![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What stimulates the A. pit to make LH/FSH?
|
Hypothalamus' GnRH
|
|
|
Describe the structure of LH/FSH by their units?
|
alpha - same in both
beta - differs |
|
|
LH acts on what cells of the testes? to do what?
|
on leydig cells to make testosterone
|
|
|
FSH acts on what cells of the testes? to do what?
|
sertoli, to make INHIBIN
|
|
|
what doesINHIBIN do?
|
inhibits A. Pit
|
|
|
How does testostertone regulate itself?
|
it inhibits Hypothalamus and A. Pit, thereby inhibiting LH/FSH release
|
|
|
Where is the earliest peak of gonadotropins?
|
2nd trimester, because the regulatory axis has not yet developed
|
|
|
what happens to gonadotrope receptors ( of the ant pit) in puberty?
|
less sensitive to test/estrogen feedback (so HIGHER)
|
|
|
What is 5 alpha recutase?
|
makes testosterone into DHT
|
|
|
what is the promoter where androgen recpetors bind?
|
HRE
|
|
|
Give some examples of continus action of androgens
|
Spermatogenesis,
secondary sex organ devo bone maturation/anablosim thicken larynx thick/darker skin |
|
|
What is the non-contiunous androgen action?
|
sexual differentiation
|
|
|
3 sexual deteminants (3g's)
|
genetics
gonads genitalia |
|
|
What does a Y chromosome do for a male?
|
gives them protein set SRY - makes gonads into testes
|
|
|
What happens to gonads if they have
(1) Sry (2) No sry |
1 - testes
2 - ovaries |
|
|
What does the Mullerian duct do?
|
makes Fallop tubes, uterus, upper vag
|
|
|
How do the testes make sure men don't have
Fallop tubes uterus upper vag? |
2 things - testes make:
1 - testosterone - get sem vesciles, vas def, epidid 2 - make Anti-mull hormone |
|
|
What does the Wolf duct do?
|
make sem ves, vas def, epid
|
|
|
What do urogenital sinus folds make in presence of DHT?
|
prostate, glands penis/shaft, scrotum
|
|
|
what do urogenital sinus folds make in lack of DHT?
|
clit, labia, minor/majora, lower vag
|
|
|
What are 3 versions of hypogonadism?
|
in utero
Eunochidism (after utero/before pub) After puberty/adult |
|
|
what is eunochidism
|
hypogonad after utero, before pub
|
|
|
what is cryptochidism
|
undescended testicles
|
|
|
What type of hypogonadism is this?
no facial hair, anemia, Increased LH/FSH, bones normal length |
after puberty primary hypogonadism
|
|
|
What type of hypogonadism is this?
no facial hair, anemia, Increased LH/FSH, no secondary sex organs |
eunochoidism
|
|
|
What type of hypogonadism is this?
no facial hair, anemia, Increased LH/FSH, no male reproductive tract |
fetal primary hypogonadism
|
|
|
What type of hypogonadism is this?
no facial hair, anemia, HIGHLH/FSh |
secondary hypogonadism
|
|
|
Primary hypogonadism is a problem with the (1) and secondary is problem with the (2)
|
1 - testes
2 - pit/hypothal |
|
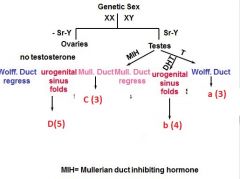
|
a - seminal vescils, vas def, epididyms
b - prostate, glands penis, shaft, scrotum c - fallopian tubes, uterus, upper vag d - lower vag, minora, majora, clit, labia |
|
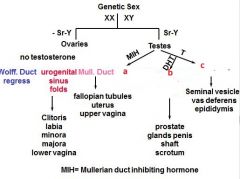
|
a - Mull Duct
b - Urogenital sinus folds c - wolf duct |
|
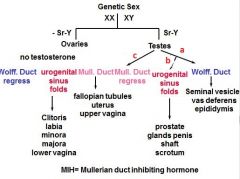
|
a - Testosterone
b - DHT C - MIH |
|
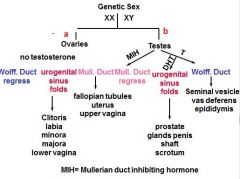
|
a - NO SRY
b - SRY |

