response to management’s concern?
A. All projects have risks. B. Risk management planning increases the probability of success for the other risk management processes. C. Risk management planning must happen before any other planning activities. D. You feel, as the project manager, that the project has too many risks to be successful. |
Answer: B
Hint: Planning is iterative. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Plan Approval
B is correct because risk management planning does increase the possibility of success for the risk management processes. A is incorrect because risk management planning is not about risk identification, but rather how to approach and conduct risk management activities. C is incorrect because this statement is not true. D is incorrect because this concern centers on risk identification and response, not the approach to risk management. |
|
|
Management has asked you, the project manager of the KJU Project, to provide an estimate of the project costs. Their decision to move forward with the project will be based on your initial estimate. You have just started the project so what estimate type will you likely provide?
A. Rough order of magnitude B. Definitive C. Budget D. Bottom-up |
Answer: A
Hint: It’s rough. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Plan Approval
A is correct because this early estimate is the rough order of magnitude estimate. B is incorrect because the definitive can be provided once the WBS has been created. C is incorrect because the budget is provided once the scope statement has been created. D is incorrect because the bottom-up is created once the WBS has been created. |
|
|
You are hiring another organization to complete a project for your organization. Which document would include information about performance reporting requirements, operation transfer issues, and post-project support of the deliverable?
A. Proposal B. Request for proposal C. Bid D. Statement of Work |
Answer: D
Hint: There’s no contract yet Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 12 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Plan Approval D is correct because the SOW provides all these elements.
A is incorrect because the proposal does not provide these elements but focuses on how the solution can be implemented. B is incorrect because the RFP asks the vendor to provide a proposal. C is incorrect because this document comes from the vendor to the buyer and is focused on price only. |
|
|
You have created the project schedule and management has asked to review the schedule. They have concerns that your labor estimates may be too aggressive. If management recommends resource leveling, what will likely happen to your project schedule?
A. Nothing. Only more labor will be added. B. Nothing. Only more costs will be added. C. The schedule will take longer to complete. D. The project duration will increase. |
Answer: D
Hint: Resource leveling flattens the resources. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Plan Approval D is correct because resource leveling will typically require the project duration to increase.
A is incorrect because there is no evidence that more labor is available, approved, or allowed. B is incorrect because there’s no evidence that more funds will be needed to complete the project work. C is incorrect because the creation of the schedule will not necessarily take longer to create. The completion of the project will likely take longer, however. |
|
|
While it’s not a project initiation activity, most projects can benefit from a project kickoff meeting. What’s the goal of the project kickoff meeting?
A. It introduces the project goal. B. It allows the project manager, the project team, and the key stakeholders to meet one another. C. It allows the project manager to gain commitment from the project team and key stakeholders for the project. D. It allows the project manager to facilitate their expert power. |
Answer: C
Hint: You want this first. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Kick-Off Meeting
C is correct because the goal of the kick-off meeting is to gain everyone’s commitment to the project. A is incorrect because the project goal is established before the kick-off meeting. B is incorrect because the project manager has likely already met the project team. In addition, this is not the goal of the meeting. D is incorrect because this statement is not valid. |
|
|
All of the following are desired outcomes of the project kick-off meeting except for which one? A. Provide clarifications on the project goals and objectives. B. Allow the team and stakeholders to know the points of contact within the project team. C. Learn how the current project may interact with other projects. D. Allow the project team to voice concerns and objections about the project scope. |
Answer: D
Hint: No nagging. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Kick-Off Meeting
D is correct because the kick-off meeting is not the place for this discussion. A, B, and C are incorrect because all of these are desired outcomes of the project kick-off meeting |
|
|
All of the following statements are false about the project kick-off meeting except for which one?
A. The project kick-off meeting is a team-building exercise. B. Only the project team members should attend the project kick-off meeting. C. The project kick-off meeting is led by the project sponsor. D. The project kick-off meeting is held during scope verification. |
Answer: A
Hint: The team is there. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Kick-Off Meeting
A is correct because this is a true statement about the project kick-off meeting. B, C, and D are incorrect because all of these are false statements about the project kick-off meeting. |
|
|
Management has asked you to create a project kick-off meeting for the GHB Project. When should the project kick-off meeting happen?
A. When the project manager has the project team assembled for the first time. B. When the project manager has approved the project plan. C. When management has approved the initial project plan. D. At the start of scope verification. |
Answer: C
Hint: The plan is needed. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Kick-Off Meeting
C is correct. The project kick-off meeting happens after the initial project plan has been approved. A is incorrect because this does not answer the question as well as C. B is incorrect because the project manager does not necessarily approve the project plan—management does. D is incorrect because this is not a valid statement. |
|
|
Your organization is partnering with a competing firm in order to complete a large construction project. You will serve as the project manager in this partnership. What is this relationship called?
A. Dual-entity project management B. Dual functional structure C. Teaming agreement D. Functional team agreement |
Answer: C
Hint: You’re on a temporary, contractual team. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 2 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Kick-Off Meeting
C is correct. When two competing entities partner together to complete a project through a contractual relationship, it is called a team agreement. A, B, and D are incorrect because none of these are valid project management terms. |
|
|
All of the following are accomplished during the project kick-off meeting except for which one?
A. The project organization is explained. B. The project goals are defined. C. The project objectives are identified. D. The project risks are examined. |
Answer: D
Hint: Not yet. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Conduct Kick-Off Meeting
D is correct because risk does not happen until later in the project planning process. A, B, and C are incorrect because all of these are true statements about the project kick-off meeting. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the HHA Project for your company. Management has asked you to present your approach to project execution. Which of the following defines how the project is executed?
A. The project management plan B. The work authorization system C. The project execution process group D. The project manager |
Answer: A
Hint: Not a person. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Execute Tasks Defined in Project Plan
A is correct because the project management plan defines how the project is executed, monitored and controlled, and closed. B is incorrect because the work authorization system tracks completed work and allows scheduled work to begin. C is incorrect because this statement is not valid for this question. D is incorrect because the project manager doesn’t solely define how the project is executed, the project team and expert judgment may also contribute. |
|
|
While project management planning is essential, planning cannot continue indefinitely. At some point, the project management team must move into project execution. All of the following actions are required to execute the project management plan except for which one?
A. Perform activities to accomplish project objectives. B. Staff, train, and manage the project team. C. Manage risks and implement risk response activities. D. Interact with other project managers. |
Answer: D
Hint: This doesn’t have to happen. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Execute Tasks Defined in Project Plan
D is correct because you, the project manager, do not always have to interact with other project managers to complete the project work. You do always have to complete choices A, B, and C. A, B, and C are incorrect because all of these are valid statements. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the NGBB Project. Your project team has failed to complete the work as the project management plan demanded. What action will the project team now have to perform with your guidance?
A. Quality control B. Defect repair C. Peer review D. Exit interview |
Answer: B
Hint: Fix it. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Execute Tasks Defined in Project Plan
B is correct because the project team will have to fix the defects in their work. A is incorrect because QC is based on inspection. The errors have already been identified so the project team must fix the errors. C is incorrect because peer review is an example of QC. The project team must fix the problems. D is incorrect because this statement is not applicable to the situation. Sorry, but you don’t get to fire your project team members. |
|
|
Harry is the project manager of the HQQ Project. Management has asked him to report on the project execution and its outcomes. Which one of the following is an output of project execution?
A. The project charter B. The cost baseline C. Change requests D. Quality control mechanisms |
Answer: C
Hint: Read the question before you change your answer. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Execute Tasks Defined in Project Plan
C is correct because change requests are outputs of project execution. A is incorrect because the project charter is not an output of project execution. B is incorrect because the cost baseline has been established based on your cost estimates and the cost budgeting activities. D is incorrect because this is not a valid answer. |
|
|
You are the project manager of a large project to install 10,000 fixtures across a campus. Your project team has been late on their assigned work and you fear the project will be late. Which one of the following provides forecasting for the project?
A. The program evaluation and review technique B. The graphical evaluation and review technique C. Risk analysis D. The estimate at completion |
Answer: D
Hint: EVM. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Execute Tasks Defined in Project Plan
D is correct because the earned value management formula—estimate at completion (EAC)—provides forecasting for the project success. A is incorrect because the program evaluation and review technique (PERT) provides time estimates, not forecasting. B is incorrect because the graphical evaluation and review technique (GERT) provides branching and loopbacks in network diagramming, not forecasting. C is incorrect because risk analysis does not provide forecasting to the level that EAC does. |
|
|
You fear that your project team is bloating their time estimates for their assigned activities. What law addresses bloated estimates?
A. The law of diminishing returns B. Parkinson’s Law C. The Pareto principle D. The contingency reserve |
Answer: B
Hint: Work expands. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 Study Guide Objective: Execute Tasks Defined in Project Plan
B is correct because Parkinson’s Law states that work will expand to fill the amount of time allotted to it. A is incorrect. The law of diminishing returns states that increased labor doesn’t always guarantee an increase in the yield, and can even diminish an organization’s overall profit. (See the PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 for more details.) C is incorrect because the Pareto principle is the 80/20 rule—for example, 80 percent of your business comes from 20 percent of your customers. D is incorrect because the contingency reserve is the time allotted for schedule slippage. (See the PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6.) |
|
Examine the exhibit. How long will the project take if Activity C in the exhibit increases by four days?
