![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
238 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The most important Iron Ore
|
Banded Iron Formations
(HINT: Mining) |
|
|
Host rock for large Gold deposits
|
Conglomerate host rock
|
|
|
Host Rock for Stratabound Sulphides
|
Limestone and/or Shale host rock
|
|
|
Reservoir for Oil and Gas
|
Sandstone, Limestone, Dolostone
|
|
|
Sedimentary rock used in Fertilizer
|
Phosphate (Apatite), Evaporite (Silvinite)
|
|
|
Sedimentary rock with Fossil Fuels
|
Coal, Oil, Shale, Tar Sands
|
|
|
Cement Raw Minerals
|
Limestone
(HINT: Industrial Mineral Use) |
|
|
Glass Raw Minerals
|
Quartz Sandstone
(HINT: Industrial Mineral Use) |
|
|
What is used in Plaster?
|
Gypsum
(HINT: Industrial Mineral Use) |
|
|
From what is Table Salt, Road Salt made?
|
Rock Salt
(HINT: Industrial Mineral Use) |
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Olivine (Silicate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Pyroxene (Silicate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Amphibole (Silicate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Biotite (Silicate)
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
Pyroxene |
(Ca,Na)(Mg,Fe,Al)(Al,Si) 2 O 6
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
Amphibole |
(Ca,Na) 2-3 (Mg,Fe,Al) 5 Si 6 (Si,A) 2 O22 (OH) 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
Biotite |
K(Mg,Fe) 3 AlSi 3 O10 (OH) 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
Plagioclase (Labradorite) |
NaAlSi 3 O 8 - CaAl 2 Si 2 O8
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
K-Feldspar |
KAlSi 3 O8
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
Quartz |
SiO 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
Muscovite |
KAl 3 Si 3 O10 (OH) 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
Talc |
Mg 3 Si 4 O 10 (OH) 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
Garnet (Almandine) |
Fe 3 Al 2 Si 3 O12
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicate)
Plagioclase (Albite) |
NaAlSi 3 O 8
|
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Chert Pebble Conglomerate |
Quartz (Chert Pebble)
|
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Quartz Sandstone |
Quartz
|
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Arkose |
K-Feldspar
Quartz Hematite |
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Greywacke |
K-Feldspar
Quartz Rock Fragments |
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Siltstone |
Quartz Rock Fragments
|
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Oolitic Limestone |
Calcite
|
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Crystalline Limestone |
Calcite
|
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Dolostone |
Dolomite
|
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Gypsum |
Gypsum
|
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Chert |
Quartz
|
|
|
MINERALOGY: (Sedimentary Rocks)
Coal |
Organic material
|
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Slate |
1. Chlorite, mica, Pyrite (Porphyroblast)
2. Shale |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Phyllite |
1. Chlorite, Muscovite
2. Shale |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Schist |
1. albite, Biotite, Quartz, Garnet (Porphyroblast)
2. Shale |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Gneiss |
1. Plagioclase, Quartz, Biotite, Garnet
2. Shale |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Augen Gneiss |
1. K-Feldspar, Amphibole, Biotite
2. Arkose, Granodiorite |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Greenschist |
1. Chlorite
2. Basalt |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Amphibole |
1. Amphibole, Plagioclase
2. Basalt |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Greenstone |
1. Chlorite
2. Basalt |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Serpentinite |
1. Serpentine
2. Peridotite |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Marble |
1. Calcite
2. Limestone |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Quartzite |
1. Quartz, Muscovite
2. Quartz Sandstone |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Hornfels |
1. N/A
2. Shale |
|
|
1. MINERALOGY & 2. PARENT: (Metamorphic Rocks)
Skarn |
1. Garnet, Epidote, Calcite
2. Limestone |
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides)
Magnetite |
Fe 3 O 4
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides)
Chromite |
FeCr2 O 4
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides)
Hematite |
Fe 2 O 3
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides)
Ilmenite |
FeTiO 3
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides)
Cassiterite |
SnO 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides)
