![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
draw glycolysis
|
this is glycolysis
|
|
|
draw glycolysis
|
kjasgd
|
|
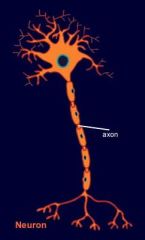
list all the parts of an axon
|
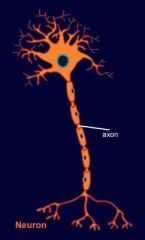
axon hillock
dendrites soma axon myelin axon terminals |
|
|
Describe chemical synaptic transmission
|
AP arrives at postsynaptic terminus and depolarizes V-sensitive Ca channels, Ca triggers synaptic vesicles loaded with say Ach(put there by a Ach/H atpase) to exocytose NT into cleft, Ach binds AchR causing a conf change to a cation selective pore(NA,K,Ca), causes a excitatory postsynaptic potential EPSP (GRADED!)
|
|
|
is an EPSP mostly Ca or Na?
|
Na
|
|
|
Miniature endplate potentials MEPPS
|
represent quantal release of NT from vesicles
|
|
|
spatial vs temporal summation
|
EPSP's are summated both temporally(in time, regarding frequency) and spacially(along many dendrites)
|
|
|
Describe an IPSP and how is works
|
GABA binds its receptor, causes a Cl conducting pore to form causing hyperpolerization
|
|
|
two main clases of NT Receptors
|
ionotropic and metabotropic
|
|
|
ionotropic
|
ligand gated ion channels direct and rapid postsynaptic effects
Nicotinic |
|
|
metabotropic
|
G-protein linked, slower, greater amplification
Muscarinic |
|
|
convergent vs divergent actions of a NT
|
divergent: ie NE activated three different signal cascades each of which does 4 different things
convergent: 7 NT's act on 7 receptors which all increase K permeability |