A. 22 B. 26 C. 16 D. No change because there is float
|
Answer: B
Hint: There is a change. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 Study Guide Objective: Execute Tasks Defined in Project Plan
B is correct because the path ACFHI is the critical path, and with four additional days of work the duration of the project will increase to 26 days. A is incorrect because this is the project duration before the change in duration for Activity C. C is incorrect because this is not valid. D is incorrect because the duration of the project has increased regardless of the float |
|
|
You are completing a project to build a park in a community. The community is hosting a meeting where residents can ask you questions and clarify the park’s goals and features. You insist that the project team attend this meeting. Why should the project team attend?
A. The team is needed to show the public the expert that you have employed to build an excellent park for them. B. The team may have answers to some of the questions the public may ask. C. The team needs to understand how the project will affect the people and vice versa. D. The team is needed to see the impact of the project on the community. |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s about people. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Common Understanding and Set Expectations
C is correct because the project team needs to see the impact of their project on the community and how the community may affect the project outcome. A is incorrect because this is not a valid reason for having the team present. B is incorrect because the project manager will be answering the questions from the community. While the project team may field some questions, this is not the best reason for their involvement. D is incorrect because this does not answer the question as completely as choice C. |
|
|
You are the project manager of a large international project. Your project team will be traveling to four different countries to complete the project work. You have required the project team to complete training regarding the customs, laws, and languages for each country they will be traveling to. What theory believes that an understanding of the culture, local language, and colloquialisms allows people to have a better understanding of the country they’re working in?
A. The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis B. Ethnocentrism C. Culture shock D. Utility function |
Answer: A
Hint: It’s not about risk. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Common Understanding and Set Expectations
A is correct. The Sapir-Whorf hypothesis states that an understanding of the culture, local language, and colloquialisms allows people to have a better understanding of the country they’re working in. B is incorrect because ethnocentrism is when an individual measures another culture by their own culture. C is incorrect because culture shock describes the initial disorientation people feel when they first arrive in a foreign culture. D is incorrect because this describes a person’s willingness to accept risk. |
|
|
The project charter must define which one of the following?
A. The risk exposure from not completing the project B. The quality assurance program the project manager must operate under C. The work authorization system the project must use D. Requirements for customer satisfaction |
Answer: D
Hint: Not QA. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Common Understanding and Set Expectations
D is correct because the charter must define the requirements for customer satisfaction. A, B, and C are incorrect because these are not valid components of the project charter. |
|
|
You are the project manager for your organization and you’re working with management and several subject matter experts to create the project scope statement. Once the statement is complete, you mention that the key project stakeholders should receive a copy of the project scope statement. Why should the key stakeholders receive a copy of the project scope statement?
A. To ensure that all of the key stakeholders have been identified. B. To ensure that all of the key stakeholders have a common understanding of the project. C. To ensure that all of the project team members are accounted for among the functional managers. D. To ensure that the project manager is identified. |
Answer: B
Hint: Understand. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Common Understanding and Set Expectations
B is correct because the project scope explains what the project will accomplish. A is incorrect because this is part of communications management. C is incorrect because this is part of human resources management. D is incorrect because this is accomplished in the project charter. |
|
|
Projects are completed by people and require ground rules to establish clear expectations. Why must the project team commit to clear guidelines on their behavior and project participation early in the project?
A. It decreases misunderstandings and increases productivity. B. It increases the project’s likelihood of success. C. It decreases storming among the project team members. D. It increases the project’s risk minimization. |
Answer: A
Hint: Two things. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Common Understanding and Set Expectations
A is correct because early commitment to clear guidelines decreases misunderstandings and increases productivity for the project team. B is incorrect. While this may be true, it is not as accurate as A. Risks, lack of quality, and other influencers could still cause the project to fail. C is incorrect because storming happens as part of team development. D is incorrect because this is not a valid statement. |
|
|
During the initial project team meeting, the project manager and the project team established ground rules for how project team meetings would operate. Tina, a project team member, is not obeying the project rules. Who has the responsibility to enforce the rules?
A. The project manager B. The project sponsor C. The project team D. The human resources department |
Answer: C
Hint: Everyone plays. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Common Understanding and Set Expectations
C is correct because all project team members share the responsibility to enforce the rules. A is incorrect because this does not answer the question fully. The project manager may lead the enforcement, but the question asks who has the responsibility—and it’s the entire project team. B is incorrect because the project team has the responsibility. D is incorrect because the project team has the responsibility. It may, in some instances, be up to the project manager to escalate the issue through the project sponsor to human resources. |
|
|
Your organization is operating in a functional structure and you’re the project manager of a newly initiated project. Who has the power on a project team in a functional organization?
A. The project manager B. The project sponsor C. The project team D. The functional manager |
Answer: D
Hint: It’s not fun for the project manager. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 2 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Common Understanding and Set Expectations
D is correct. The functional managers have the power in a functional organization. A is incorrect because the project manager has little or no authority in a functional organization. B is incorrect because it’s the functional manager with the power, not the project sponsor. C is incorrect because the project team does not have the power in a functional structure. |
|
|
Betsy is the project manager of the JGB Project for her organization. She would like to solicit seven vendors for a price to supply 1000 fixtures for her project. What type of a document would Betsy issue to the vendors in this scenario?
A. A request for proposal B. A request for quote C. A request for information D. An invitation for a bidders’ conference |
Answer: B
Hint: How much? Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 12 Study Guide Objective: Implement the Procurement of Project Resources
B is correct because a request for quote only wants a fee for the procured goods or services. A is incorrect because a request for proposal wants ideas and suggestions on how to complete the work. C is incorrect because a request for information is asking the vendor to provide information on their goods or services. D is incorrect because a bidder’s conference allows the bidders to meet to ask for clarifications on the provided statement of work. The question is focused on the price for the fixtures, so a quote is what’s needed from the vendors. |
|
|
Your organization needs to procure training classes. There are many training companies that you can hire, but you prefer to work with one particular vendor. This is an example of which market condition?
A. Oligopoly B. Sole source C. Single source D. Qualified seller list |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s not the tricky one. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 12 Study Guide Objective: Implement the Procurement of Project Resources
C is correct because a single-source market means they prefer to work with one particular vendor. A is incorrect because an oligopoly describes a market condition where the actions of one vendor affects all of the others (for example, oil, airfare, and software). B is incorrect because a sole source means there is only one vendor available. D is incorrect because this is simply a list of vendors that your organization allows you to do business with. |
|
|
Your organization has tasked you with business development. Specifically, they’d like to bid on government-based contracts. Where will you likely find information on government contracts that your organization could bid on?
A. Newspapers B. Historical information C. Sales channels D. City hall |
Answer: A
Hint: Every Sunday. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 12 Study Guide Objective: Implement the Procurement of Project Resources
A is correct because you’ll often find advertisements in the newspaper of pending government contracts. B is incorrect because historical information is activity that has already been completed. C is incorrect because this is too vague of an answer. D is incorrect because not all government contracts are available through city hall; consider federal contracts, military, and other agencies. |
|
|
You are trying to determine if you should make or buy a piece of software. If you create the software, it’ll cost your organization $45,000 to create it and $3,400 each month to support it. A vendor, however, can create the software for $12,000 and will charge you $0.17 per transaction, per month. According to your calculations, you’ll have 31,400 transactions each month. What should you do?
A. Hire the vendor if the software will be kept longer than 17 months. B. Hire the vendor if the software will be replaced within 17 months. C. Hire the vendor if the transactions will be less than 30,000 per month. D. Make the software and reduce your monthly expenses by paying the vendor for the transactions. |
Answer: B
Hint: (Build-buy)/(Monthly fee difference) Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 12 Study Guide Objective: Implement the Procurement of Project Resources
B is correct because the software will “pay for itself” if it is used 17 months or longer. This can be calculated by finding the difference of the build and buy, which is $33,000. Then, you find the difference of the monthly fees, which is $1,938. Divide the $33,000 by $1,938 and this tells you how long the vendor’s solution will be valid. If the software is to be kept longer than 17 months, it would be more cost effective to build the software than to buy it. A is incorrect because after 17 months the build solution is a better choice. C is incorrect because the question already explains that the permonth transaction will be more than 30,000. D is incorrect because this is not a valid choice (especially for the vendor). |
|
|
You are the project manager of a construction project for a new client. The client has asked that you include an outdoor deck as part of the project—something your company doesn’t normally do, but you agree to take on this project component using a contractor to build the seating deck. For this portion of the project, you would like to use a time and materials contract. What must this contract type have?
