![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is theNHS definition of stress? |
The feeling of being under too much mental or emotional pressure. Pressure turns into stress when you feel unable to cope. People have different ways of reacting to stressful situations so something that feels stressful to one person may be motivating to another. |
|
|
What are the three most significant life changing events? |
1. death of a spouse 2. divorce 3. jail term |
|
|
How do we define a 'stressful life event' |
1. challenges us beyond our limits and requires various re-adjustments to our routines 2. appraised as being uncontrollable and unpredictable 3. elicit immediate but also long-term psycho-physiological responses |
|
|
What 6 bodily functions/organs are often most affected by stressful life events? |
1. brain 2. heart 3. immune system 4. adrenal gland 5. ovaries 6. testes |
|
|
Give an example of a (replication study) that has linked stress to illness |
Spurgeon et al., 2001 5000 patients asked to detail the stressful life events they'd experienced in the last year Positive correlation between number of life change units and likelihood of falling ill |
|
|
What evidence is there that stress hormones (give examples) can reduce immune system function |
catecholamines corticosteroids
Marucha et al., 1998 - students heal slower during exam period than at other times in the year
|
|
|
What specific bodily and hormonal changes are characteristic of increased stress, e.g. in students before an exam. |
Decreased T-cell activation and decreased cytokine secretion |
|
|
Why do positive mood and humour correlate negatively with illness? |
They are associated with greater secretion of immunoglobin (antibodies) |
|
|
Why have most early studies looking at links between cancer and stress been discarded? |
Because they looked at stressful life events in the year preceding diagnosis, years after the disease would have been starting to grow |
|
|
What two aspects of reacting to situations determines one's response? |
perception and appraisal of the situation:
primary appraisal of actual threat secondary appraisal of ability to cope |
|
|
What are the three major coping strategies that people invoke |
1. problem-focused: attempts to change external situation, often through some planned action
2. emotion-focused: attempts to change own emotional reaction to situation
3. avoidance: attempts to distract oneself |
|
|
What are the three components of hardiness according to Kobasa (1979) |
1. belief in personal control over events 2. commitment to full involvement in life 3. enjoyment of challenge and opportunity |
|
|
Does hardiness predict level of distress after adverse life events? |
No, but executives who were high in hardiness factors were significantly less likely to develop illness than others exposed to comparable stress. |
|
|
What links are there between cardiovascular health and job satisfaction? |
Karasek et al., 1982 10 year longitudinal study of 900 men and women 'high strain' jobs predicted heart problems |
|
|
What does the hypothalamus-pituary-adrenal axis do? What can sudden activation lead to? |
It releases endocrine hormones which can lead to cardiac arrest and arteriosclerosis |
|
|
What is Freidman and Rosenhan's (1974) Type A/B personality theory? |
People are one of the two, type B or type A
Type A: hostile, competitive, impatient, aggressive, workaholic
Type B: relaxed, placid and unambitious
Type A are more likely to develop cardiovascular disease |
|
|
What is the main psychometric problem of the Type A/B theory? |
Various components of the type A personality did not correlate with each other |
|
|
Eysenck and Fulker factor analysed scores on the Type A/B questionnaire and found what correlations? |
Type A = high on N and E |
|
|
What meta-analyses results were found when the link between heart disease and 'type A personality' was tested?
What was found to be a better predictor? |
<2% of the variance in risk of heart disease was explained
hostility |
|
|
What is a 'type D' personality? |
Depressed and socially inhibited
a neurotic introvert? takes longer to recover from heart attacks |
|
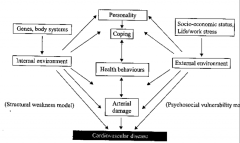
What type of model is this? Fill in the structural weaknesses and psychosocial vulnerabilities leading to cardiovascular disease |
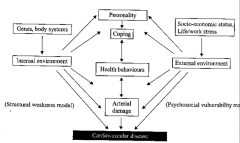
A transactional model |
|
|
Define resilience |
A positive adaptation after a stressful life event or adverse situation; the ability to bounce back from a negative experience. |
|
|
List 5 factors of resilience |
1. having caring and supportive relationships inside and outside the family 2. the capacity to make realistic plans and take steps towards carrying them out 3. a positive view of yourself and confidence in your strengths and abilities 4. the capacity to manage strong feelings and impulses 5. skills in communication and problem solving |
|
|
What relationship did Ong et al. (2006) find in his 45-day diary study of older people looking at resilience and daily emotions |
Those in the low resilience group had more significant inverse relationships between the number of positive and negative emotions they experience. High resilience people retain a fairly constant balance. |
|
|
is neuroticism more related to subjective somatic symptoms or to organic symptoms of illness? |
somatic symptoms |
|
|
What relevant associations have been found with religiousness? |
Associated with lower anxiety and depression, better physical health and longer life
BUT not when religiousness is engaged in for utilitarian reasons |
|
|
Give an example of a study demonstrating personality effects on sun-protective behaivour |
Brayne et al., 1998 123 Australian adolescents given the EPQ and then asked about their sun-protective behaviour
Negatively related to psychoticism but unrelated to neuroticism and extroversion |
|
|
Give an example of a study demonstrating personality effects on exercise-related behaviour |
Rhodes et al., 2002 Extroversion is an independent predictor of exercise |
|
|
How do smokers score on N, C, A, E and O? |
Higher on N Lower on C and A
No difference on E or O
Smokers were more impulsive, less persevering, less able to resist cravings and sought more stimulation than non-smokers |
|
|
Which personality factors of the following predict which health behaviours?
conscientiousness agreeableness neuroticism emotional intelligence rational coping emotion-focussed coping |
C: non-smoking, not drinking alcohol, exercise and healthy diet A: not drinking alcohol and healthy diet N: smoking EI: exercise and healthy diet rational coping: healthy diet emotion-focused coping: smoking and unhealthy diet |
|
|
What personality characteristic predicts longevity? |
conscientiousness |
|
|
What are the two most consistent predictors within conscientiousness of longevity? |
Traditionalism and self-control |
|
|
What three things does high conscientiousness predict? |
1. greater compliance with medical advice 2. uptake of breast cancer screening 3. HIV disease progression |
|
|
What is the range of patient compliance with medical advice? |
10-50% |
|
|
Give three reasons why patient compliance tends to be so low |
1. low conscientiousness 2. patients beliefs conflict with instructions/treatment 3. patients forget advice from doctor |
|
|
How many more studies have been done on depression and health than on happiness and health |
20x as many |
|
|
What is positive affect? |
The feelings that reflect a level of pleasurable engagement with the environment such as happiness, joy, excitement, enthusiasm and contentment. |
|
|
What measure is used to determine effects of PA? |
PANAS - orthogonal factors of positive and negative affect |
|
|
Positive affect is associated with which three health outcomes? |
1. lower morbidity 2. decreased symptoms and pain 3. increased longevity among older community-dwelling individuals |
|
|
What effect does IQ have on mortality? |
At 11 years old an IQ of 115 predicts 70% chance of being alive at 76
At 11 years old an IQ of 85 predicts <50% chance of being alive at 76
|
|
|
What effect does IQ have on likelihood to die from non-illness (i.e. accident)? |
Twice as likely if IQ=85 than if IQ=115 |