Cuperite |
Cu 2 O
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Bornite |
Cu 5 FeS 4
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Galena |
PbS
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Sphalerite |
ZnS
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Chalcopyrite |
CuFeS 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Pyrrhotite |
Fe (1-x) S
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Cinnabar |
HgS
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Pyrite |
FeS 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Molybdenite |
MoS 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Stibnite |
Sb 2 S 3
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Chalcocite |
Cu 2 S
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Nickeline |
NiAs
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Sulphides)
Arsenopyrite |
FeAsS
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Tungstates)
Scheelite |
CaWoO 4
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Tungstates)
Wolframite |
(Fe,Mn)WO 4
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Native Element)
Graphite |
C
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides & Hydroxides)
Corundum |
Al 2 O 3
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides & Hydroxides)
Bauxite (Gibbsite) |
Al(OH) 3
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides & Hydroxides)
Goethite |
FeO(OH)
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Oxides & Hydroxides)
Limonite |
FeO(OH) * nH 2 O
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Halides)
Halite |
NaCl
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Halides)
Sylvite |
KCl
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Carbonates, Sulfates, & Phosphates)
Siderite |
FeCO 3
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Carbonates, Sulfates, & Phosphates)
Rhodochrosite |
MnCO 3
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Carbonates, Sulfates, & Phosphates)
Azurite/Malachite |
Cu 3 (CO 3) 2 (OH) 2 / Cu 2 CO 3 (OH) 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Carbonates, Sulfates, & Phosphates)
Barite |
BaSO 4
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Carbonates, Sulfates, & Phosphates)
Gypsum |
CaSO 4 * 2 H2O
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Carbonates, Sulfates, & Phosphates)
Celestite |
SrSO 4
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Carbonates, Sulfates, & Phosphates)
Apatite |
Ca 5 (PO4) 3 (F,Cl,OH)
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicates)
Talc |
Mg 3 Si 14 O 10 (OH) 2
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicates)
Kaolinite |
Al 2 Si 2 O 5 (OH) 4
|
|
|
FORMULA: (Silicates)
Vermiculate |
(Mg,Ca) 0.3 (Mg,Fe,Al) 3 (Al, Si) 4 O 10 (OH) 4 * 8 H 2 O
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Plagioclase (Labradorite)
(Silicates) |
|

Name the MIneral and Family
|
Plagioclase (Albite)
(Silicate) |
|

Name the Mineral and family
|
k-feldspar (silicate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Quartz (Silicate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Muscovite (Silicate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Talc (Silicate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Garnet (Almandine)
(Silicate) |
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Chert Pebble conglomerate
(Sedimentary) |
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Quartz Sandstone
(Sedimentary) |
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Arkose
(Sedimentary) |
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Siltstone (Sedimentary)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Greywacke (Sedimentary)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Oolitic Limestone
(Sedimentary) |
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Crystalline Limestone
(Sedimentary) |
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Dolostone
(Sedimentary) |
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Gypsum
(Sedimentary) |
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Coal
(Sedimentary) |
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Slate (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Phyllite (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Schist (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Augen Gneiss (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Gneiss (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Amphibole (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Greenschist (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Serpentinite (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Marble (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Quartzite (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Hornfels (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Skarn (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Rock and Type