A. The signature of the purchasing agent B. An end date for the procured work C. A not-to-exceed clause D. Addendums for each change in the project work |
Answer: C
Hint: Not the signature, necessarily. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 12 Study Guide Objective: Implement the Procurement of Project Resources
C is correct because a T&M contract must have a not-to-exceed (NTE) clause, otherwise the cost can spin out of control. A is incorrect because while a signature is needed on most contracts, a T&M demands an NTE clause... or else. B is incorrect because not all T&M contracts require an end date. D is incorrect because changes can spur new contracts, be covered by the existing T&M contract, or have addendums. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the Home Automation Project. You are uncertain what the fee will be for wiring the home with bundled cable so you hire a vendor to examine the home and create an estimate for the SOW you’ve prepared. You’ll use this estimate from the vendor to measure all other estimates from vendors that want to bid on the installation of the bundled cable. What is this estimate called?
A. Budget estimate B. Definitive estimate C. Good faith estimate D. Should-cost estimate |
Answer: D
Hint: Woulda-coulda. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 12 Study Guide Objective: Implement the Procurement of Project Resources
D is correct because a should-cost estimate, also known as an independent estimate, is prepared in-house or by a third party. This estimate then measures all other estimates against it. A is incorrect because this defines the mid-stage estimate for the entire project. B is incorrect because this is the most-detailed estimate based on the WBS for the entire project. C is incorrect because this is not a valid term. |
|
|
You have invited seven vendors to create proposals for a portion of your project work. As part of the invitation, however, the vendor must have a mechanical engineer on their project team or they cannot offer a proposal. The mechanical engineer requirement is an example of which one of the following?
A. Resource constraint B. Resource requirement C. Screening system D. Project requirement |
Answer: C
Hint: Not a constraint. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 12 Study Guide Objective: Implement the Procurement of Project Resources
C is correct because the requirement to have the mechanical engineer “screens out” the vendors that do not qualify. A, B, and D are all incorrect because in this instance the mechanical engineer is needed to offer a proposal. The question does not say the project requires the mechanical engineer at all—only to submit a proposal. |
|
|
Management would like you, the project manager, to create a chart showing when resources will be utilized on your project. What chart is management asking you to create?
A. A Gantt chart B. A resource histogram C. A network diagram D. A Pareto chart |
Answer: B
Hint: Not Henry. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Manage Resource Allocation
B is correct because a resource histogram is a bar chart that shows utilization of resources across time. A is incorrect because a Gantt chart, from Henry Gantt, is a scheduling tool that shows project activities across a timeline or calendar. C is incorrect because a network diagram shows the flow of activities. D is incorrect because a Pareto chart is typically used in quality control activities and shows categories of failure within a project. |
|
|
You are the project manager in a projectized organization. You believe in the Expectancy Theory. Which one of the following mechanisms will promote and reinforce desired behavior from your project team?
A. Expert judgment B. Lectures and motivational speeches C. Rewards D. Punishments for poor project performance |
Answer: C
Hint: Oh goody! Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Manage Resource Allocation
C is correct because rewards and recognition are ideal methods for promoting desired behavior. A is incorrect because expert judgment won’t reinforce desired behavior from the project team. B is incorrect because lectures and motivational speeches are not as effective as rewards and recognition systems. D is incorrect because there’s no incentive to do well, only an incentive to not do poorly. |
|
|
A project team comprised of people that spend little or no time meeting face to face is known as what?
A. A dysfunctional project team B. A non-collocated project team C. A virtual project team D. An E-team |
Answer: C
Hint: Virtually possible. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Manage Resource Allocation
C is correct because virtual teams are comprised of people that don’t spend much time working face to face with other project team members. A and D are incorrect because these terms are not valid. B is incorrect because this describes a project team that is not all located in one locale. |
|
|
You are a project manager consultant for a new project that will utilize a virtual team. Virtual teams make all of the following possible except for which one?
A. Including people with mobility handicaps B. Including people that work from home offices C. Allowing projects to progress that otherwise would have been cut due to travel expenses D. Reducing the amount of time dedicated to meetings and communications |
Answer: D
Hint: You still have this. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Manage Resource Allocation
D is correct because this is a false statement about virtual teams. A, B, and C are incorrect because each is a true statement about virtual teams. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the KHY Project. This project involves 45 project team members from across your matrix-structured organization and will last for 18 months. You have requested a central meeting room for communications, project information, testing equipment, and other project-related activities. This room is called what?
A. A resource request B. A facility resource request C. A war room D. The project headquarters |
Answer: C
Hint: You don’t declare it. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Study Guide Objective: Manage Resource Allocation
C is correct because a war room is a meeting room for project support. A, B, and D are incorrect because these terms are not valid. |
|
|
Your project is slipping and you would like to add more labor to complete effort-driven activities sooner. What is this called?
A. Cost increase B. Crashing C. Risk increase D. Fast tracking |
Answer: B
Hint: Kaboom! Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 Study Guide Objective: Manage Resource Allocation
B is correct because crashing means that the project manager adds resources in efforts to complete activities faster. A is incorrect because this is a typical effect of crashing. C is incorrect because this is a typical effect of fast tracking. D is incorrect because fast tracking allows phases to overlap. |
|
|
You are the project manager for your organization and you’ve told management that you’ll be using the critical chain method for this project. Management is unaware of this approach and they want to know more about it. What is the critical chain method?
A. It utilizes just-in-time ordering. B. It finds the longest path to project completion and allows float on the other activities in the project. C. It is a schedule network analysis that accounts for limited resources. D. It is a project network diagram with the project float exposed. |
Answer: C
Hint: Not CPM. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 Study Guide Objective: Manage Resource Allocation
C is correct because the critical chain method accounts for limited resources. For example, a structural engineer may be needed on two concurrent activities, but she can only work on one activity at a time. A is incorrect because this scheduling method is not applicable to this scenario. B is incorrect because this describes the critical path method. D is incorrect because this is the critical path method. |
|
|
Several project team members want to schedule vacation days in July, but you need to confirm if Jane, a network engineer, has already scheduled her vacation. Which calendar will tell you, the project manager, if Jane is available on July 17?
A. The resource calendar B. The project calendar C. The project schedule D. The HR calendar |
Answer: A
Hint: Jane’s a resource. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 Study Guide Objective: Manage Resource Allocation
A is correct because Jane is a resource and resource calendars are specific to each resource on the project. B is incorrect because the project calendar determines when project work is allowed. C is incorrect because the project schedule shows the mapping of the project work. D is incorrect because this term is not valid. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the KJP Project. You, the project team, and the project sponsor are working together to complete quality management planning. The stakeholder has compared your current project scope to a recently completed project that utilized Six Sigma techniques in their project. This is called what?
A. Quality assurance B. Quality control C. Statistical analysis D. Benchmarking |
Answer: D
Hint: Comparisons. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Implement Quality Management Plan
D is correct because benchmarking is when one project is compared to another. A is incorrect because QA is the organization-wide program for quality. B is incorrect because QC is an inspection to determine the existence of quality. C is incorrect because statistical analysis is the examination of statistics and production. |
|
|
Your project team does not know how to install the new materials you’ll be using in your project. You hire a trainer to teach the team how to install the project. The costs of the trainer are described as what?
A. The cost of conformance to quality B. Sunk costs C. Team development D. The cost of doing business |
Answer: A
Hint: Got to do it, or else. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Implement Quality Management Plan
A is correct because training is an example of the cost of conformance to quality. If you don’t train the project team, then quality will suffer. B is incorrect because sunk costs describes monies spent on project work that has failed and that cannot typically be recovered. C is incorrect because team development involves activities to facilitate team cohesion. The costs, in this question, are not attributed to team development. D is incorrect because this is not an example of the costs of doing business. These costs are unique to this project. |
|
|
You are the project manager of a project that must operate by your organization’s quality policy. Management has decided to examine your project’s processes to determine if you are following the quality policy. This review process is known as what?
A. Quality control B. Quality assurance C. Quality audit D. Quality planning |
Answer: C
Hint: Looking for proof of compliance. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Implement Quality Management Plan
C is correct because a quality audit examines a project to determine if the project is complying with an organization’s quality policies. A is incorrect because QC examines the project work to determine the quality of the project deliverables. B is incorrect because QA is the company quality policy. D is incorrect because quality planning constitutes those activities that determine how the project will adhere to the quality demands of the organization. |
|
|
Quality control and quality assurance are needed in every project. Which one of the following is an example of quality assurance?
A. A Pareto chart B. A control chart C. Inspection D. A Six Sigma program |
Answer: D
Hint: Started at Motorola. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Implement Quality Management Plan
D is correct because Six Sigma is a quality assurance program. A, B, and C are incorrect because each is a quality control tool. |
|
You are the project manager of the NJQ Project and you have created a chart as in the exhibit. What is the area highlighted in the chart called?
A. Out of control B. Within control C. Rule of Seven D. Improvement of quality
|
Answer: C
Hint: It’s not out. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Implement Quality Management Plan
C is correct because the result of seven measurements in a row on one side of the mean in a control chart is called the “Rule of Seven.” This is an assignable cause. A is incorrect because out of control means one measurement exceeds the control limits. B is incorrect because in control means that the result of one measurement stayed within the control limits. D is incorrect because the Rule of Seven doesn’t always signal quality improvement. It could, in some instances, signal that the mean is set too low for the project. |
|
|
You are a project manager and you want to perform some analysis of defects and problems that have been discovered in the project. Which chart can reveal factors that might be linked to potential problems within your project?
