![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
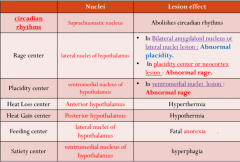
What is the hypothalamus, and what are its most important features? |
The hypothalamus is an organ that: 1)Connects the endocrine system with the nervous system 2)Major component of the limbic system and acts as an output pathway. |
|
|
The hypothalamus helps control 5 important body functions, what are they? |
1)Controls blood pressure and electrolytes(Drinking(Thirst center) and salt appetite) 2)Regulates body temperature 3)Regulates energy metabolisim(By eating, digestion, appetite etc) 4)Regulates reproductive functions 5)Regulates response to stress by regulating the function of the adrenal glands. |
|
|
-BP,BT,RES |
|
|
|
What is the cyclic phenomena, and whats another name given for it? |
Circadian rhythm, it is the rhythm of the body that is controlled 24 hours and it includes: 1)Secrtion of hormones (ACTH, pineal hormone melatonin) 2)Sleep-wake cycle 3)Activity patterns 4)Body temperature rhythms |
|
|
What is the primary pace maker for the cyclic phenomena(Circadian rhythm)? |
Suprachiasmatic nucleas of the hypothalamus. |
|
|
How does the hypothalamus control emotions? |
The hypothalamus is responsible for the control of 2 important emotions, 1)Rage centers 2)Placidity centers |
|
|
Most human beings maintain normal homeostasis by a balance between placidity and rage. |
- |
|
|
Where are rage centers? |
Rage centers are centers found in the lateral hypothalamic nucleas. |
|
|
What stimulates rage centers, and what inhibits it? |
Stimulated by: Amygdaloid nucleus and limbic system Inhibited by: Neocortex and placidity center (Ventromedial hypothalamic nuclease. |
|
|
Where is the placidity center found? |
It is found in Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleas. |
|
|
What causes abnormal placidity? |
Bilateral destruction of Amglydoid nucleus. |
|
|
What happens if it was followed by subsequent destruction of the ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus? |
Rage. |
|
|
What causes extreme rage (Rage and sham reaction)? |
Destruction of the Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus. Destruction of the neocortex Stimulation of the Amglydoid nucleas |
|
|
Discuss lesions of rage centers |
- |
|
|
How does the hypothalamus control temperature? |
In the hypothalamus, we have 2 nuclei, Anterior nuclei: For heat loss Posterior nuclei: For heat gain |
|
|
What stimuates the anterior nuclei? |
The anterior nuclei (Heat loss) is stimulated by heat. It then causes heat loss by vasodilation and sweating. It release norepinphren |
|
|
What happens if there was a lesion in the anterior hypothalamic nucleus? |
Hyperthermia |
|
|
What stimulates the posterior nuclei? |
Posterior nuclei (Heat gain) is stimulated by cold. It then causes shivering to lose heat. The neurotransmiiter is serotonin. |
|
|
What happens if there was a lesion in the posterior nuclei? |
There would be no heat gain, Hypothermia |
|
|
Exposure to hot temperature leads to? |
Activation of the posterior hypothalmic nuclei |
|
|
Exposure to cold temperature leads to? |
Activation of the heat gain, Posterior nuclei. |
|
|
Mechanisim of fever? |
The cytokines produced by bacteria resets the anterior (Preoptic nuclei of the hypothalamus) and causes increase in temperature |
|
|
What is the preoptic hypothalmic nuclei? |
The anterior nucleus of the hypothalamus. |
|
|
How does the hypothalamus affect food intake? |
We have 2 food centers in the hypothalamus 1)Feeding center 2)Satiety center |
|
|
Where is the feeding center found? |
In the lateral hypothalamic nucleus |
|
|
Where is the Satiety center found? |
In the Ventromedial nucleus |
|
|
What happens if we stimulate the feeding center? |
Feeding: Hunger Satiety: Cessation of food |
|
|
What happens if there was a lesion in the Ventromedial nucleus(Satiety center) |
Leads to hypothalmic obesity, or hyperphagia. |
|
|
What are the 4 afferent hypothesis of food centers? |
1)The lipostatic hypothesis: Release of leptin 2)The Glucostatic hypothesis: Release of glucose 3)The Thermostatic hypothesis: Increase temp. 4)Gut peptide hypothesis: Release of GIT hormon Release of all those inhibits the feeding and activates satiety |
|
|
What is leptin? |
Leptin This hormone released from adipose tissue acts on thehypothalamus to decrease food intake and increase energyconsumption. It decreases the activity of neuropeptide Y neurons and increasesthe activity of POMC-secreting neurons. |
|
|
Effects of lesion in the hypothalamus? |
Endocrine disorders: diabetes insipidus . Sleep disturbances. Hyperthermia or hypothermia. Hyperphagia or anorexia. Autonomic disturbances: sweating, VD or VC. Placidity or rage. Obesity. Sexual disturbances. |
|
|
Summary of lesions: |
|