|
Greenstone (Metamorphic)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Magnetite (Oxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Chromite (Oxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Hematite (Oxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Hematite (Oxide)
|
|
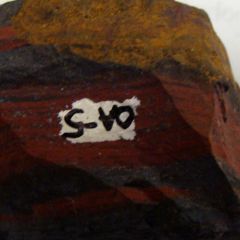
Name the Mineral and Family
|
Hematite (Oxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Ilmenite (Oxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Cassiterite (Oxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Cuperite (Oxides)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Bornite (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Galena (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Sphalerite (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Chalcopyrite (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Pyrrhotite (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Cinnabar (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Pyrite (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Molybdenite (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Stibnite (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Chalcocite (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Nickeline (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Arsenopyrite (Sulphide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Graphite (Native Mineral)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Scheelite (Tungstate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Corundum (Oxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Corundum (Oxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Bauxite (Gibbsite)
(Hydroxide) |
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Goethite (Hydroxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Halite (Halide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Sylvite (Halide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Limonite (Hydroxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Siderite (Carbonate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Rhodochrosite (Carbonate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Rhodochrosite (Carbonate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Rhodochrosite (Carbonate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Barite (Sulfate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Celestite (Sulfate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Azurite (Blue)
Malachite (Green) (Hydroxide) |
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Celestite (Hydroxide)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Apatite (Phosphate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Apatite (Phosphate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Apatite (Phosphate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Apatite (Phosphate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Kaolinite (Silicate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Talc (Silicate)
|
|

Name the Mineral and Family
|
Vermiculate (Silicate)
|
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Olivine |
LUSTRE: Glassy
HARDNESS: 6.5 - 7 CLEAVAGE: None STREAK: White OTHER: Olive Green color, granular |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Pyroxene (Augite) |
LUSTRE: Glassy
HARDNESS: 5 - 6 CLEAVAGE: Blocky (2 dir @ 90 degrees) STREAK: White OTHER: |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Amphibole (Hornblende) |
LUSTRE: Glassy
HARDNESS: 5 - 6 CLEAVAGE: Prismatic (Wedge-like, 2 dir @ 56 degrees & 124 degrees) STREAK: white OTHER: |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Biotite |
LUSTRE: Glassy, splendent
HARDNESS: 2.5 - 3 CLEAVAGE: Basal STREAK: White or Brownish OTHER: |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Plagioclase (Labradorite) |
LUSTRE: Glassy
HARDNESS: 6 CLEAVAGE: Blocky STREAK: White OTHER: Twin Striations |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Plagioclase (Albite) |
LUSTRE: Glassy
HARDNESS: 6 CLEAVAGE: Blocky STREAK: White OTHER: Twin Striations |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
K-Feldspar |
LUSTRE: Glassy
HARDNESS: 6 CLEAVAGE: Blocky STREAK: White OTHER: |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Quartz |
LUSTRE: Glassy to Greasy
HARDNESS: 7 CLEAVAGE: None STREAK: White OTHER: Conchoidal fracture, Hexagonal Prism |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Muscovite |
LUSTRE: Glassy, Pearly
HARDNESS: 2 - 2.5 CLEAVAGE: Basal STREAK: White OTHER: |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Talc |