A. An Ishikawa diagram B. A control chart C. A Pareto chart D. A flowchart |
Answer: A
Hint: Fishy. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Implement Quality Management Plan
A is correct because an Ishikawa diagram, also called a cause-and-effect diagram, reveals potential problems that contribute to effects. B is incorrect because control charts show if a project is stable and predictable. C is incorrect because Pareto charts show categories of failure. D is incorrect because flowcharts help analyze how problems occur. |
|
|
You are the project manager of a large project that spans the United States. Your project team is non-collocated so your communication and travel demands are high. You’ve made it known that no changes can enter the project unless the stakeholder wanting the change completes a change request through your web-based change request form. It has come to your attention that Scotty, a developer in Phoenix, has been allowing stakeholders to request changes to his work. What must you do in this scenario?
A. Implement corrective action so Scotty won’t allow any more changes to the project work without using the change control system. B. Inspect the changes that have entered the project and then have Scotty reverse any changes you do not approve of. C. Meet with Scotty and his supervisor to discuss what discipline is most appropriate. D. Meet with your project team members and key stakeholders in Phoenix and discuss in detail the change management processes you’ve established. |
Answer: A
Hint: Poor Scotty. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 3 Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Changes
A is correct because you want to implement corrective actions to prevent the problem from happening again. B is incorrect because you are not following the change control system or preventing the problem from happening again. C is incorrect because you are Scotty’s supervisor when it comes to project discipline. D is incorrect. While this choice seems appropriate, not all of the project team members or the stakeholders are circumventing the change control system—just Scotty in this instance. As the project manager, you need to address the problem directly. In addition, the question states that all of the project team members and stakeholders are located throughout the United States, not just in Phoenix. |
|
|
Congratulations! You’ve finished the project work and are performing quality control. You are about to enter scope verification and management would first like to examine all of the changes that have been requested and their status. Management wants to see which changes have been approved and declined. Where can you find all of this information?
A. You will only have records of the change requests that have been approved as declined change requests are discarded. B. You will only have records of the change requests that have been declined because all approved changes are incorporated into the project scope and the time and cost baselines are updated. C. The Configuration Management System D. The Risk Register |
Answer: C
Hint: You better have both. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Changes
C is correct because the Configuration Management System included the process for submitting, tracking, reviewing, and approving proposed changes. A and B are incorrect because you will keep declined and approved change requests. D is incorrect because this is not relevant with change request tracking. |
|
|
Where will a project manager find information on how the project’s product characteristics can be changed?
A. The project charter B. The Configuration Management System C. The project scope D. The change control board |
Answer: B
Hint: Don’t be bored. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Changes
B is correct because that’s what the Configuration Management System does. A is incorrect because the project charter authorizes the project work. C is incorrect because the project scope defines the project work. D is incorrect because the CCB may approve or decline changes based on the change control system the project is using. |
|
|
You have a project that must be finished by July 30 or your organization will have to pay fines and penalties. Management is adamant that you do not exceed more than $125,000 for the project budget. The project is nearing completion but you will likely miss the target end date. What can you do to meet the project end date without spending more dollars on the project?
A. Nothing. You will have to spend more money to complete on time because you will need to buy more labor. B. Crash the project. C. Add lag to the project. D. Trim the project scope of everything that is not affected by the fines and penalties. |
Answer: D
Hint: Lose the fat. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Changes
D is correct because while it does assume there are things to trim in the project scope, it is the only option that won’t increase costs and complete the project by the scheduled end date. A is incorrect because this statement is not true. B is incorrect because crashing the project means you’ll be adding labor, which will drive costs. C is incorrect because lag is positive time (or waiting time), so this will actually cause the project to be late. |
|
|
Your project continues to stall because of additional changes to the project scope. You’ve asked that all changes to the project scope stop unless the changes are truly needed for the success of the project scope as it was approved. Management, however, has demanded a change to the project. What must be examined?
A. The change request and its impact on the entire project B. The change request and the cost to implement the change C. The change request and the time to implement the change D. The change request and the purpose for the change |
Answer: A
Hint: Integrated Change Control. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Changes
A is correct because the change may affect all or some of the knowledge areas: time, cost, quality, communications, risk, human resources, procurement. B is incorrect because it only addresses cost. C is incorrect because it only addresses time. D is incorrect because it only addresses the change request. |
|
|
Your project team has incorporated some minor changes into their project work as directed by the customer. You agree that these changes are needed. What is this an example of?
A. Fluid change control B. Integrated change control C. Expert judgment D. Scope creep |
Answer: D
Hint: It’s not good. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Changes
D is correct because uncontrolled changes are called scope creep. A is incorrect because this term is not valid. B is incorrect because integrated change control requires documented changes to follow a set of rules of reviewing and approving change requests. C is incorrect because expert judgment is when an expert helps you, the project manager, make the best decision. In this instance, no one helped with the decision, it was just implemented without any review or consideration. |
|
|
Holly is the project manager of the UIM Project for her company. A new change request has moved through the change control board and it was approved. Now Holly needs to incorporate the change into the project to reflect the additional scope requirements. All of the following are results of approved changes except for which one?
A. Project charter updates B. Project scope updates C. WBS updates D. WBS dictionary updates |
Answer: A
Hint: Not the big one. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Changes
A is correct because the charter is not updated as a result of an approved change request. B is incorrect because the scope may be updated as a result of an approved change request. C is incorrect because the scope may be updated as a result of an approved change request. D is incorrect because the scope may be updated as a result of an approved change request. |
|
|
Project management requires cost control, which can mean tradeoffs and additional funds for changes. Currently, your project is running over on costs due to unknown unknowns. What can you do?
A. Nothing because unknown unknowns are risks. B. Propose to management to obtain more funds to counteract the unknown unknowns. C. Propose to management to utilize the management contingency reserve. D. Prepare an assessment of why the project has failed due to the unknown unknowns. |
Answer: C
Hint: Only for emergencies.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Actions and Workarounds
C is correct because the management contingency reserve is an amount of funds set aside for unplanned events that consume the project budget.
A is incorrect because while unknowns may be risks, this is not the best response. B is incorrect because it does not answer the question as completely as C. D is incorrect because the project has not failed at this point. |
|
|
Bob is a project manager in a functional organization. He disagrees with the project sponsor on how some activities of the project should commence. The project sponsor, however, insists that Bob have the project team begin working on the project. What should Bob do?
A. Instruct the project team to begin working on the project. B. Object to the project sponsor’s manager. C. Document the disagreements in a formal report for lessons learned when the project fails. D. Instruct the project team to work only on critical path activities. |
Answer: A Hint: No fun for the project manager.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 2Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Actions and Workarounds
A is correct because the project sponsor is in charge in a functional organization. In addition, it’s permissible to have disagreements regarding the project work as long as the disagreements don’t hinder the project from moving forward.
B is incorrect because Bob is operating in a functional organization. C is incorrect because there’s no reason for Bob to document the issues in a formal report. In addition, this answer implies that the project will fail while the question does not stress the magnitude of the problem or disagreement. D is incorrect because the project team should work on the activities as planned, not only the activities on the critical path. |
|
|
You need a vendor to ship a piece of software for your project immediately so your project team can install the software over the holiday weekend. Because of the holiday weekend, however, no one will be able to accept the package when the delivery company attempts to deliver the package. Which one of the following is an example of an appropriate workaround?
A. Don’t start the project work activities until after the holiday when the mailroom can accept the package. B. Fly to the vendor’s location to pick up the package in person. C. Have the vendor deliver the software to one of the team member’s homes so they have the software delivered directly to them. D. Demand a discount from the vendor because of the shipping error. |
Answer: C Hint: There’s no error.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Actions and Workarounds
C is correct because this workaround allows the project team member to receive the software before the project is scheduled to start.
A is incorrect because this will delay the project. B is incorrect because this workaround will increase costs and would be a waste of time. D is incorrect because there is no error with the shipping. A discount would not get the software to the project team member’s home as needed. |
|
|
The project vendor you selected to provide materials for your project cannot deliver. You need the materials by the end of the week. The change control board agrees that you should call another vendor that has slightly higher prices but can deliver as needed. This is an example of which one of the following?
A. A workaround B. A contingency plan C. A transference D. Mitigation |
Answer: A
Hint: It’s not planned.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Actions and Workarounds
A is correct because this is an example of a workaround. B is incorrect because a contingency plan is pre-planned, whereas a workaround is a response to an immediate risk. C is incorrect because transference transfers the risks to another party. D is incorrect because mitigation is a planned attempt to reduce or eliminate the impact of a known risk. In this instance, the risk was not known. |
|
|
The project team has completed some of the project work incorrectly. You’ve instructed the project team to redo the work. What must happen next?
A. Conduct an analysis of the delay because of the rework. B. Conduct an analysis of the cost increase because of the rework. C. Review each project team member’s performance. D. Review the defect repair. |
Answer: D Hint: Make sure everything is correct.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Actions and Workarounds
D is correct because the repair must be reviewed for accuracy.
