![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the bones of the Neurocranium |
Bones of the Neurocranium :- i)Frontal bone ii)Parietal bones (2) iii)Temporal bones (2) iv)Occipital bone v)Sphenoid bone vi)Ethmoid bone |
|
|
Name the bones of the Viscerocranium |
Bones of the Viscerocranium :- i)Maxillae (2, then fuse) ii)Nasal bones (2) iii)Zygomatic bones (2) iv)Palatine bones (2) v)Lacrimal bones (2) vi)Inferior conchae (2) vii)Vomer viii)Mandible ix)Hyoid |
|
|
Name the unpaired bones of the Neurocranium |
There are four unpaired bones of the neurocranium: 1)ethmoid, 2)sphenoid, 3)frontal, 4)occipital. |
|
|
Name the paired bones of the Neurocranium |
There are 2 sets of paired bones of the Neurocranium:(2x2=4) i)Parietal bones (2) ii)Temporal bones (2) |
|
|
Name the paired bones of the Viscerocranium |
There are 6 sets of paired bones of the Viscerocranium:-(6x2=12) i)Maxillae (2, then fuse) ii)Nasal bones (2) iii)Zygomatic bones (2) iv)Palatine bones (2) v)Lacrimal bones (2) vi)Inferior conchae(2) |
|
|
Name the unpaired bones of the Viscerocranium |
There are four unpaired bones of the Viscerocranium :
1)Vomer 2)Mandible 3)Hyoid |
|
|
Name the bones of the viscerocranium formed byintramembranous growth |
NOTE:All bones of the viscerocranium(except the mandibularcondyle) form byintramembranous growth Bones of the Viscerocranium formed by intramembranous growth :- i)Maxillae (2, then fuse) ii)Nasal bones (2) iii)Zygomatic bones (2) iv)Palatine bones (2) v)Lacrimal bones (2) vi)Inferior conchae(2) vii)Vomer viii)Mandible (except the mandibular condyle) ix)Hyoid |
|
|
Which is the weakest part of the skull? |
The pterion is considered the weakest part of the skull. NOTE: Deep to the pterion runs the middle meningeal, which maybe damaged with trauma to the pterion. |
|
|
Which bone forms the floor of the middle cranial fossa? |
Petrous part of the temporal bone forms the floor of the middle cranial fossa and separates middle and posterior cranial fossae. |
|
|
Which bone separates middle and posterior cranial fossae? |
Petrous temporal bone forms the floor of the middle cranial fossa and separates middle and posterior cranial fossae. |
|
|
Name an important artery located in the middle cranial fossa. |
Middle meningeal artery islocated in middle cranial fossa(exits foramen spinosum). |
|
|
Name the bones that form the Anterior Cranial Fossa |
The 3 bones that form the Anterior Cranial Fossa are:- ( switch OFf the Central Email Security Server) 1)Orbital plates of the Frontal bone, 2)Cribriform plates of the Ethmoid bone, and 3)Small wings of Sphenoid bone |
|
|
Name the bones that form the Middle Cranial Fossa |
The 2 bones that form the Middle Cranial Fossa are:- (Giant Snails are PeSTs)
1)Greater wings of the Sphenoid bone ,and 2)Petrous and the Squamous portions of the Temporal bones |
|
|
Name the bones that form the Posterior Cranial Fossa |
The bones that form the Posterior Cranial Fossa are:- (SMarT Ox) 1)Squamous and Mastoid portion of Temporal bones and 2)Occipital bone |
|
|
What are the contents of the Anterior Cranial Fossa? |
The 4 contents of the Anterior Cranial Fossa are:- (FC FC) 1)Frontal lobes 2)Cribriform plate 3)Foramen cecum 4)Crista galli |
|
|
What are the contents of the Middle Cranial Fossa ? |
The contents of the Middle Cranial Fossa are:- (POT CST For Maggie, Roti, Spicy Omelet)
1) Pituitary 2) Optic foramen 3) Temporal lobes 4) Carotid canal 5) Superior orbital fissure 6) Trigeminal ganglion 7)Foramen Magnum 8)Foramen Rotundum 9)Foramen Ovale 10)Foramen Spinosum |
|
|
What are the contents of the Posterior Cranial Fossa ? |
The contents of the Posterior Cranial Fossa are:- (OBC IJ FH) 1)Occipital lobes 2)Brain stem 3)Cerebellum 4)Internal acoustic meatus 5)Jugular foramen 6)Foramen magnum 7)Hypoglossal canal |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Foramen cecum is present. |
Foramen cecum is present in 1)Frontal and 2)Ethmoid bones |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Foramen cecum |
Emissary vein passes through Foramen cecum |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Greater palatine foramen is present. |
Greater palatine foramen is present in the Palatine bone |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Greater palatine foramen |
Greater palatine nerve, artery, vein pass through the Greater palatine foramen |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Lesser palatine foramen is present. |
Greater palatine foramen is present in the Palatine bone |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Lesser palatine foramen |
Lesser palatine nerve, artery, vein pass through the Lesser palatine foramen |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Incisive canal is present. |
