![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Alveoli has a Large surface area of about _____ |
(60–80 m2 ). Each alveolus is 1 cell layer thick. Total air barrier is 2 cells across (2 m). |
|
|
There 500,000 respiratory bronchiole. T/f |
True |
|
|
There are ~ 400 million airsac. T/f |
False 300 million |
|
|
There are 2 types of alveoli cells; namely |
Alveolar type I: Structural cells. Alveolar type II: Secrete surfactant. |
|
|
As alveoli radius decreases, surfactant’s ability to lower surface tension ____________. |
Increases |
|
|
Disorders related to the surfactants are; |
RDS. ARDS |
|
|
The muscle of Expiration is the InternalIntercostal muscles. The accessorymuscles of expiration are |
Rectusabdominis, Transversus abdominis, Internal and external oblique mucles. |
|
|
The muscles of Inspiration are |
Diaphragmand External Intercostal muscle. |
|
|
Expedition occur during Contraction of diaphragm, increases thoracic volume vertically. T/f |
False Inspiration( Active) |
|
|
During inspiration ; Alveolar changes from ___ to ____ mm Hg.Intrapleural changes from ____ to ____ mmHg.Transpulmonary pressure = ____ mm Hg. |
Alveolar changes from 0 to -3 mm Hg.Intrapleural changes from -4 to -6 mmHg.Transpulmonary pressure = +3 mm Hg. |
|
|
Expiration Pressure changes during Intrapulmonary pressure changes from __ to ___ mm Hg. Intrapleural pressure changes from ___to ____ mm Hg. Transpulmonary pressure = ___ mm Hg. |
Intrapulmonary pressure changes from -3 to +3mm Hg. Intrapleura pressure changes from -6 to -3 mm Hg. Transpulmonary pressure = +6 mm Hg. |
|
|
Three Processes ofRespiration; |
Pulmonary ventilation (breathing) physical movement of air into and out of lungs inspiration - active expiration - usually passive Pulmonary (external) respiration gas exchange at lung Tissue (internal) respiration gas exchange at tissues |
|
|
Decreases pressure (Boyle’s law – volume inversely related to pressure) is related to inhalation. T/f |
True |
|
|
There are 4 lung volumes, mention them |
Tidal Inspiratory reserve Expiratory reserve Residual.
TIrREr |
|
|
_______ is the volume of gas inspired or expired in an unforced respiratory cycle. |
Tidal volume |
|
|
Tidal Volume = |
~500 ml |
|
|
_________ is themaximum volume of Gas that can be inspired during forced breathing in addition to Tidal volume |
Inspiratory Reserved volume |
|
|
Inspiratory reserved volume = |
~3100 ml |
|
|
_____ is the maximum volume of gas that can be expired during force breathing. |
Expiratory Reserved volume |
|
|
Expiratory reserve volume = |
~1200 ml |
|
|
_____ is the volume of gas remaining after maximum expiration |
Residual volume |
|
|
Residual volume = |
~1200 ml |
|
|
Lung capacities are classified into 4 type; |
Vital capacity Inspiratory capacity Functional residual capacity Total lung capacity VIFT. |
|
|
________ is the amount of gas that can be Expired after Maximum inspiration. |
Vital Capacity |
|
|
Vital capacity = |
~4800 |
|
|
________ is the amount of gas that can be inspired after a normal Tidal expiration. |
Inspiratory capacity |
|
|
_________ is the amount of gas remaining after NTE ( normal tidal expiration ) |
Functional Residual Capacity |
|
|
Inspiratory capacity = |
~3600 ml |
|
|
Functional Residual capacity = |
~2400 ml |
|
|
_______ is the Total amount of gas in the lungs after maximum inspiration |
Total Lungs capacity |
|
|
Each hemoglobin has 4 polypeptide chains and 4 hemes. In the center of each heme group is 1 atom of iron that can combine with 1 molecule of oxygen. T/f |
True |
|
|
Hemoglobin does not lose an electron when it combines with 02. T/f |
True |
|
|
________Has iron in the oxidized form (Fe3+ ). Lacks electrons and cannot bind with 02. |
Methemoglobin |
|
|