A is incorrect because the repair must be correct before the project can move forward. If the repair is assumed to be correct, then the review of the time delay may be inaccurate because of future rework, waste, or a series of failures because of the inaccurate rework. B is incorrect because the repair must be reviewed for accuracy first. C is incorrect because this is not the most pressing issue at this point in the project. |
|
|
Quality control is managed by Terry, a quality engineer on your project. Terry reports that she’ll need some time and resources to complete quality control on the project deliverables. Terry also reports the tools she’ll use as part of the quality control activities. All of the following are quality control tools Terry could use except for which one?
A. Control charts B. Baseline updates C. Flowcharting D. Inspection |
Answer: B
Hint: No changes.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8Study Guide Objective: Implement Approved Actions and Workarounds
B is correct because this is not a quality control tool. A baseline update reflects changes to the project’s scope, cost, or schedule baseline.
A is incorrect because this is a quality control tool. Control charts show fluctuations from the project’s mean. C is incorrect because this is a quality control tool. Flowcharts show the flow of work, information, or data through a defined system. D is incorrect because this is a quality control tool. Inspection is the primary quality control tool Terry will use. |
|
|
As a project manager, you may rely on organizational theories to help you better manage the project team. Which organizational theory believes that an absence of hygiene agents will demotivate a project team?
A. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs B. Ouchi’s Theory Z C. Herzberg’s Theory of Motivation D. McGregor’s X and Y |
Answer: C
Hint: Not an ouchie.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9Study Guide Objective: Improve Team Performance
C is correct because Herzberg’s Theory of Motivation states that hygiene agents, such as a paycheck, won’t motivate people, but their absence will demotivate.
A is incorrect because Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs identifies the seven needs we all pursue. B is incorrect because Ouchi’s Theory Z is based on the Japanese management style. D is incorrect because McGregor’s X and Y is a description of management’s view of its employees. The X believe that project team members must be micromanaged. The Y believe that project team members can be self-led. |
|
|
Which organization theory believes that project teams can be self-led?
A. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs B. Ouchi’s Theory Z C. Herzberg’s Theory of Motivation D. McGregor’s X and Y |
Answer: D
Hint: Not an ouchie.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9Study Guide Objective: Improve Team Performance
D is correct because McGregor’s X and Y is a description of management’s view of its employees. The X managers believe that project team members must be micromanaged. The Y managers believe that project team members can be self-led.
C is incorrect because Herzberg’s Theory of Motivation states that hygiene agents, such as a paycheck, won’t motivate people, but their absence will demotivate. A is incorrect because Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs identifies the seven needs we all pursue. B is incorrect because Ouchi’s Theory Z is based on the Japanese management style. |
|
|
McClelland’s Theory of Needs states that there are three needs that we all have. The needs are developed over time and through life experiences. What is the name of the analysis which determines an individual’s driving need?
A. The Myers-Brigg test B. The Thematic Apperception Test C. The Big Five Personality Test D. The Accurate Personality Test |
Answer: B
Hint: Tit for TAT.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9Study Guide Objective: Improve Team Performance
B is correct. The Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) can determine if power, achievement, or affiliation drives an individual.
A is incorrect. The Myers-Brigg test is based on the work of Carl Jung, not McClelland. C is incorrect. The Big Five Personality Test was developed by Paul Costa and Robert McCrae. D is incorrect because this is not a valid test for determining driving needs. |
|
|
June is the project manager of her project and wants to recognize team members that have contributed to the project work in a significant way each month. June decides that she’ll award one team member the title of “Team Member of the Month.” This person will get to park in a reserved parking space and will receive one paid day off from the project. What is the danger in June’s plan for rewards and recognition?
A. There is no danger. This is an example of a reward and recognition system. B. Only project team members that have activities during the month can be awarded the title. C. Only one team member can be awarded the title per month. D. The project manager chooses the team member, not the project team. |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s not good for everyone.Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9Study Guide Objective: Improve Team Performance
C is correct because this is an example of a zero sum reward. Only one team member can be awarded the title.
A is incorrect because this is an example of a zero sum reward. B is incorrect because it doesn’t fully answer the question. D is incorrect because this is not the issue of the reward. Regardless of who chooses the reward, only one team member can receive the award. |
|
|
All of the following are true statements about the staffing management plan except for which one?
A. The staffing management plan provides information about when project team members may be released from the project team. B. The staffing management plan provides information about staff acquisition. C. The staffing management plan provides information about project safety. D. The staffing management plan provides information about project quality. |
Answer: D Hint: Isn’t there another plan for this one?Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9Study Guide Objective: Improve Team Performance
D is correct because this is a false statement about the staffing management plan. The quality management plan defines quality expectations.
A, B, and C are incorrect because each is a true statement about the staffing management plan. |
|
|
You are the project manager for your organization which will utilize contract labor on your project. The labor will be part of a union workforce. Which plan defines union contracts?
A. The project plan B. The procurement management plan C. The staffing management plan D. The risk management plan |
Answer: C
Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 9 Hint: Not risky.Study Guide Objective: Improve Team Performance
C is correct because the staffing management plan does define compliance issues with union contracts.
A is incorrect because this is too broad an answer. B is incorrect because this plan defines the procurement policies of the organization. D is incorrect because this plan defines risk management for the project. |
|
|
You are a project manager for your organization. Your project has a BAC of $400,000 and is expected to last one year. The project work is scheduled to be completed in equal amounts each month. Currently, the project is in month three but is only 20 percent complete. You have spent $35,000 to complete the work. What is the earned value for this project?
A. Negative $20,000 B. $80,000 C. $100,000 D. Not enough information to know |
Answer: B Hint: Find the percent complete. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7Study Guide Objective: Measure Project Performance
B is correct. The earned value for this project is 20 percent complete. The formula is EV= % complete × BAC.
A is incorrect. The EV is not a negative number because it is 20 percent complete. C is incorrect because $100,000 is the planned value amount. D is incorrect. There is enough information to calculate the formula. |
|
|
You are a project manager for your organization. Your project has a BAC of $400,000 and is expected to last one year. The project work is scheduled to be completed in equal amounts each month. Currently the project is in month three but is only 20 percent complete. You have spent $35,000 to complete the work. What is the planned value for this project?
A. $20,000 B. $35,000 C. $80,000 D. $100,000 |
Answer: D Hint: Find out how much should have been spent. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7Study Guide Objective: Measure Project Performance
D is correct. The planned value is the amount the project should have spent to reach this point in the schedule. Because the project is schedule to last one year with the work completed in part each month, month three represents 25 percent of the project, or $100,000.
A is incorrect because $20,000 is not the planned value. B is incorrect because $35,000 is the actual cost. C is incorrect because $80,000 is the earned value. |
|
|
You are a project manager for your organization. Your project has a BAC of $250,000 and is expected to last ten months. Currently the project is in month six and is 40 percent complete, but the project was expected to be 60 percent complete by this time. You have spent $125,000 to complete the work. What is the cost performance index of the project?
A. 80 B. 1.25 C. $125,000 D. .80 |
Answer: D Hint: Double-check your work. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7 Study Guide Objective: Measure Project Performance
D is correct. The cost performance index is calculated by dividing the earned value by the actual costs. In this instance, the formula is CPI = 100,000/125,000. This results in .80.
A is incorrect. The CPI is .80, not 80. B is incorrect because this is not the right value. C is incorrect. The CPI is not a dollar amount, so this value is incorrect. |
|
|
You are a project manager for your organization. Your project has a BAC of $250,000 and is expected to last ten months. Currently the project is in month six and is 40 percent complete, but the project was expected to be 60 percent complete by this time. You have spent $125,000 to complete the work. What is the schedule performance index of the project?
A. .80 B. .67 C. $67,000 D. $80,000 |
Answer: B Hint: Not a dollar amount. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7 Study Guide Objective: Measure Project Performance
B is correct. The schedule performance index (SPI) is calculated by dividing the earned value by the planned value. In this instance, the formula is $100,000/150,000 = .67.
A is incorrect. This is the value of the cost performance index. C and D are incorrect because the SPI is not a dollar amount. |
|
|
You are the project manager for your organization and you’re examining several projects you’re managing for your company. In your analysis, you’ve noticed that one of your projects has an SPI of .80. A project with an SPI of .80 means what?
A. The project is behind schedule. B. The project is ahead of schedule. C. The project is losing money. D. The project is 80 percent complete. |
Answer: A Hint: SPI is the schedule performance index. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7 Study Guide Objective: Measure Project Performance
A is correct. A schedule performance index of .80 means the project is behind schedule. The closer to “1” the SPI is, the better the project.
B is incorrect. An SPI of .80 means the project is behind schedule, not ahead. C is incorrect. While the project likely will result in being over budget due to the labor demands to complete the project, the SPI deals with the project schedule. D is incorrect. An SPI does not reflect the percent complete of the project. |
|
|
You are the project manager for your organization and you’re examining several projects you’re managing for your company. In your analysis, you’ve noticed that one of your projects has a CPI of .98. A project that has a CPI of .98 means what?
A. The project is late. B. The project is making money. C. The project has to spend one dollar for every 98 cents worth of work it receives. D. The project is 98 percent complete. |
Answer: C
Hint: CPI is the cost performance index. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7 Study Guide Objective: Measure Project Performance
C is correct. A project with a CPI of .98 has to spend one dollar for every 98 cents worth of work it receives.