LUSTRE: Pearly, Greasy
HARDNESS: 1 CLEAVAGE: Basal STREAK: White OTHER: Soapy feel |
|
|
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
Garnet (Almandine) |
LUSTRE: Glassy-resinous
HARDNESS: 6.5 - 7.5 CLEAVAGE: None STREAK: White OTHER: Crystal Form |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Chert Pebble Conglomerate |
TEXTURE: Gravel-sized, rounded, very poorly sorted
STRUCTURE: |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Quartz Sandstone |
TEXTURE: Sand-sized, rounded, very well sorted
STRUCTURE: |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Arkose |
TEXTURE: mostly sand-sized, subangular, poorly sorted
STRUCTURE: |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Greywacke |
TEXTURE: sand-sized, subrounded, moderately sorted
STRUCTURE: |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Siltstone |
TEXTURE: Silt-sized, well sorted
STRUCTURE: parallel bedding, plant fossils |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Oolitic Limestone |
TEXTURE: Oolitic
STRUCTURE: |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Crystalline Limestone |
TEXTURE: Crystalline
STRUCTURE: |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Dolostone |
TEXTURE: Crystalline
STRUCTURE: |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Gypsum |
TEXTURE: Crystalline
STRUCTURE: |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Chert |
TEXTURE: Crystalline
STRUCTURE: |
|
|
COMPOSITION: (Sedimentary)
Coal |
TEXTURE:
STRUCTURE: parallel bedding |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Slate |
TEXTURE: Slaty cleavage, Porphyroblastic
FACIES: Zeolite |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Phyllite |
TEXTURE: GlossyéSheen, Cleavage
FACIES: Prehnite |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Schist |
TEXTURE: schistosity, porphyroblastic
FACIES: Lower Greenschist |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Gneiss |
TEXTURE: Gneissic
FACIES: Lower Amphibolite |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Augen Gneiss |
TEXTURE: Gneissic, Porphyroblastic
FACIES: Upper Amphibolite |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Greenschist |
TEXTURE: Schistosity
FACIES: Greenschist |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Amphibolite |
TEXTURE: Lineation
FACIES: Amphibolite |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Greenstone |
TEXTURE: Nonfoliated
FACIES: Greenschist |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Serpentinite |
TEXTURE: Nonfoliated
FACIES: |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Marble |
TEXTURE: Nonfoliated
FACIES: At least Greenschist |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Quartzite |
TEXTURE: Crystalline, weakly foliated
FACIES: At least Greenschist |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Hornfels |
TEXTURE: Nonfoliated
FACIES: Hornfels |
|
|
COMPOSITION (Metamorphic)
Skarn |
TEXTURE: Nonfoliated
FACIES: Hornfels |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Oxides)
Magnetite |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Black STREAK: Black HARDNESS: 6 OTHER: Strongly Magnetic, Iron Ore |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Oxides)
Chromite |
LUSTRE: Metallic to Sub-metallic
COLOR: Black to Brownish-Black STREAK: Dark Brown HARDNESS: 5.5 OTHER: No cleavage, Weakly Magnetic, Only Chromium Ore |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Oxides)
Hematite |
LUSTRE: Metallic in crystals and dull in earthy varieties
COLOR: Reddish-Brown to Black STREAK: Red HARDNESS: 5.5 - 6.5 OTHER: Iron Ore, Pigments, Gems |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Oxides)
Ilmenite |
LUSTRE: Metallic to Sub-metallic
COLOR: Iron Black STREAK: Black to Brownish-Red HARDNESS: 5.5 - 6 OTHER: Major source of Titanium |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Oxides)
Cassiterite |
LUSTRE: adamantine to Sub-metallic
COLOR: Brown, yellow or Black STREAK: White HARDNESS: 6 - 7 OTHER: Principle ore of Tin |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Oxides)
Cuperite |
LUSTRE: Sub-metallic to Adamantine
COLOR: Red of various shades STREAK: HARDNESS: 3.5 - 4 OTHER: An ore of Copper |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Bornite |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Brownish-Bronze (Purple or Blue) STREAK: Grayish black HARDNESS: 3 OTHER: An ore of copper |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Galena |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Lead Gray STREAK: Lead Gray CLEAVAGE: Cubic (3 dir) HARDNESS: 2.5 OTHER: Only source of Lead, Important ore of Silver |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Sphalerite |
LUSTRE: Resinous (Adamantine)