Incisive canal is present in the Maxilla |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Incisive canal |
Nasopalatine nerve passes through the Incisive canal |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Supraorbital foramen is present. |
Supraorbital foramen is present in the Frontal bone |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Supraorbital foramen |
Supraorbital nerve, artery, vein pass through the Supraorbital foramen |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Infraorbital foramen is present. |
Infraorbital foramen is present in the Sphenoid and maxilla |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Infraorbital foramen |
Infraorbital nerve (V2), artery, and vein pass through the Infraorbital foramen |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Optic canal is present. |
Optic canal is present in theSphenoid bone. |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Optic canal |
Optic nerve (II) and ophthalmic artery pass through the Optic canal |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Superior orbital fissure is present. |
Superior orbital fissure is present in the Sphenoid bone (between greater and lesser wings) |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Superior orbital fissure |
The structures which pass through the Superior orbital fissure are :- (OATTS) 1)Oculomotor (III), 2) Abducens (VI), 3) Trochlear (IV), 4)Trigeminal(V1–lacrimal, frontal, andnasociliary nerves), and 5)Superiorophthalmic vein |
|
|
Name the vein which passes through the Superior orbital fissure |
Superior ophthalmic vein passes through the Superior orbital fissure |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Inferior orbital fissure is present. |
Inferior orbital fissure (leads to infraorbital foramen) . It is present in the Sphenoid and maxilla |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Inferior orbital fissure |
The structures which pass through the Superior orbital fissure are :- 1)V2, 2)Infraorbital vessels, 3)Ascending branches of sphenopalatine ganglion |
|
|
Name the bone(s) in which Foramen rotundum is present |
Foramen rotundum is present in Sphenoid bone. |
|
|
Name the structure(s) which pass through the Foramen rotundum |
V2 passes through the Foramen rotundum |
|
|
Name the bone in which the Foramen ovale is present |
Sphenoid |
|
|
Name the structures which pass through the Foramen ovale |
1)V3, 2)parasympathetic fibers from CN IX via lesser petrosal nerve, 3)accessory meningeal artery |
|
|
Name the bone in which the Foramen spinosum is present |
Sphenoid |
|
|
Name the structures which pass through the Foramen spinosum |
Middle meningeal artery and vein pass through the Foramen spinosum |
|
|
Name the bone in which the Petrotympanic fissure is present |
The Petrotympanic fissure is present in the Temporal bone |
|
|
Name the structures which pass through the Petrotympanic fissure |
1)Chorda tympani,and 2)anterior tympanic artery pass through the Petrotympanic fissure |
|
|
Name the bone in which the Foramen lacerum is present |
Foramen lacerum is present in the Temporal and sphenoid bones |
|
|
Name the structures passing through the Foramen lacerum |
Greater and deep petrosal nerve and parasympathetic fibers from CN VII via nervus intermediate, pass through the Foramen lacerum |
|
|
Name the bone in which the Internal acoustic meatus is present |
Internal acoustic meatus is present in the Temporal bone (petrous) |
|
|
Name the structures passing through the Internal acoustic meatus |
VII and VIII pass through the Internal acoustic meatus |
|
|
Name the bone in which theStylomastoid foramen is present |
Stylomastoid foramen is present in the Temporal Bone |
|
|
Name the structures passing through the Stylomastoid foramen |
Facial nerve (VII) passes through the Stylomastoid foramen |
|
|
Name the bone in which the Jugular foramen is present |
Jugular foramen is present in the Temporal and Occipital bones |
|
|
Name the structures passing through the Jugular foramen |
Structures that pass through the Jugular foramen are:- 1)IJV, 2)glossopharyngeal (IX), 3)Vagus (X), and 4)Spinal accessory (XI) nerves |
|
|
Name the bone in which the Foramen magnum is present |
Foramen magnum is present in the Occipital bone |
|
|
Name the structures passing through the Foramen magnum |
The structures passing through theForamen magnum are:- 1)Medulla oblongata/spinal cord, 2)Vertebral arteries, 3)Spinal accessory nerve |
|
|
Name the bone in which the Mandibular foramen is present |
Mandibular foramen is present in the Mandible I |
|
|
Name the structures passing through the Mandibular foramen |
Inferior alveolar nerve,artery, vein pass through the Mandibular foramen |
|
|
Name the bone in which the Mental foramen is present |
Mental foramen is present in the Mandible |
|
|
Name the structures passing through the Mental foramen |
