![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
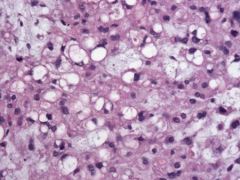
Where is this most commonly found?
|
This is a Chordoma. They are found at the distal and proximal ends of the spinal chord.
|
|
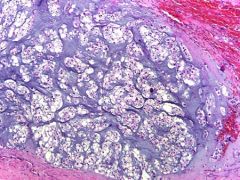
Stains to diff this from chondrosarc?
|
EMA, CK positive in this (chordoma). S-100 positive in both.
|
|
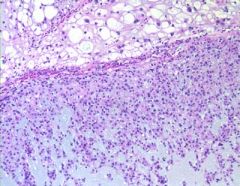
What is this?
|
Chordoma
|
|
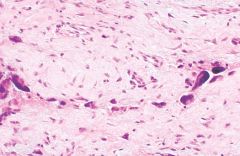
What is this?
|
Giant cell fibroblastoma
|
|
|
What is the juvenile equivalent to DFSP?
|
Giant cell fibroblastoma
|
|
|
What cytogenetic abnormality is seen in both DFSP and Giant cell fibroblastoma?
|
t(17;22) PDGFb-COL1a1(type 1 collagen)
|
|
|
What IP stain is positive in Giant cell fibroblastoma?
|
CD34, it is considered the juvenile equivalent to DFSP which is also CD34 +. Both show t(17;22)
|
|
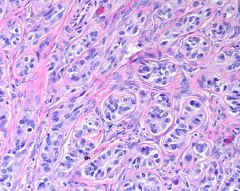
Testicle - what is it?
|
Sertoli cell tumor
-classically associated with gynecomastia although infrequent |
|
|
What testicular tumor is associated with Puetz-Jegher's syndrome?
|
A tumor that is intermediate between large cell calcifying sertoli cell tumor and sex cord stromal tumor with annular tubules.
|
|
|
What ovarian tumor is associated with Puetz Jegher's syndrome?
|
Sex cord stromal tumor with annular tubules
|
|
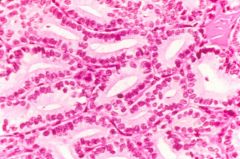
Ovarian tumor, what is it?
|
Sertoli cell tumor
|
|
|
What age group show the peak frequency in sertoli cell tumor?
|
35-50 y/o (mean 45)
|
|
|
What feature of well-differentiated sertoli cell tumors is unique among testicular neoplasms?
|
tubule formation
|
|
|
What histologic features are most helpful differentiating a sertoli tumor without tubules from a seminoma?
|
Sertoli- small round nuclei
Seminoma- larger square nuclei (irregular contours) A subpopulation of Sertoli have cytoplasmic vacuolization (diagnostic) |
|
|
What syndrome is associated with bilateral large cell calcifying sertoli tumors of the testicle?
|
Carney's syndrome - Cardiac and cutaneous (eyelid) myxomas, myxoid mammary fibroadenomas, adrenal nodular dysplasia with cushings, large cell calcifying sertoli tumor
|
|
|
Testicular tumor that presents with gynecomastia without virilism?
with virilism? |
Sertoli cell tumor (33%)
Leydig cell tumor |
|
|
Large cell calcifying sertoli cell tumor unlike sertoli tumor (NOS) is negative for EMA and is notably strongly positive for what?
|
S-100
Sertoli (NOS) is weakly positive |
|
|
What are the two most important stains for differentiating sertoli cell tumor (NOS) from seminoma. (one positive, one negative)
|
PLAP (and CD117)- positive in seminoma
Inhibin- positive in sertoli cell tumor |
|
|
T/F Chordomas follow a benign course and rarely recur.
|
False
There are usually repeated episodes of recurrence and metastases is common. |
|
|
What tumor is associated with androgen insensitivity syndrome.
|
Sertoli cell adenoma
In undecended testis, likely just hyperplasia but can be very large. |
|
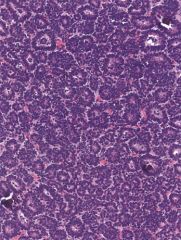
kidney tumor. Sensitive IP stain?
|
This is a metanephric adenoma. It is thought to be related to Wilm's tumor; both are WT1 positive
|
|
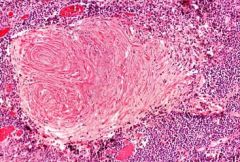
Lung; what is this?
|
Silicotic nodule/Silicosis
|
|
|
When silicotic nodules expand and become confluent, what is this disease entity called?
|
Progressive massive fibrosis (complicated silicosis)
|
|
|
Nodules in silicosis are distributed diffusely but tend to be most numerous where?
|
Upper lobes
|
|
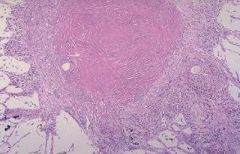
What causes this?
|
This is silicosis caused by inhalation of fine particles of silica most often in the form of quartz, tridymite or cristbalite.
|
|
|
What is the key architectural feature of litoral cell angioma?
|
Papillary structures
|
|
|
What does litoral cell angioma stain positive for that other vascular tumors do not stain for?
|
CD21
|