COLOR: Yellow, Brown to Black (Fe-Rich) STREAK: white to yellow and brown CLEAVAGE: 6 cleavages (too fine grained to show) HARDNESS: 3.5 - 4 OTHER: Important Zinc Ore, inportant source of Cadmium, indium, gallium, and Germanium |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Chalcopyrite |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Brass-Yellow STREAK: Greenish-Black HARDNESS: 3.5 - 4 OTHER: Important Copper ore |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Pyrrhotite |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Brownish-Bronze STREAK: Black HARDNESS: 4 OTHER: Magnetic, Mined for associated Nickel, Copper, Platinum, also source of Sulphur |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Cinnabar |
LUSTRE: Adamantine to Earthy
COLOR: Red to Brownish-Red STREAK: Red (Scarlet) HARDNESS: 2.5 OTHER: Only important source of Mercury |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Pyrite |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Pale Brass-Yellow STREAK: Greenish to Brownish Black HARDNESS: 6 - 6.5 FRACTURE: Uneven, brittle OTHER: Mined for association with Gold and Copper, also a source of Sulphur |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Molybdenite |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Lead Gray STREAK: Grayish-Black CLEAVAGE: One HARDNESS: 1 - 1.5 OTHER: Greasy Feel, Principle ore of Molybdenum |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Stibnite |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Lead-Gray to Black STREAK: Grayish-Black CLEAVAGE: Two HARDNESS: 2 OTHER: Striations on Crystal Faces, Chief ore of Antimony |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Chalcocite |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Lead-Gray or tarnishing to dull black STREAK: HARDNESS: 2.5 - 3 (some soft, some sooty) OTHER: one of the most profitable Copper ores, secondary mineral in many ore bodies in a zone called the supergene enrichment zone |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Nickeline |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Pale Copper-Red tarnishing to Gray FRACTURE: uneven HARDNESS: 5 - 5.5 OTHER: Minor ore of Nickel |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulphides)
Arsenopyrite |
LUSTRE: Metallic
COLOR: Silver-White CLEAVAGE: Poor HARDNESS: 5.5 - 6 OTHER: Major ore of Arsenic, can contain small amounts of Gold as impurity |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Tungstates)
Scheelite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous to Adamantine
COLOR: White, Yellow, Green, Brown STREAK: White CLEAVAGE: two HARDNESS: 4.5 - 5 OTHER: fluorescence, ore of Tungsten, more important in the US |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Tungstates)
Wolframite |
LUSTRE: Sub-metallic
COLOR: Black to Brown STREAK: Black to Brown CLEAVAGE: One HARDNESS: 4 - 4.5 OTHER: Chief ore of Tungsten, used for filaments for electric lamps, heating elements for electrical furnaces, tungsten Carbide is important compound in metal working, mining, and petroleum industries |
|
|
PROPERTIES (Native Elem.)
Graphite |
LUSTRE:Metallic
COLOR: Black STREAK: Black CLEAVAGE: One HARDNESS: 1 - 2 OTHER: Greasy Feel, used in steel and electric industries, lubricant, pencil lead |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Oxides)
Corundum |
LUSTRE: Adamantine-vitreous
COLOR: Usually some shade of Brown, Pink or Blue (ruby-Red, sapphire-any other color) HARDNESS: 9 OTHER: Gemstone or used as an abrasive |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Hydroxides)
Bauxite (Gibbsite) |
LUSTRE: Dull-Earthy
COLOR: White-Gray HARDNESS: 1 - 3 OTHER: Aluminum ore |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Hydroxides)
Goethite |
LUSTRE: Adamantine to Dull, Silky in certain varieties
COLOR: Yellowish Brown to Dark Brown CLEAVAGE: Two HARDNESS: 5 - 5.5 OTHER: Iron ore |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Hydroxides)
Limonite |
LUSTRE: Amorphous
COLOR: Yellowish Brown OTHER: Not a true mineral, composed of hydrated Iron Oxide minerals, mostly goethite, Iron ore |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Halides)
Halite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous
COLOR: Colorless or White CLEAVAGE: Cubic HARDNESS: 2.5 OTHER: Salty taste, used in Chemical Industry, road salting, food industry |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Halides)
Sylvite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous
COLOR: Colorless or White, varying with impurities CLEAVAGE: Cubic HARDNESS: 2 OTHER: Salty-Bitter Taste, Used as fertilizers |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Carbonates)
Siderite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous
