![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
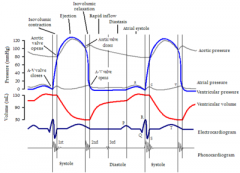
Describe the events that occur during physiological systole |
|
|
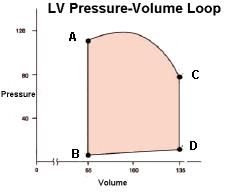
Explain the pressure volume loop shown. explain how to calculate SV and ejection fraction |
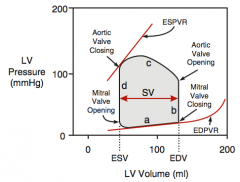
PV loop shows the ventricles relationship of pressure to volume.
|
|
|
Describe the shape and contraction of the left ventricle compared to the Right ventricle |
- Inward/ radial - longitudinal (base comes closer to apex) - rotational motion (apex twist relative to the base)
|
|
|
Explian these terms:
|
2. SV = Amount of blood ejected each beat = LVEDV - LVESV (peak volume - minimal volume) 3. CO = the amount of blood the heart pumps in one minute = SV x HR |
|
|
List the differences between the right ventricle and the left ventricle. |
Right ventricle has
|

