![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The glomeruli exist in the __________ of the kidney
|
cortex
|
|
|
The henle's loop of the ____________ nephron extends into the inner medulla. The henle's loop of the ___________ nephron extends only to the outer medulla
|
juxta-glomerular; superficial
|
|
|
The majority of innervation to the juxtaglomerular apparatus is from the _________
|
sympathetics
|
|
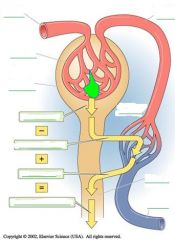
fill in the blanks
|
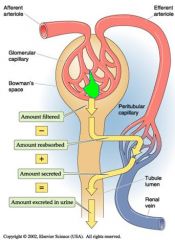
|
|
|
The _________ tubule reabsorbs water, Na+, Cl and other essential organic copounds from the glomerular filtrate
|
proximal
|
|
|
The loop of henle reabsorbs more _______ than _______
|
Na/Cl; water
|
|
|
Distal and connecting tubules reabsorb a __________ amount of water and salt
|
small
|
|
|
Why are the distal/connecting tubules so important in reabsorbption of salt/water?
|
they are very responsive to ADH and aldosterone
|
|
|
aldosterone increasing the reabsoption of _________
|
Na+ and Cl
|
|
|
ADH increases the reabsorption of ________
|
water
|
|
|
ANP increases _______ _________
|
Na+ excretion
|
|
|
Kf = __________ x _________
|
hydraulic permeability; surface area
|
|
|
GFR = ________ x __________
|
Kf; NFP (net filtration pressure)
|
|
|
What force, physiologically, forces fluid out of the glomerular capillaries?
|
Pgc
|
|
|
What two forces oppose ultrafiltration?
|
oncotic pressure of glomerular capillaries; hydrostatic pressure of bowman's capsule
|
|
|
afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction __________ Pgc
|
decreases
|
|
|
efferent vasoconstriction _________ Pgc
|
increases
|
|
|
decreased RBF ________ GFR
|
decreases
|
|
|
Filtration Fraction = ___________ / ____________
|
GFR/RPF (renal plasma flow)
|
|
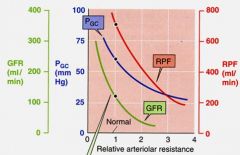
This graph shows _________ arteriolar vasoconstriction
|
afferent
|
|
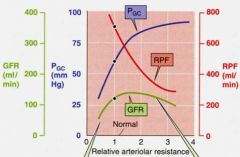
This graph shows _________ arteriolar vasoconstriction
|
efferent
|
|
|
a nephrectomy would show ____________ GFR because the ___________ resistance of the __________ arteriole
|
increased; decreased; afferent
|
|
|
AngII antagonists ___________ GFR because of the __________ resistance of the ____________ arteriole
|
decrease; decreased; efferent
|
|
|
_______ __________ maintains GFR with decreased RBF
|
SNS stimulation (AngII as well)
|
|
|
paracrines from the macula densa cause the ___________ arteriole to vasoconstrict/vasodialate
|
afferent
|
|
|
when the macula densa senses a decrease in NaCl, it causes the _____________ of the ___________ arteriole
|
vasodilation; afferent
|
|
|
RAAS and SNS vaso______. What is their net effect?
|
constrict (afferent and efferent); decreased RPF with little or no change in the GFR
|
|
|
ADH vaso________. What is it's net effect?
|
contricts; normally GFR and RPF remain constant
|
|
|
Does ANP vasoconstrict or vasodilate? What is it's net effect?
|
vasocontricts the efferent and vasodilates the afferent; Increases GFR and RPF (also inhibits renin secretion)
|
|
|
Dopamine causes vaso______
|
dilation
|