Mental nerve, artery, and vein pass through the Mental foramen |
|
|
Name the components of the ethmoid bone and state their function. |
The components of the Ethmoid are:- (CO CAF Lp SLAM PLN=Cribby Oswal & Chris Attach False Lateral plate to SLAM Perpendicular plate of Nose) 1)Cribriform plate:- Olfactory foramina. 2)Crista galli :-Attaches to falx cerebri. 3)Lateral plates:-Contain ethmoid sinuses,lamina papyracea, superior and middle nasal conchae. 4)Perpendicular plate:- Superior part of nasal septum. |
|
|
Name the components of the Sphenoid bone and state their function. |
The components of the Sphenoid are:- (Bs Glo LM: Big Guy Less Money) (BeSt GLow from Less Optic SA & Medium PH) 1)Hollow body :Sella turcica and sphenoidal sinuses. 2)Greater wings :Lateral orbital wall and roof ofinfratemporal fossa. 3)Lesser wings: Optic canal, superior orbitalfissue, anterior clinoid process 4)Medial and lateral pterygoid plate : Lateral pterygoid plate is attachment for both medial and lateral pterygoidmuscles; medial pterygoid plateends as a hamulus (tensor velipalatine muscle hooks around this). |
|
|
Name the foramina contained in the Greater Wing of Sphenoid |
The greater wing of sphenoidcontains three foramina: (ROS) 1)rotundum, 2)ovale, 3)spinosum(middle cranial fossa). |
|
|
How many bones constitute the orbit? Name them. |
BONES OF THE ORBIT The orbit comprises 7 bones: (Special Large Parcel FroM ZEe) 1■ Sphenoid 2■ Lacrimal 3■ Palatine 4■ Frontal 5■ Maxilla 6■ Zygoma 7■ Ethmoid |
|
|
Name the vessel which constitutes the major blood supply of the eye. |
#The ophthalmic artery(a branch of the internalcarotid artery, ICA) is themajor blood supply to theorbit and eye. #It enters theorbit with the optic nerve viathe optic canal. |
|
|
Name the structures that the upper and lower orbital plates are continuous with. |
The upper orbital septum iscontinuous with the levatorpalpebrae superioris (ULPS) Thelower orbital septum iscontinuous with the tarsalplate. (LTP) |
|
|
Give two synonyms for the zygomatic bone |
The zygomatic bone is also referred to as the malar bone or cheekbone. |
|
|
Name the parts of the orbit that are formed by the Zygomatic bone. |
The Zygomatic bone forms a part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit. |
|
|
Name the bones that the Zygomatic bone articulates with. |
The Zygomatic bone articulates with the :- 1)Maxilla (anteriorly), 2)Temporal bone (posteriorly), and 3)frontal bone (superiorly). |
|
|
Name the bones that form the zygomatic arch. |
ZYGOMATIC ARCH is formed by temporal process of zygomatic bone and zygomatic process oftemporal bone. |
|
|
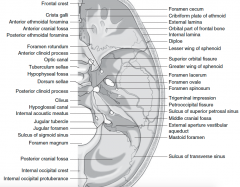
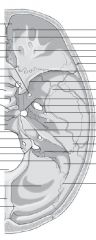
Frontal crest Crista galli Anterior ethmoidal foramina Anterior cranial fossaPosterior ethmoidal foramina Foramen rotundumAnterior clinoid process Optic canalTuberculum sellaeHypophyseal fossaDorsum sellaePosterior clinoid process Clivus Hypoglossal canalInternal acoustic meatus Jugular tubercleJugular foramenSulcus of sigmoid sinus Foramen magnumPosterior cranial fossaInternal occipital crestInternal occipital protuberance Foramen cecum Cribriform plate of ethmoid External laminaOrbital part of frontal bone Internal lamina Diploe Lesser wing of sphenoid Superior orbital fissure Greater wing of sphenoid Foramen lacerumForamen ovaleForamen spinosumTrigeminal impressionPetrooccipital fissureSulcus of superior petrosal sinus Middle cranial fossaExternal aperture vestibularaqueductMastoid foramenSulcus of transverse sinus |
|
|
Name the parts of the maxillary bones. |
The Maxillary Bones consists of a body and four processes: 1.zygomatic, 2.frontal, 3.alveolar, and 4.palatine. |
|
|
Enlist the boundries that the maxilla forms |
Forms boundaries of three cavities. (MON) 1■ Roof of the mouth (palate). 2■ Floor of the orbit. 3■ Floor and lateral wall of the nose. |
|
|
Name the Fossae formed by the maxilla |
Forms two fossae (It Pp) 1 ■ Infratemporal 2■ Pterygopalatine. |
|
|
Name the Fissures formed by the maxilla |
Forms two fissures. (Io Pm) ■ Infraorbital. ■ Pterygomaxillary. |
|
|
Boundries of Infratemporal fossa |
ANTERIOR -(PM) Posterior Maxilla POSTERIOR-(AT Shoppers stop) Articular tubercle of the temporal bone, Spine of the sphenoidal bone MEDIAL-(LPgS) Lateral Pterigoid plate of sphenoid LATERAL-MR Mandibular Ramus ROOF-GS Greater wing of Sphenoid (with foramen ovale, CN V3) FLOOR-MP Meadial Pterigoid muscle (superior surface where it inserts into the mandible) |
|
|
Boundries of Pterygopalatine fossa |
ANTERIOR- Maxilla POSTERIOR- Pterygoid plates MEDIAL- Nasal fossa LATERAL- Infratemporal fossa ROOF- Greater wing of Sphenoid (opens into inferior orbital fissure) FLOOR- Pyramidal process of palatine bone (inferior ends contain palatine canal) |

