![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Transformation |
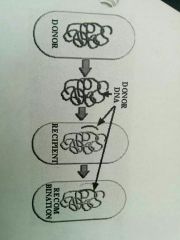
A piece of donor DNA is taken up by a recipient bacterium and through recombination it is incorporated into the recipient's DNA. This is a source of genetic variation. |
|
|
Three virus genes |
Coat proteins: protection of nucleic acid. Replicase: codes for nucleic acid replication, needed for continuation of genetic material. Movement protein: moving around host organism. |
|
|
Conjugation |
Bacterial mating where genetic info between two bacteria is passed. Source of genetic variation. |
|
|
Crown gall |
Agrobacterium tumefaciens |
|
|
Pathovar |
In bacteria a subspecies or group of strains that can infect only plants within a certain genus or species. |
|
|
Viruliferous |
Said of a vector containing a virus and capable of transmitting it. |
|
|
Viroids |
Small, low molecular weight RNA that can infect plant cells, replicate themselves and cause disease. |
|
|
Virus |
A submicroscopic obligate parasite consisting of nucleic acid and protein. |
|
|
Encapsidation |
Coat protein gene responsible for this |
|
|
4 Virus symptom development |
Systemic, local lesions, latent virus live symptomless on a host called symptomless carrier, masked. |
|
|
Virus symptoms |
Mosaics and ring spots. Also stunting, yellows, pitting, distortion |
|
|
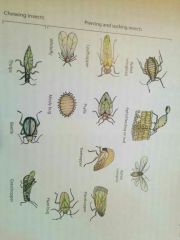
Insect vectors |
|
|
|
Nonpersistent viruses |
Stylet-borne viruses persist in the vector for only a few to several hours. |
|
|
Semipersistent viruses |
Viruses persist in vector for 1-4 days |
|
|
Circulative and persistent viruses |
Viruses that are acquired by their vectors through their mouth parts accumulate internally and then are passed through tissues of the vector and introduced into plants again via the mouth parts of the vector |
|
|
Virus shapes |

|
|
|
Bacterial morphology |
Cell wall, slime layer or capsule maybe, flagella (either polar or peritrichous, all over), most rod shaped except for filamentous Strptomyces. Large circular chromosome, occasionally small circular plasmid. Reproduce by binary fission, also do conjugation. |
|
|
Identifying bacteria |
Gram staining, nutritionally different media, enzymes produced, pathogenicity, serological methods, pcr |
|
|
Blight |
A disease characterized by general and rapid killing of leaves, flowers and stems. |
|
|
Burrill |
1878, first to transmit disease in plants in fire blight. Father of phytobacteriology |
|
|
Mary dell Chilton |
1977 agrobacterium tumefaciens physically transfers part of its plasmid |
|
|
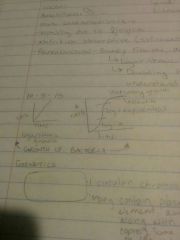
Bacterial growth |
|
|
|
Genetic variation in bacteria |
Transformation (-physical uptake of a piece of DNA or whole plasmid DNA. Conjugation Transduction-phage-mediated DNA transfer |
|
|
Bacteria |
Mostly facultative saprophytes |
|
|
Ice nucleation |
P. Syringae, Steve lindow bacteria deleted gene |
|
|
Beijerinck |
Father of virology, contagium vivum fluidum |
|
|
Icosahedron |
20 sided virus |