_________heme is combined with carbon monoxide. The bond with carbon monoxide is 210 times stronger than the bond with oxygen. Transport of 02 to tissues is impaired. |
Carboxyhemoglobin |
|
|
Anemia: [Hemoglobin] below normal. Polycythemia: [Hemoglobin] above normal. What's wrong |
Nill |
|
|
Hemoglobin production controlled by erythropoietin Is stimulated by ____ delivery to kidneys. |
PC02 |
|
|
Loading/unloading depends:
|
•P02 of environment. •Affinity between hemoglobin and 02 |
|
|
With Decreased pH, increased temperature, andincreased 2,3 DPG: Affinity of hemoglobin for 02___________ |
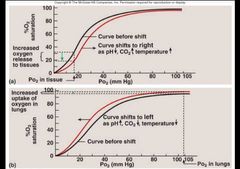
Decreases. Greater unloading of 02 Shift the curve to the right. |
|
|
Effect of 2,3 DPG on 02Transport |
Anemia:RBCs total blood [hemoglobin] falls, eachRBC produces greater amount of 2,3 DPG.Since RBCs lack both nuclei and mitochondria,produce ATP through anaerobic metabolism. Fetal hemoglobin (hemoglobin f):Has 2 y-chains in place of the B-chains.Hemoglobin f cannot bind to 2,3 DPG.Has a higher affinity for 02 |
|
|
Control of Respiration can be divided into 2; |
Neural control: This is influence of nerve cells of the central nervous system on the regulation of breathing Chemical control:This is the regulation of breathing due to input from receptors sensitive to the chemical composition of the blood. |
|
|
Neural Control Divided into |
Voluntary Control : Located in the cerebral cortex Responsible for breathholding. Involuntary Control : Located in the Pons and Medulla Responsible for the automatic control of breathing |
|
|
The primary portions of the brainstem that control ventilation are the ______&_______ |
Medulla oblongata and Pons. |
|
|
What are the two respiratory nuclei in medulla oblongata |
Inspiratory center (dorsal respiratory group, DRG) • more frequently they fire, more deeply you inhale • longer duration they fire, breath is prolonged, slow rate Expiratory center (ventral respiratory group, VRG) • involved in forced expiration |
|
|
Dorsal Respiratory Group are also known as _______ |
I-Neurons |
|
|
_________Sets the basic respiratory rate & Stimulates the inspiratory muscles to contract (diaphragm) |
Dorsal Respiratory Group |
|
|
The signals DRG sends for inspiration start weakly and steadily increase for ~ 2 sec. This is called a ________ and produces a gradual inspiration. |
Ramp The ramp then stops abruptly for ~ 3 sec and the diaphragm relaxes. |
|
|
Ventral Respiratory Group are also called |
E neurons |
|
|
VRG is inactive during normal and quiet respiration. T/f |
True |
|
|
Activities of medullary rhythmicity center is influenced by pons. T/f |
True |
|
|
________ Promotes inspiration by stimulating the I neurons in the medulla. |
Apneustic center |
|
|
__________ Antagonizes the apneustic center. Inhibits inspiration |
Pneumotaxic center: |
|
|
Rate and depth of ventilation adjusted to maintain arterial PC02 of _____mm Hg |
40 mm Hg. |
|
|
_______ is More sensitive to changes in arterial PC02. |
Central Chemoreceptors
H+ cannot cross the blood brain barrier. C02 can cross the blood brain barrier and will form H2C03. Lowers pH of CSF. • Directly stimulates central chemoreceptors. |
|
|
Peripheral chemoreceptors:Are not stimulated directly by changes in arterial PC02 • T/f |
Stimulated by rise in [H+] of arterial blood.Increased [H+] stimulates peripheral chemoreceptors. |
|
|
Peripheral chemoreceptors are stimulated by __________ while central chemoreceptors are stimulated by _______________ |
Peripheral = rise in [H+] of arterial blood Central = changes in the arterial PCO2 Note H+ can not cross blood brain barrier, CO2 can and will form H2CO3 |
|
|
Lower pH of cerebrospinal fluid directly stimulates central chemoreceptor |
True |