A is incorrect. There is no evidence that the project is late. B is incorrect because the project is actually losing money with this CPI, not making it. D is incorrect because a CPI of .98 does not mean the project is 98 percent complete. |
|
|
You are the project manager of a project to install new light fixtures throughout several factories. The project is expected to last one year and has a BAC of $750,000. The project is now in month four and has a CPI of .89. Which one of the following statements is true about this project? A. The project is performing well. B. The project spends one dollar for 89 cents of work. C. The project will likely finish under budget. D. The project will likely finish in alignment with the cost baseline. |
Answer: B
Hint: CPI = EV/AC Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7 Study Guide Objective: Measure Project Performance
B is correct. The project with a CPI of .89 is not doing too well. For every dollar the project spends, it loses 11 cents.
A is incorrect. The project is not performing well. C is incorrect. The project will likely finish over budget. D is incorrect. The probably won’t be in alignment with the cost baseline. |
|
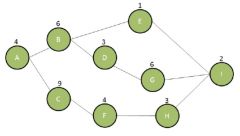
Examine the exhibit. You are the project manager for your organization. You’re working with your project team to help them understand the concept of the critical path in a project. If the exhibit represents your project, what is the critical path?
A. ABEI B. ABDGI C. ACFHI D. IGDBA
|
Answer: C
Hint: Find the longest path to completion. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 6 Study Guide Objective: Execute Tasks Defined in Project Plan
C is correct. The critical path is the longest path of duration from the project start to its completion. In this example, the critical path is the sum of duration for tasks ACFHI at 22 days.
A is incorrect. The path of ABEI is only 13 days. B is incorrect. The path of ABDGI is 21 days. D is incorrect. To find the critical path, add up the duration of the path moving forward, not backward. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the NHQ Project for your company. You are working with your project team and the project sponsor to create a stakeholder management strategy. You want to determine the needed level of interaction among the project stakeholder. What document will best help you complete this task?
A. The project charter B. The stakeholder registry C. The stakeholder management plan D. The project management plan |
Answer: C
Hint: You’re executing a plan. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 13 Study Guide Objective: Manage Stakeholder Engagement
C is correct. The stakeholder management plan is an input to management stakeholder engagements. This plan defines the needed levels of interactions of the project stakeholders.
A is incorrect. The project charter authorizes the project and the project manager, but it doesn’t define the interactions among the project stakeholders. B is incorrect. The stakeholder registry defines the project stakeholders, their communication preferences, and project concerns. D is incorrect. The stakeholder management plan is part of the project’s management plan, but this isn’t the best answer for the question because the stakeholder management plan is most specific. |
|
|
Harry is the manager of a software development project for his company. In this project, Harry is utilizing an issue log. What should Harry do with the issue log when issues have been resolved?
A. Delete the issue log. B. Delete the resolved issues from the log. C. Update the project risk register because the issue is no longer relevant to the project success. D. Update the issue log. |
Answer: D
Hint: Don’t delete anything. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 13 Study Guide Objective: Manage Stakeholder Engagement
D is correct. When an issue has been resolved, Harry should update the issue log to reflect the status of the issue as resolved.
A is incorrect. The issue log should not be deleted because it will become part of the organizational process assets. B is incorrect because the issue should be marked as resolved, not deleted. C is incorrect because the issue log is separate from the risk register. |
|
|
You are preparing for stakeholder engagement in your project. All of the following items will be needed as part of stakeholder engagement except for which one?
A. The project management plan B. The issue log C. Work performance data D. The risk management plan |
Answer: D
Hint: Not risky. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 13 Study Guide Objective: Manage Stakeholder Engagement
D is correct because the risk management plan is not an input to the control stakeholder engagement process. There are four inputs to this process: the project management plan, issue logs, project documents, and work performance data.
A is incorrect because the project management plan is an input to the control stakeholder engagement process. B is incorrect because the issue log is an input to the control stakeholder engagement process. C is incorrect because work performance data is an input to the control stakeholder engagement process. |
|
|
Management has compared your project to a similar project that’s just been completed in your organization. This finished project was deemed successful. This is benchmarking. What is the goal of this comparison?
A. To provide a basis by which management may measure performance of your project. B. To provide a basis by which management may measure all projects. C. To provide a basis by which management may measure the completed project. D. To provide a basis by which management may measure project managers. |
Answer: A
Hint: Not the project managers. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Measure Project Performance
A is correct because management wants to determine how your project is fairing in comparison to a completed project that they’ve already deemed successful.
B is incorrect because benchmarking is most useful for similar projects, though it is possible to benchmark projects that are not in the same discipline. C is incorrect because management has already deemed the finished project as successful. D is incorrect because the goal is to measure your project, not you. |
|
|
In the early stages of a project, this event is easy to accept. Later in the project it is difficult to accept. What is the event?
A. Change B. Risk C. Team development D. Scope verification |
Answer: A
Hint: The further the project is from completing, the higher the risk and uncertainty. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 2 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
A is correct. Change is easily accepted in the beginning of a project. As the project moves toward completion, change is harder to incorporate.
B is incorrect. Risk is only accepted based on its impact of the project and the performing organization’s utility function. Recall that the utility function is an organization’s willingness to accept risk. C is incorrect. Team development happens throughout the project. D is incorrect. Scope verification happens throughout the project at phase completion, at major project deliverables, and at project completion. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the NHB Project. You’ve just learned that the cost of materials will increase by 10 percent due to a hurricane along the Gulf Coast. You would like to update the cost baseline to reflect these unanticipated changes. What system will allow you to make these changes?
A. The change control system B. The cost change control system C. The change control board D. The cost management system |
Answer: B
Hint: It’s money. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 7 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
B is correct because procedures on how to change the cost baseline are documented in the cost change control system.
A is incorrect because this does not answer the question as completely as B. C is incorrect because the CCB may be part of the change control system, but B answers the question completely. D is incorrect because this term is not valid. |
|
|
Charles, the carpenter for the XHG project, has made a change to the wood floor he’s installing. He decided that the floor should be installed at an angle because of a doorway in the living room. You inspect the installed wood floor and agree with his decision. This is an example of which one of the following?
A. Expert judgment B. Ineffective change control C. Corrective action D. Self-led teams |
Answer: B
Hint: It’s not good. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
B is correct because the change was made by Charles on his own accord. The change control system was not followed.
A is incorrect because expert judgment is using an expert to help make the best decision. No consultation was done on the change. C is incorrect because corrective action is correcting a problem to get the project work back into scope. D is incorrect because Charles did not consult, document, or involve the project team in his decision. |
|
|
You are the project manager for your organization and you’re working with the project team to define the change control system. You want to capture the correct information when changes are presented and analyzed for your project. Which one of the following must be completed for each change that is proposed for a project?
A. The project charter must be examined. B. The project life cycle costs must be reviewed. C. The change must be reviewed for any associated risks. D. The benefit/cost ratio must be reviewed. |
Answer: C
Hint: Review it. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
C is correct because integrated change control calls for all of the knowledge areas, including risks, to be reviewed for the impact of the proposed change.
A is incorrect because the charter does not have to be examined. B is incorrect because the life cycle costs concern the cost of the project’s deliverable once it’s in production. In some instances, life-cycle costing may be appropriate, but not in every instance of a change request. D is incorrect because benefit/cost ratios are a method for selecting projects, not evaluating change requests. |
|
|
You are the project manager of a software development project. In this project, you will approve or decline proposed changes before they are incorporated into the project plan. You have recently approved a change that will increase the project’s costs. What must you do next?
A. Prepare a cost variance report. B. Examine the overall impact of the change request on the project. C. Examine the direct costs of the change. D. Change the project’s cost baseline to reflect the added change. |
Answer: D
Hint: It’s about change. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
D is correct because the project’s baselines must be changed to reflect the added change.
A is incorrect because there’s no reasons to create a variance report; it’s a change not a cost overrun. B is incorrect because this is part of the process to approve the change request. The change request has already been approved in this instance. C is incorrect because this is part of the process to approve the change request. The change request has already been approved in this instance. |
|
|
A vendor has proposed a change to the work you’ve contracted them to do for your project. The vendor says it is because of the hardware installed on your company’s server. Your hardware technician says this is not true, that the hardware installation is accurate and there is no need for the change. What should you do with the proposed change?
A. Discard the change request and ask the vendor to continue as planned. B. Accept the vendor’s proposed change because it’s their contract to complete the work. C. Enter the change request into the SOW update for consideration. D. Add the change request to the project’s change control system for consideration. |
Answer: D
Hint: Add it. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
D is correct because this is a proposed change. It should be documented and reviewed for consideration. Just because the change is considered doesn’t mean that it will necessarily be implemented.
A is incorrect because discarding the change offers no documentation in case the change is actually needed. B is incorrect because the change should be added to the change control system for review, not just assigned to the vendor to complete. C is incorrect because changes don’t go into the SOW at this point. |
|
|
You are the project manager for an organization completing a project for your customer. Your boss approaches you and asks that you add a few features to the deliverable your project team is creating as part of the project. What should you do next?