COLOR: Light Dark Brown CLEAVAGE: Rhombohedral HARDNESS: 3.5 - 4 OTHER: Minor ore of Iron |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Carbonates)
Rhodochrosite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous
COLOR: Rose-red STREAK: White CLEAVAGE: Rhombohedral HARDNESS: 3.5 - 4 OTHER: Minor ore of Manganese |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Carbonates)
Azurite/Malachite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous
COLOR: Blue/Green CLEAVAGE: Two but rarely seen HARDNESS: 3.5 - 4 OTHER: Minor ore of Copper, ornamental and gem mineral |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulfates)
Barite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous
COLOR: Colorless-white CLEAVAGE: One perfect HARDNESS: 3 - 3.5 OTHER: Feels heavy, 80% used as drilling mud, additive to cement, rubber, and raw material for barium chemicals |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulfates)
Gypsum |
LUSTRE: Vitreous (Pearl or Silky)
COLOR: Colorless-White (Blueish) CLEAVAGE: One perfect HARDNESS: 2 OTHER: used in cement, wallboard, Plaster-of-Paris, paint filler, toothpaste, pharmaceuticals |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulfates)
Celestite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous to Pearly
COLOR: Colorless-light blue CLEAVAGE: Three (One perfect) HARDNESS: 3 - 3.5 OTHER: Used in glazes for ceramics, in Strontium nitrate for fireworks, to produce strontium salts used in the refining of beet sugar |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Phosphates)
Apatite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous-Subresinous
COLOR: Light Green, some Brown CLEAVAGE: One poor HARDNESS: 5 OTHER: Used mainly as fertilizer, also in chemical and pharmaceutical indutries |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Silicates)
Talc |
LUSTRE: Pearly-Greasy
COLOR: White, Gray, Light Green CLEAVAGE: One Poor HARDNESS: 5 OTHER: Greasy Feel, ingerdient in paint, ceramics, insecticides, roofing, paper, and talcum powder |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Silicates)
Kaolinite |
LUSTRE: Dull-Earthy, Crystal Plates pearly
COLOR: White, often colored by impurities CLEAVAGE: One HARDNESS: 2 OTHER: Production of ceramics, Filler for paint, rubber and plastics, Largest use is in the paper industry to produce glossy paper |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Silicates)
Vermiculate |
LUSTRE: Pearly
COLOR: Yellow-Brown CLEAVAGE: One HARDNESS: 1.5 OTHER: Construction, agricultural, horticultural, and industrial markets such as asbestos substitutions, heat insulation, animal feed, soil conditioner, potting mixes, drilling muds, paints |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulfates)
Barite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous
COLOR: Colorless-white CLEAVAGE: One perfect HARDNESS: 3 - 3.5 OTHER: Feels heavy, 80% used as drilling mud, additive to cement, rubber, and raw material for barium chemicals |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulfates)
Gypsum |
LUSTRE: Vitreous (Pearl or Silky)
COLOR: Colorless-White (Blueish) CLEAVAGE: One perfect HARDNESS: 2 OTHER: used in cement, wallboard, Plaster-of-Paris, paint filler, toothpaste, pharmaceuticals |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Sulfates)
Celestite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous to Pearly
COLOR: Colorless-light blue CLEAVAGE: Three (One perfect) HARDNESS: 3 - 3.5 OTHER: Used in glazes for ceramics, in Strontium nitrate for fireworks, to produce strontium salts used in the refining of beet sugar |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Phosphates)
Apatite |
LUSTRE: Vitreous-Subresinous
COLOR: Light Green, some Brown CLEAVAGE: One poor HARDNESS: 5 OTHER: Used mainly as fertilizer, also in chemical and pharmaceutical indutries |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Silicates)
Talc |
LUSTRE: Pearly-Greasy
COLOR: White, Gray, Light Green CLEAVAGE: One Poor HARDNESS: 5 OTHER: Greasy Feel, ingerdient in paint, ceramics, insecticides, roofing, paper, and talcum powder |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Silicates)
Kaolinite |
LUSTRE: Dull-Earthy, Crystal Plates pearly
COLOR: White, often colored by impurities CLEAVAGE: One HARDNESS: 2 OTHER: Production of ceramics, Filler for paint, rubber and plastics, Largest use is in the paper industry to produce glossy paper |
|
|
PROPERTIES: (Silicates)
Vermiculate |
LUSTRE: Pearly
COLOR: Yellow-Brown CLEAVAGE: One HARDNESS: 1.5 OTHER: Construction, agricultural, horticultural, and industrial markets such as asbestos substitutions, heat insulation, animal feed, soil conditioner, potting mixes, drilling muds, paints |

