![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who proposed the idea of continental drift? |
Alfred Wegener |
|
|
When was the idea of continental drift proposed? |
1912 |
|
|
What was the idea of continental drift? |
-continents were connected in one land mass called Pangaea that broke apart 200 million years ago -they drifted into the positions they're in now |
|
|
Why was the idea of continental drift not accepted by the scientific community? |
Wegener couldn't explain how the continents moved |
|
|
What are the five pieces of evidence to support continental drift? |
-puzzle like fit of the continents -animal fossils (mesosaurus) -plant fossils (glossopteris) -climate (glacial deposits found in warm continents) -rocks (similar structures in continents that were once connected) |
|
|
Who proposed the idea of seafloor spreading? |
Harry Hess |
|
|
What is seafloor spreading? |
-seafloor separates and magma comes up through crack
-new seafloor moves away from the ridge, cools, and sinks |
|
|
What are the two pieces of evidence that support seafloor spreading? |
-older rocks are farther away from the ridges -rocks track the magnetic field changes |
|
|
When was the idea of plate tectonics proposed? |
1960's |
|
|
What does the idea of plate tectonics explain? |
explains the features and movement of Earth's surface |
|
|
What theory is formed by putting together seafloor spreading and continental drift? |
plate tectonics |
|
|
What are plates made from? |
parts of the crust and upper mantle |
|
|
What layer do plates move on? |
asthenosphere |
|
|
What are the three types of plate boundaries? |
divergent convergent transform |
|
|
What causes the plates to move? Describe how it works. |
convection
Hot fluid rises to the surface, cools, sinks, heats, rises, etc. |
|
|
Describe a divergent boundary |
plates moving apart |
|
|
What forms at a divergent boundary? |
mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys
|
|
|
Describe a convergent boundary |
-plates moving together -denser plate goes below the other one |
|
|
What can form at a convergent boundary? |
mountains and volcanoes |
|
|
Describe a transform boundary |
-plates slide past each other - different speeds, same direction -different directions |
|
|
What happens at transform boundaries? |
earthquakes |
|
|
How do scientists test the rate of movement of plates? |
satellites and lasers |
|
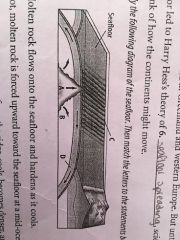
Molten Rock flows onto the seafloor and hardens as it cools ____ Hot, molten rock is forced upward toward the seafloor at a mid-ocean ridge ____ New seafloor moves away from the ridge, cools, becomes denser, and sinks ____ Molten rock pushes sideways in both directions as it rises, moving the mantle with it ____ |
C A D B |
|
|
large, ancient landmass that was composed of all the continents joined together |
Pangaea |
|
|
theory that Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into plates that float and move around on a plasticlike layer of the mantle
|
plate tectonics |
|
|
plasticlike layer of Earth on which the lithospheric plates float and move around
|
asthenosphere |
|
|
Wegener's hypothesis that all continents were once connected in a single large landmass that broke apart about 200 million years ago and drifted slowly to their current positions
|
continental drift |
|
|
Harry Hess' theory that new seafloor is formed when magma is forced upward toward the surface at a mid-ocean ridge |
seafloor spreading |
|
|
current in Earth's mantle that transfers heat in Earth's intereior and is the driving force for plate tectonics |
convection current |
|
|
rigid layer of Earth about 100 km thick, made of the crust and part of the upper mantle |
lithosphere |
|
|
a large section of Earth's oceanic or continental crust and rigid, upper mantle that moves around on the asthenosphere |
plate |