A. Instruct the team to add the features. B. Consult with the customer about the features your project team is adding to the project scope. C. Ask the customer if they would like the features as part of the deliverable. D. Add the features but document them in an approved change request. |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s not your deliverable. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
C is correct because the customer must approve any changes to the project deliverable.
A is incorrect because the customer must first approve proposed changes. B is incorrect because the project manager must gain approval from the customer in order to make the changes. D is incorrect because it circumvents the change management process. |
|
|
Your functional manager asks you to add features to the project scope to consume the remaining dollars in the project budget. This is an example of which one of the following?
A. Gold plating B. Change control C. Functional management D. Cost of quality |
Answer: A
Hint: Sounds nice, but it’s not. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
A is correct because adding features to the project scope just to consume the project budget is called gold plating.
B is incorrect because this does not answer the question as completely as A. C is incorrect because the organizational structure does not change that this is gold plating. D is incorrect because this answer is not relevant to this question |
|
|
You are the project manager of a project that has a preset budget and must be completed within six months. You’ve completed the first phase of your project. The stakeholder, however, wants to know why one of the changes you and he discussed was not implemented into the deliverable. During the original conversation about the change, the stakeholder wanted to perform a cost-benefits analysis, which he reported the results of to you. What’s your response?
A. The change was not needed. B. The change would have cost too much. C. The change would have taken too long to deliver. D. The change request was never documented for the change control system. |
Answer: D
Hint: Do it right. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
D is correct because in the change control system all changes should be formally documented. Undocumented change requests should not be processed or implemented.
A is incorrect because the change may have been needed but the failure to follow the change control system prevents the change from entering the project scope. B is incorrect because there’s no mention of how much the change would cost the project. C is incorrect because there’s no mention of how much additional time the change would require. |
|
|
Which one of the following statements about changes to the project scope is correct?
A. All changes should be formally documented. B. All changes require additional project time. C. All changes require additional project funding. D. All changes follow the rules of the change control system. |
Answer: A
Hint: Ask yourself, “Do all changes require this?” Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Verify and Manage Changes to the Project
A is correct because all changes, approved or otherwise, should be formally documented.
B is incorrect because not all changes require additional time. C is incorrect because not all changes require additional funding. D is incorrect because not all changes, unfortunately, follow the change control system. Some changes are unauthorized, but they occur anyway. |
|
|
John is the project manager of the BHQ Project. This project is to create new software for a client. John insists on a documented approach to quality control for the software deliverable. Quality control focuses on what activity?
A. Quality assurance B. Quality management C. Inspection D. Acceptance |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s work. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
C is correct because quality control focuses on prevention and inspection.
A is incorrect because quality assurance is a management process to ensure that the project employs all processes to meet requirements. B is incorrect because this term is not valid. D is incorrect because this term applies to scope verification. |
|
|
You are the project manager for your organization and you’ve identified several mistakes in the project deliverables. You’d like to investigate the issue more closely and your project sponsor recommends you create an Ishikawa diagram. What is an Ishikawa diagram?
A. A control chart B. A fishbone diagram C. A scatter diagram D. A Pareto chart |
Answer: B
Hint: Hooked you. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
B is correct because an Ishikawa diagram is also called a fishbone diagram. It’s also known as a cause-and-effect diagram.
A is incorrect because a control chart is used to predict performance. C is incorrect because a scatter diagram shows the pattern of relationship between two variables. D is incorrect because a Pareto chart shows categories of failure. |
|
Examine the exhibit. What is the highlighted area in the following chart called?
A. The mean B. The Rule of Seven C. The control limit D. Six Sigma
|
Answer: B
Hint: Not Sigma. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
B is correct because whenever there are seven measurements in a row all on one side of the mean, this is called the Rule of Seven. It is an assignable cause.
A is incorrect because the mean is represented by the solid bar in the middle of the control chart. C is incorrect because the control limits are the top and bottom lines in the control chart. D is incorrect because Six Sigma is a quality assurance program invented by Motorola. |
|
|
Management wants a histogram that demonstrates the number of defects that were caused by equipment failure, software errors, human errors, and drive conflicts. What type of histogram is management asking for?
A. A cause-and-effect diagram B. A control chart C. A Pareto chart D. A flowchart |
Answer: C
Hint: 80/20. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
C is correct because a Pareto chart is a histogram that shows categories of failure.
A is incorrect because a cause and effect diagram seeks to identify why the failures happened, while a Pareto chart only wants to identify the categories of failure. B is incorrect because a control chart tracks success and failures as a whole—not by individual errors. D is incorrect because a flowchart shows the flow of work or processes within a system. |
|
|
Jim is the project manager of the BHQ Project for his company. This project is a manufacturing project for a new client. Beth, the project sponsor, has asked Jim to create a chart that will help the stakeholders see the history of the project work and any variations to the project mean. This chart, however, must be measured against a timeline. Which type of quality control chart shows the history and pattern of variation?
A. A run chart B. A flowchart C. A Pareto chart D. A network diagram chart |
Answer: A
Hint: On your mark... Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
A is correct. Run charts show the history and pattern of variation.
B is incorrect because a flowchart shows the flow of work or processes within a system. C is incorrect because a Pareto chart is a histogram that shows categories of failure. D is incorrect because a network diagram chart demonstrates the flow of activities within a project. |
|
|
Pi is the project manager for her organization. Management has asked her to identify the quality control tools she’ll use in the project. All of the following are examples of quality control tools except for which one?
A. Inspection B. Defect repair review C. Statistical sampling D. Quality audits |
Answer: D
Hint: Organization-wide. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
D is correct because quality audits are a tool used for quality assurance.
A is incorrect because inspection is a QC tool. B is incorrect because defect repair review is a QC tool. C is incorrect because statistical sampling is a QC tool. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the BHQ Manufacturing Project. In this project, you have utilized a control chart to measure project performance of repeatable activities. You are examining a control chart. When should processes be adjusted?
A. When the control chart’s mean is too low. B. When the control chart’s mean is too high. C. When the process is within acceptable limits. D. When the process is outside of acceptable limits. |
Answer: D
Hint: Fix the problem. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
D is correct because processes outside of acceptable limits should be adjusted to bring the process into acceptable limits.
A is incorrect because the mean represents the average or predicted average for the results. B is incorrect because the mean represents the average or predicted average for the results. C is incorrect because processes within acceptable limits should not be adjusted. |
|
|
As part of your construction project, there are several standards and regulations that you must accommodate in the project work. What is the difference between a standard and a regulation?
A. Standards and regulations are essentially the same. B. Standards are determined by the Organization for InternationalStandards, while regulations are specific to each industry. C. Standards are optional, while regulations vary by industry. D. Standards are optional, while regulations are not. |
Answer: D
Hint: Don’t go to jail. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 1 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
D is correct because standards are guidelines, which are optional, while regulations are never optional.
A, B, and C are incorrect because each is a false statement about regulations and standards. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the HNN Project. Your team needs safety training in order to install several of the components in your project. The cost of this training is known as which one of the following?
A. Team development B. Cost of quality C. Cost of nonconformance D. Variable costs |
Answer: B Hint: The training is needed in order to complete the project. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
B is correct because the cost of training is considered a cost of quality.
A is incorrect because training is one method of team development, but the cost of training is not. C is incorrect because the cost of nonconformance to quality is the costs that will occur if quality is not obtained. D is incorrect because variable costs describes costs that fluctuate within a project. |
|
|
All project managers should set expectations for the quality of the project. These expectations should be clearly defined as part of the quality management plan. All of the following are quality planning tools except for which one?
A. Force field analysis B. Flowcharts C. Brainstorming D. Inspection |
Answer: D
Hint: Not Spock! Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 8 Study Guide Objective: Ensure Project Deliverables Conform to Quality Standards
D is correct because inspection is a quality control tool, not a quality planning tool. You’ll inspect the results of the project work well after the quality planning occurs.
A is incorrect because this is an example of a quality planning tool. B is incorrect because this is an example of a quality planning tool. C is incorrect because this is an example of a quality planning tool. |
|
|
An organization’s willingness to accept risk is known as what?
A. The entrepreneurial spirit B. An autocratic belief C. The utility function D. Risk threshold |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s not a threshold. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
C is correct because the utility function is the term used to describe an organization’s willingness to accept risk.
A is incorrect because this term is not valid. B is incorrect because this describes project management leadership, not risk. D is incorrect because the term describes a condition that a risk event is pending or has come to fruition. |
|
|
You are the project manager for a new software development project for a client. You are explaining to the client the approach you’ll use to identify, plan, and manage the risks within the project. Which best describes when risk identification occurs?
A. Early in the project B. During project initiation C. Iteratively D. As scheduled by the risk management plan |
Answer: C
Hint: Over and over. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
C is correct because risk identification is an iterative process. The project team must proactively look for risks.
A is incorrect because risk doesn’t happen only early in the project, but throughout the project. B is incorrect because risk identification doesn’t happen in initiation, but iteratively throughout the project. D is incorrect because risk identification happens sans schedule, as needed. |
|
|
Your project sponsor has asked you to review some of the risks of the project with him. In particular, the project sponsor wants to define some of the root causes of risks. Which component will help you, the project manager, identify the root causes of risk?
