![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
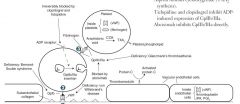
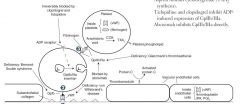
What are the different steps of platelet plug formation?
|
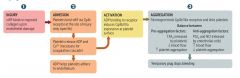
1. Injury
2. Adhesion 3. Aggregation |
|
|
What are the first factors to bind together upon endothelial damage?
|
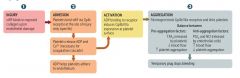
Circulating vWF binds to the collagen within the vessel wall
|
|
|
What is the molecule that platelets bind to in the wall of a vessel when injury occurs?
|
to vWF via GpIb
|
|
|
What is released by platelets to assist in the coagulation cascade?
|
Calcium
ADP |
|
|
What is the action of ADP on platelets?
|
Helps platelets to adhere to the endothelium by inducing GpIIb/IIIa expression at the platelet surface
|
|
|
What occurs during the aggregation stage of platelet plug formation?
|
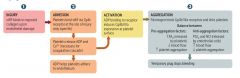
Fibrinogen binds GpIIb/IIIa receptors and links factors
|
|
|
What are pro-aggregation factors?
|
TXA2
Decreased blood flow Increased platelet aggregation |
|
|
What are anti-aggregation factors?
|
PGI2, NO
Increased blood flow Decreased platelet aggregation |
|
|
What is the mechanism of clopidogrel?
|
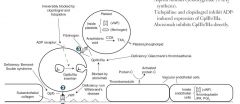
Irreversable blockage of the ADP receptor, inhibiting platelet aggregation
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of ticlopidine?
|
Irreversible blockage of the ADP receptor, inhibiting platelet aggregation
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of abciximab?
|
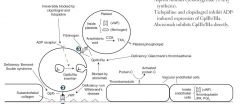
Direct inhibition of GpIIb/IIIa; inhibition of fibrinogen binding to platelets
|
|
|
What syndrome is deficient in GpIb?
|
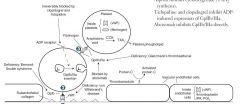
Bernard Soulier syndrome
|
|
|
What syndrome is deficient in GpIIb/IIIa?
|
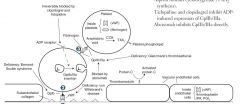
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia
|
|
|
What factors are released by platelets during thrombogenesis?
|
vWF
Fibrinogen TXA2 |
|
|
What are the factors related to thrombogenesis that are contained within vascular endothelial cells?
|
vWF
Thromboplastin tPA, PGI2 |
|
|
With respect to ESR, what are causes of RBC aggregation?
|
Acute-phase reactants within plasma
|
|
|
What are causes of increased ESR?
|
Infections
AI diseases Malignant neoplasma UC Pregnancy |
|
|
What are some autoimmune diseases that have increased ESR?
|
SLE
RA Temporal arteritis |
|
|
What are some causes of decreased ESR?
|
Polycythemia
Sickle cell anemia CHF Microcytosis Hypofibrinogenemia |
|
|
What is the mechanism of asprin?
|
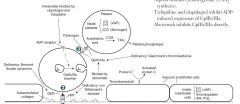
Inhibition of cyclooxygenas--> decreased TXA2 synthesis
In this way asprin inhibits clotting (TXA2 is pro-aggregation factor) |

