![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Phototrophs
|
Some autotrophic protists are photosynthetic
|
|
|
Phagotrophs
|
Ingest visible particles of food NY pulling them into intracellular vesicles called food vacuoles or phagosomes
|
|
|
Pseudopods
|
False feet, chief means of locomotion among amoebas
|
|
|
Mixotroph
|
Protists that are both phototrophic and heterotrophic
|
|
|
Osmotroph
|
Protists that ingest food in soluble form
|
|
|
Budding
|
Sometimes the daughter cell is considerably smaller than its parent and then grows to adult size
|
|
|
Cyst
|
A thick-walled unicelular life stage produced by many protists that can remain dormant during stressful periods is known as cysy
|
|
|
A distinguishing characteristic of red algae is that
|
They lack flagella and centrioles
|
|
|
How do choanoflagellates use their collar in their feeding?
|
They use it to filter bacterial cells from the water
|
|
|
Features of cilliates
|
- they have alveoli under the plasma membrane
- they have contractile and food vacuoles - they use cilia for locomotion - they have a macronucleus and a micronucleus |
|
|
Order steps in paramecyum as they occur
|
1) food enters the gullet
2) food passes into food vacuoles 3) enzymes and hcl digest food particles 4) food vacuoles empty their content |
|
|
Diplomonads and parabadalids are similar in that they
|
Have two nuclei and multiple flagella
|
|
|
The flagellum of choanoflagellates os surrounded by a funnel-shaped contractile_______composed of closely placed_______
|
Collar, filaments
|
|
|
Most amoeba are________, but some are_______, and they live in the soil as well as freshwater.
|
Free living, parasitic
|
|
|
Cite common free features of diplomonads and parabasalids
|
- they have two nuclei
- they move using flagella - they feed using groove on their side |
|
|
In living organisms with alternative generation life cycle, which of the following is a haploid generation?
|
Gametophyte
|
|
|
Choanoflagellates have (a) ________ emergent flagella (um)
|
Single
|
|
|
Supergroup Chromalveolates are distinguished from other protists based on the presence of
|
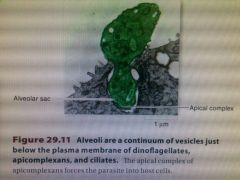
Flattened vesicles called alveoli, stacked in a continuous layer below their plasma membranes
|
|
|
Life stages and cycles of Plasmodium
|
Sporozoites - enter the liver, reproduce asexually
Merozoites - multiply inside red blood cells and are released Gametocystes - are ingested by another, previously uninfected mosquito, where they develop into gametes and reproduce sexually |
|
|
Multicellularity has arisen
|
Multiple times among eukaryotes
|
|
|
Choanoflagellates feed on_____, which they strain out of the water using filaments in their______
|
Bacteria, collar
|
|
|
The______ generation in land plants is diploid
|
Sporophyte
|
|
|
Features that may be found in chlorophytes
|
Asexual reproduction, unicellular, flagella
|
|
|
Cells of epidermis
|
Layer of specialized cells representing the dermal tissue system, covers the surfaces of plant structure and forms the surface layer of a scale
|
|
|
Cell wall
|
a thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell. This layer of cellulose fiber gives the cell most of its support and structure. The cell wall also bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant.
|
|
|
Plant cell diagram
|

Cell wall
|
|
|
Cell wall
|
Forms the boundary of each of this plant cell. The cell wall is external to the living cell, lying outside the plasma membrane
|
|
|
Parenchyma cells
|
Parenchyma cells are the most common and least specialized cell type in flowering plants. Their size and shape vary considerably, but they tend to have a boxy shape with rounded edges and corners.
|