A. The project team B. Expert judgment C. Project scope D. Risk register |
Answer: D
Hint: Not a person. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
D is correct because the risk register includes the root causes of risk.
A is incorrect because the project team may contribute to the root cause analysis, but the risk register is the component that stores the root cause of identified risk. B is incorrect because experts may contribute to the root cause analysis, but the risk register is the component that stores the root cause of identified risk. C is incorrect because the project scope does not contribute to or supply the root cause of risks. |
|
Based on the following table, what is the needed contingency reserve?
A. -11,600 B. 11,600 C. 4000 D. 120 percent of the project budget
|
Answer: B
Hint: You don’t get it all. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
B is correct because the contingency reserve is found by multiplying the probability times the impact. The sum of the expected monetary value equates, in positive numbers, to the amount of the contingency reserve.
A is incorrect because this is a negative number. The contingency reserve is a positive number. C is incorrect because this is an incorrect calculation for the contingency reserve. D is incorrect because this statement is false. |
|
|
Management wants you, the project manager, to create a matrix to quickly show the probability of each risk in your project. What is management asking for?
A. A probability-impact matrix B. A risk rating matrix C. An RAG rating matrix D. A risk owner’s matrix |
Answer: A
Hint: You can create these for qualitative and quantitative risk analysis. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
A is correct because this matrix identifies the probability, impact, and overall risk score for the project.
B and D are incorrect because neither term is valid. C is incorrect because an RAG rating is represented by a red-amber-green rating for risk identification or risk activity. |
|
|
You would like to use a simulation to predict a project’s success based on the number of identified risks and their overall impact. What method could you use?
A. PERT B. GERT C. A Monte Carlo Simulation D. A risk simulation |
Answer: C
Hint: It’s not a gamble. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
C is correct because a Monte Carlo Simulation can be used to determine the likelihood of a project’s success.
A is incorrect because PERT is a time-estimating formula. B is incorrect because GERT is a network diagramming technique. D is incorrect because this answer is not valid for this question. |
|
|
You have identified a risk that may cause safety concerns for the workers completing the task. You’ve decided to hire a third party to complete this work because the risk is too great to accept internally. Which risk response is this?
A. Mitigation B. Acceptance C. Avoidance D. Transference |
Answer: D
Hint: Someone is doing the risky work. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
D is correct because transference is when someone else owns the risk—usually for a fee. The risk doesn’t go away.
A is incorrect because mitigation is any effort to reduce or eliminate the risk. B is incorrect because acceptance means just that—the risk has been accepted. C is incorrect because avoidance is changing the project management plan to avoid the risk altogether. |
|
|
You’ve identified a risk with your project team that may cause major delays in your project. There’s nothing you can do about the risk, however, because of the nature of the project work. Which risk response will you likely choose?
A. Acceptance B. Avoidance C. Exploit D. Mitigate |
Answer: A
Hint: Not much you can do. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
A is correct because you are forced to accept the risk.
B is incorrect because avoidance implies that the risk can be taken out of the project, but in this instance it cannot because the risk is inherent to the project work. C is incorrect because exploit is a risk response when the risk is identified as a positive risk or opportunity. D is incorrect because mitigate is a response to lower or eliminate the risk impact. In this instance, there’s nothing that can be done about the risk. |
|
|
You are the project manager of a large project for your organization. Management has just called to let you know that they will be participating in a new risk audit that will begin next week. What is a risk audit?
A. It is a process to see what risks are within a project. B. It is a process to determine the risk exposure for a project. C. It is a process to determine the effectiveness of the risk responses. D. It is a process to determine the costs of risks. |
Answer: C
Hint: Not money. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
C is correct because a risk audit determines the effectiveness of risk responses.
A is incorrect because this answer describes the risk identification process. B is incorrect because this answer describes the risk analysis process. D is incorrect because this answer describes the expected monetary value performed in quantitative risk analysis |
|
|
The largest risk in your project has just occurred. This risk event has depleted nearly all of your risk contingency reserve. What must happen next?
A. The project must be scrapped. B. The project must be reviewed for additional risks. C. The project manager and the project team must complete reserve analysis. D. The project manager must ask for additional funds. |
Answer: C Hint: Find the problem first. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 11 Study Guide Objective: Monitor All Risks
C is correct because when a risk depletes the contingency reserve, it calls for reserve analysis in relation to the amount of remaining risks within the project.
A is incorrect because the project likely won’t need to canceled because of the risk event.B is incorrect because this event is iterative. D is incorrect because there’s no evidence yet if additional funds are needed. |
|
|
Your project just got canceled. You were nearly 60 percent done. What should happen next?
A. Bill for 60 percent of the contracted fee. B. Determine why the project has failed. C. Complete scope verification. D. Offer your resignation. |
Answer: C Hint: Don’t quit. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Final Acceptance for the Project
C is correct because even though the project’s been canceled, you need to complete scope verification.
A is incorrect because the contract for the project will determine what will happen in this scenario. In addition, internal projects may have no contract. B is incorrect because there’s no evidence that the project has failed. There could be other reasons why the project has been canceled, such as advancements in technology or a shift in the market. D is incorrect because this isn’t valid. It may feel valid, but it’s not the best choice. |
|
|
Marci wants to know the difference between scope verification and quality control. What’s the difference?
A. QC is concerned with inspection, while scope verification is concerned with the quality. B. QC is concerned with the correctness of the deliverables, while scope verification is concerned with the acceptance of the project scope. C. QC and scope verification are the same. D. QC is concerned with the correctness of the deliverables, while scope verification is concerned with the acceptance of the project deliverables. |
Answer: D
Hint: Read carefully. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Final Acceptance for the Project
D is correct because scope verification is concerned with the acceptance of the project deliverables.
A is incorrect because this is not a true statement about scope verification. B is incorrect because this is not a true statement about scope verification. C is incorrect because while QC and scope verification both rely on inspection, they are not the same thing. QC happens without the project customers, while scope verification happens with them. |
|
|
You are the project manager of the NHG Project. Your project is to create 8453 custom doorknobs for a hotel. Your project team has completed the work, the customer has agreed to the project deliverables, and has signed off on the project work. The customer, however, asks you to drop off the doorknobs to the next project team that will install the work. You agree to do this. When you deliver the doorknobs to the next project team, their project manager asks when your team will arrive to help install the doorknobs. What should you do?
A. Nothing. Your project is done. B. Nothing. Your project team has moved onto other projects. C. Complete a change request for the installation of the doorknobs. D. Consult with the customer to see if they’d like you to help install the doorknobs—for a fee. |
Answer: A
Hint: Done is done. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 5 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Final Acceptance for the Project
A is correct because the project is done.
B is incorrect because, regardless of the team’s status, the project has been completed. C is incorrect because there’s no need to do a change request—the project is completed. D is incorrect because your project is done. It’s up to the project manager of the installation project to request for additional labor if he feels it’s needed. |
|
|
You have hired a vendor to complete a project for your organization. The vendor presents the project as complete but you disagree with the completeness of the project. What should you do?
A. Create a change request for the vendor. B. Consult the project sponsor for advice. C. Reference the details of the contract for the acceptance of the project deliverables. D. Reference the details of the local law for processes of arbitration. |
Answer: C
Hint: A deal’s a deal. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 12 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Financial, Legal, and Administrative Closure
C is correct because the contract stipulates the terms for project acceptance.
A is incorrect because a change request isn’t needed unless you are adding deliverables to the project scope. B is incorrect because the project sponsor may need to be included in the discussion, but the best choice is to consult the contract first. D is incorrect because the contract should be consulted before any options of arbitration. |
|
|
A project team has just completed the final work packages for a project. The project manager needs to find the final CPI for the project. The BAC was $250,000, but the actual costs came in at $286,000. What’s the final CPI?
A. .87 B. $286,000 C. -$36,000 D. The earned value information is needed to answer this question. |
Answer: A
Hint: The project work is 100 percent complete. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapters 4 and 7 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Financial, Legal, and Administrative Closure
A is correct because the CPI is found through the formula EV/AC. In this instance, the EV is $250,000, which is 100 percent of the BAC because the project is complete.
B is incorrect because this is the final AC for the project. C is incorrect because this is the cost variance for the project. D is incorrect because the EV information is supplied in the question. |
|
|
A project has just finished the final work packages. Management has deemed that this project is a failure because the project came in late and over budget. Management wants to know why the project has failed. Which closing process can answer management’s question?
A. Scope verification B. Administrative closure C. Lessons Learned D. Contract closeout |
Answer: B
Hint: Not a lesson. Reference: PMP Study Guide, Chapter 4 Study Guide Objective: Obtain Financial, Legal, and Administrative Closure
B is correct because administrative closure does include analyzing project success and failure.
A is incorrect because scope verification verifies the project deliverables. C is incorrect because lessons learned is part of administrative closure, which answers this question more completely. D is incorrect because there’s no evidence that a contract was even used in this project. In addition, A answers the question. |

