![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Current moving toward the negative electrode causes _________ deflection on the ECG
|
downward
|
|
|
What part of the ECG represents Atrial depolarization?
|
P wave
|
|
|
What part of the ECG represents AVN, bundle of His and bundle fiber depolarization?
|
P-R segment
|
|
|
What part of the ECG represents Atrial, AVN, bundle of His and bundle fiber depolarization?
|
P-R interval
|
|
|
What is the difference between an interval and a segment?
|
segments are the flat lines of the ECG, intervals include waves
|
|
|
What is represented by the QRS interval on the ECG?
|
Ventricular depolarization
|
|
|
During what part of the ECG is the ventrical fully depolarized?
|
S-T segment
|
|
|
What portion of the ECG represents the duration of ventricular systole?
|
Q-T interval
|
|
|
What does the T wave represent on the ECG?
|
rapid ventricular repolarization
|
|
|
What does the S-T interval represent on the ECG?
|
Repolarization of the ventricles
|
|
|
What is assumed to be the zero baseline on the ECG?
|
T-P segment
|
|
|
How much time does 5mm on the ECG mark?
|
0.2 seconds
|
|
|
What will slowing AVN conduction do to the ECG?
|
prolong the P-R interval
|
|
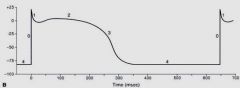
What do 1, 2, 3 and 4 correlate to on an ECG?
|
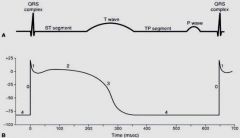
|
|
|
which ECG leads are in the 'frontal plane'?
|
Limb leads (I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF)
|
|
|
which ECG leads are in the 'horizontal plane'?
|
Chest leads (V1-V6)
|
|
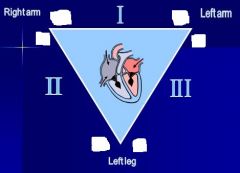
Fill in the polarities of each lead
|
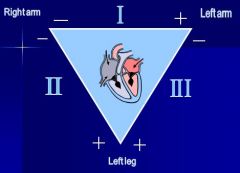
|
|
|
does the QRS interval of the aVR lead deflect up or down?
|
down (because the positive electrode is on the right side, everything is opposite to the leads with the positive electrode on the left side)
|
|
|
QRS is highest on which chest lead?
|
V5
|
|
|
QRS is lowest on which chest lead?
|
V1
|
|
|
If a patient has an R-R interval spanning 3 large boxes (15mm), what is his heart rate?
|
100bpm (60 / 0.6)
|
|
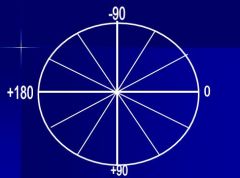
Label all six limb leads and their positive ends
|
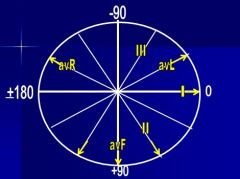
|
|
|
The mean QRS vector is in what direction?
|
down and to the (patient's) left
|
|
|
A normal mean QRS vector is between ___ and ___ degrees.
|
0 and +90
|
|
|
The electrical axis (mean QRS vector) is displaced ___________ hypertrophy and _________ infarction
|
towards, away from
|
|
|
Right Axial Deviation is indicated by a Vector between ____ and ____
|
+90, +180
|
|
|
Left Axial Deviation is indicated by a Vector between ____ and ____
|
-90, 0
|
|
|
What is the name for a Vector between +180 and -90?
|
Northwest
|
|
|
If QRS is positive in lead I and negative in lead aVF, the patient is experiencing ________________
|
Left Axis Deviation
|
|
|
If QRS is negative in lead I and negative in lead aVF, the patient is experiencing ____________
|
Extreme Right Axis Deviation (Northwest)
|
|
|
If QRS is negative in lead I and positive in lead aVF, the patient is experiencing _____________
|
Right Axis Deviation
|
|
|
If QRS is positive in lead I and positive in lead aVF, the patient is __________
|
Normal (to thumbs up)
|
|
|
If lead I is your most isoelectric lead and aVF QRS is positive, what is your mean axis?
|
+90 (normal)
|
|
|
If lead aVL is your most isoelectric lead and lead III QRS is negative, what is your mean axis?
|
-150 (northwest)
|
|
|
The most isoelectric chest lead is V2, this indicates a _______ _______
|
rightward rotation
|

